Digital SAT Math Last Minutes Revision Sheet - New Syllabus
DSAT Math Blue book reference

DSAT Math Formula Sheet: Algebra
Linear Equations in One Variable
- Standard form: \( ax + b = 0 \)
- Solution: \( x = -\dfrac{b}{a} \)
Linear Equations in Two Variables
- General form: \( ax + by = c \)
- Slope-intercept form: \( y = mx + b \)
- Slope: \( m = \dfrac{\Delta y}{\Delta x} = \dfrac{y_2 – y_1}{x_2 – x_1} \)
- Point-slope form: \( y – y_1 = m(x – x_1) \)
Linear Functions
- Function form: \( f(x) = mx + b \)
- Rate of change (slope): \( m \)
- Intercept: value of \( f(x) \) when \( x = 0 \): \( f(0) = b \)
Systems of Two Linear Equations in Two Variables
- General system:
\( a_1x + b_1y = c_1 \)
\( a_2x + b_2y = c_2 \) - Solutions:
- One solution (lines intersect): consistent and independent
- No solution (parallel lines): inconsistent
- Infinite solutions (same line): dependent
- Substitution or elimination methods used to solve
Linear Inequalities in One or Two Variables
- One variable: \( ax + b < c \), \( \leq, \geq, > \)
- Two variables: \( y < mx + b \), etc.
- Flip inequality sign when multiplying/dividing by a negative number
- Graphical region: shade above/below the line depending on inequality
DSAT Math Formula Sheet: Advanced Math
Equivalent Expressions
- Distributive Property: \( a(b + c) = ab + ac \)
- Combining like terms: \( ax + bx = (a + b)x \)
- Factoring: \( ax^2 + bx + c = (mx + n)(px + q) \) (where applicable)
- Difference of squares: \( a^2 – b^2 = (a – b)(a + b) \)
- Perfect square trinomial: \( a^2 \pm 2ab + b^2 = (a \pm b)^2 \)
Nonlinear Equations in One Variable
- Quadratic form: \( ax^2 + bx + c = 0 \)
- Quadratic formula: \( x = \dfrac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 – 4ac}}{2a} \)
- $\text{Discriminant} =b^2-4 a c$ ,
- VIETA’S FORMULAS $x_1+x_2=-\frac{b}{a} \quad \text { and } \quad x_1 x_2=\frac{c}{a}$
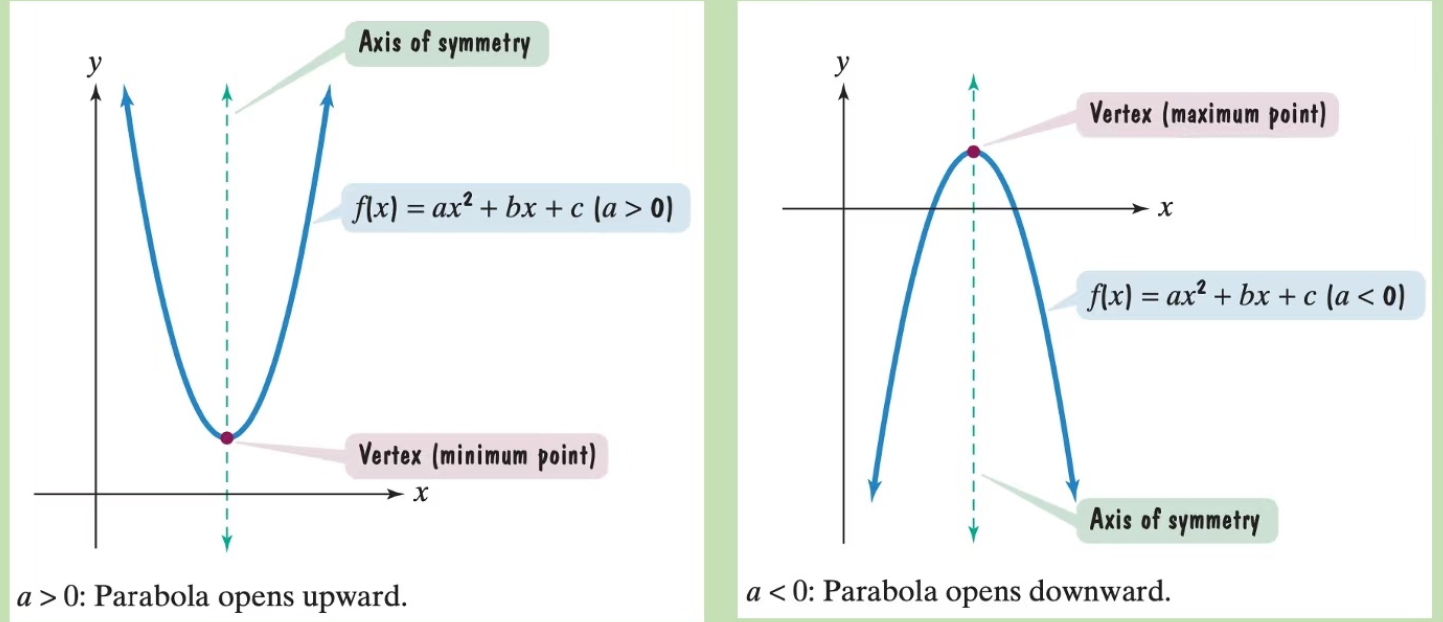
- Minimum and Maximum: Quadratic Functions
- 1. If $a>0$, then $f$ has a minimum that occurs at $x=-\frac{b}{2 a}$. This minimum value is $f\left(-\frac{b}{2 a}\right)$.
