Question
Which of the following algae contains mannitol as reserve food material ? [NEET 2021]
(a) Ectocarpus
(b) Gracilaria
(c) Volvox
(d) Ulothrix
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Ectocarpus is a cosmopolitan marine brown seaweed. Mannitol is stored as a food reserve in Ectocarpus.
Other options can be explained as :- Grocilaria is also a type of red algae that is notable for its economic importance. Reserved food found in Gracilaria is in the form of floridean starch, which is similar to amylopectin and glycogen in structure.
– In Volvox (green algae), stored food material is starch and the major pigments are chlorophyll a and $d$. Some may store food as oil droplets.
– Ulothrix is a genus of non-branching filamentous green algae, starch molecule is the reserved food.
Question
Which of the following algae produces carrageen? [NEET 2021]
(a) Green algae
(b) Brown algae
(c) Red algae
(d) Blue-green algae
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Carrageen is a common name give to polysaccharides (carbohydrates) that are extracted from seaweeds like red algae. Carrageen is known for its gelling properties and it is one of the industrial source of carrageenan that is utilised as a stabilizer and thickner of milk products. It can be harmful to immune system, in severe cases it leads to internal bleeding.
Question
Phycoerythrin is the major pigment in [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) red algae
(b) blue-green algae
(c) green algae
(d) brown algae
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Phycoerythrin is the major pigment in red algae or modophytes. The photosynthetic pigments in red algae include chlorophyll-a, carotenoids and phycobilins. Phycoerythrin belongs to the phycobilins. These pigments are soluble in water.
Question
Which of the following pairs is of unicellular algae? [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) Gelidium and Gracilaria
(b) Anabaena and Volvox
(c) Chlorello and Spirulina
(d) Laminaria and Sargassum
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Chlorella and Spirulina are unicellular algae as they are rich in proteins and hence used as food supplements by space travellers. Gelidium, Gracilaria; Laminaria and Sargassum are multicellular. Volvox is colonial.
Question
Which one is wrongly matched? [NEET 2018]
(a) Gemma cups – Marchantia
(b) Biflagellate zoospores – Brown algae
(c) Uniflagellate gametes -Polysiphonia
(d) Unicellular organism – Chlorella
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Polysiphonia is a red algae. In it sexual reproduction is of oogamous type. The male sex organ, spermatangium produces non-flagellate male gametes.
In Brown algae, sexual reproduction varies from isogamy, anisogamy to oogamy. In isogamy and anisogamy both the gametes are motile while in oogamy only male gametes are motile. These motile gametes have two unequal laterally attached flagella.
Chlorella is a unicellular organism. It is green algae belonging to class Chlorophyta. In Marchantia, gemma cups are found on its dorsal surface. It contains gammae which help in vegetative propagation.
Question
Zygotic meiosis is characteristic of [NEET 2017]
(a) Marchantio
(b) Fucus
(c) Funaria
(d) Chlamydomonas
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
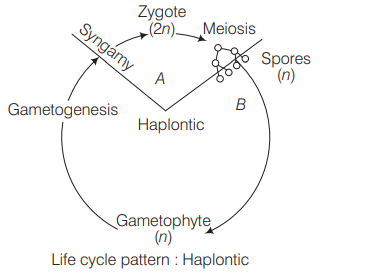
Zygotic meiosis is represented in the haplontic life cycle of many algae including
Chlamydomonos. In such a life cycle, all cells are haploid except zygote. This is because meiosis occurs in the zygote itself resulting into four haploid cells that give rise to hapolid plants.
Question
An example of colonial alga is [NEET 2017]
(a) Chlorella
(b) Volvox
(c) Ulothrix
(d) Spirogyra
Answer/Explanation
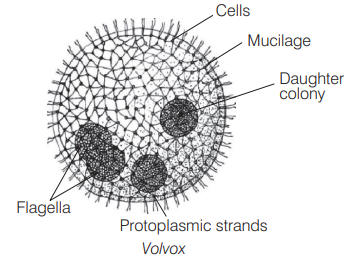
Ans. (b)
Volvox is a fresh water green hollow ball-like colonial alga. Its colony has a fixed number of cells (500-60000). It is called coenobium.