- 2. If $a<0$, then $f$ has a maximum that occurs at $x=-\frac{b}{2 a}$. This maximum value is $f\left(-\frac{b}{2 a}\right)$.
- In each case, the value of $x$ gives the location of the minimum or maximum value. The value of $y$, or $f\left(-\frac{b}{2 a}\right)$, gives that minimum or maximum value.

- Square root property: \( x^2 = k \Rightarrow x = \pm \sqrt{k} \)
- Cubic or higher degree polynomials solved by factoring or substitution
Systems of Equations Involving Nonlinear Functions
- Example system:
\( y = ax^2 + bx + c \)
\( y = mx + b \) - Substitute one equation into the other to solve for variable(s)
- Solutions correspond to points of intersection of graphs
Nonlinear Functions
- Quadratic function: \( f(x) = ax^2 + bx + c \)
- Vertex form: \( f(x) = a(x – h)^2 + k \)
- Absolute value function: \( f(x) = |x| \)
- Piece wise function : $y=f(x)= \begin{cases}-x, & x<0 \\ x^2, & 0 \leq x \leq 1 \\ 1, & x>1\end{cases}$
- Exponential functions (basic): \( f(x) = a \cdot b^x \), \( b > 0, b \neq 1 \)
- Rules for Exponents:
- If $a>0$ and $b>0$, the following hold for all real numbers $x$ and $y$.
- $a^x \cdot a^y=a^{x+y}$
- $\frac{a^x}{a^y}=a^{x-y}$
- $\left(a^x\right)^y=\left(a^y\right)^x=a^{x y}$
- $a^x \cdot b^x=(a b)^x$
- $\left(\frac{a}{b}\right)^x=\frac{a^x}{b^x}$
- If $a>0$ and $b>0$, the following hold for all real numbers $x$ and $y$.
DSAT Math Formula Sheet: Problem-Solving & Data Analysis
Ratios, Rates, Proportional Relationships, and Units
- Ratio: \( \dfrac{a}{b} \) means “a to b”
- Rate: ratio comparing two quantities with different units (e.g., miles per hour)
- Proportion equation: \( \dfrac{a}{b} = \dfrac{c}{d} \) → cross-multiply: \( ad = bc \)
- Unit conversions: multiply by conversion factor \( \dfrac{\text{desired unit}}{\text{given unit}} \)
Percentages
- Percent to decimal: \( \% = \dfrac{\text{percent}}{100} \)
- Percent increase/decrease: \(\text{Percent change} = \dfrac{\text{New} – \text{Original}}{\text{Original}} \times 100\% \)
- Percent of a number: \( \text{Part} = \text{Percent} \times \text{Whole} \)
1-Variable Data: Distributions and Measures of Center and Spread
- Mean (average): \( \bar{x} = \dfrac{\sum x_i}{n} \)
- Median: middle value when data is ordered
- Mode: most frequent value
- Range: \( \text{Max} – \text{Min} \)
- Interquartile Range (IQR): \( Q_3 – Q_1 \)
- Standard deviation (informal): measure of spread around mean
2-Variable Data: Models and Scatterplots
- Scatterplot shows relationship between two variables
- Correlation describes strength and direction of linear relationship (positive, negative, none)
- Line of best fit (trend line) models approximate linear relation
- Equation of line: \( y = mx + b \)
Probability and Conditional Probability
- Probability of event \( A \): \( P(A) = \dfrac{\text{Number of favorable outcomes}}{\text{Total number of outcomes}} \)
- Complement rule: \( P(\text{not } A) = 1 – P(A) \)
- For independent events \( A \) and \( B \): \( P(A \text{ and } B) = P(A) \times P(B) \)
- Conditional probability: \( P(A|B) = \dfrac{P(A \text{ and } B)}{P(B)} \)
Inference from Sample Statistics and Margin of Error
- Margin of error (approximate): \( \text{ME} = \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{n}} \) (where \( n \) is sample size)
- Increasing sample size decreases margin of error
- Sample statistics estimate population parameters
Evaluating Statistical Claims: Observational Studies and Experiments
- Observational study: researcher observes without intervention
- Experiment: researcher imposes treatment or intervention
- Correlation does not imply causation
- Beware of bias, confounding variables, and sampling errors
DSAT Math Formula Sheet: Geometry & Trigonometry
Area and Volume
- Area of rectangle: \( A = l \times w \)
- Area of square: \( A = s^2 \)
- Area of triangle: \( A = \dfrac{1}{2} \times \text{base} \times \text{height} \)
- Area of parallelogram: \( A = b \times h \)
- Area of trapezoid: \( A = \dfrac{1}{2} (b_1 + b_2) \times h \)
- Area of circle: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
- Outer Surface Area of a Cylinder:
- Hollow cylinder $A=2 \pi r h$ (no ends)
- Open cylinder $A=2 \pi r h+\pi r^2$ (one end)
- Solid cylinder $A=2 \pi r h+2 \pi r^2$ (two ends)
- Volume of rectangular prism: \( V = l \times w \times h \)
- Volume of cube: \( V = s^3 \)
- Volume of cylinder: \( V = \pi r^2 h \)
- Volume of cone: \( V = \dfrac{1}{3} \pi r^2 h \)
- Volume of sphere: \( V = \dfrac{4}{3} \pi r^3 \)
Lines, Angles, and Triangles
- Line Formulas:
- Slope formula: \( m = \dfrac{y_2 – y_1}{x_2 – x_1} \)
- Point-slope form: \( y – y_1 = m(x – x_1) \)
- Slope-intercept form: \( y = mx + b \)
- Standard form: \( Ax + By = C \)
- Parallel lines: same slope
- Perpendicular lines: slopes are negative reciprocals (\( m_1 \cdot m_2 = -1 \))
- Distance and Midpoint:
- Distance between two points: \(d = \sqrt{(x_2 – x_1)^2 + (y_2 – y_1)^2} \)
- Midpoint of a segment: \(M = \left( \dfrac{x_1 + x_2}{2}, \dfrac{y_1 + y_2}{2} \right) \)
- Sum of interior angles of triangle: \( 180^\circ \)
- Sum of interior angles of polygon: \( (n – 2) \times 180^\circ \)
- Triangle inequality: \( \text{sum of any two sides} > \text{third side} \)
- Pythagorean theorem (right triangle): \( a^2 + b^2 = c^2 \)
- Special right triangles:
- 45°-45°-90° triangle sides: \( x, x, x\sqrt{2} \)
- 30°-60°-90° triangle sides: \( x, x\sqrt{3}, 2x \)
- Angle relationships:
- Complementary angles: sum to \( 90^\circ \)
- Supplementary angles: sum to \( 180^\circ \)
- Vertical angles: equal
- Alternate interior angles (parallel lines): equal
Trigonometry (Right Triangles)
- Sine: \( \sin \theta = \dfrac{\text{opposite}}{\text{hypotenuse}} \)
- Cosine: \( \cos \theta = \dfrac{\text{adjacent}}{\text{hypotenuse}} \)
- Tangent: \( \tan \theta = \dfrac{\text{opposite}}{\text{adjacent}} \)
- Basic identities: \( \tan \theta = \dfrac{\sin \theta}{\cos \theta} \)
Circles
- Circumference: \( C = 2 \pi r \)
- Area: \( A = \pi r^2 \)
- Arc length: \( \text{Arc length} = \dfrac{\theta}{360^\circ} \times 2 \pi r \)
- Area of sector: \( \text{Sector area} = \dfrac{\theta}{360^\circ} \times \pi r^2 \)
- Equation of circle with center \( (h,k) \) and radius \( r \): \( (x – h)^2 + (y – k)^2 = r^2 \)
DSAT Math Test Content Breakdown
Algebra
- Linear Equations & Inequalities
- Systems of Linear Equations/Inequalities
~35% | 13–15 questions
Advanced Math
- Polynomial, Quadratic, Nonlinear & Exponential Functions
- Radical, Rational, & Absolute Value Equations
~35% | 13–15 questions
Problem Solving & Data
- Rates, Ratios, Proportions
- Percentages & Probability
- Data Representations & Statistical Claims
~15% | 5–7 questions
Geometry & Trigonometry
- Area, Perimeter, and Volume
- Lines, Angles, Triangles, and Circles
- Trigonometry
~15% | 5–7 questions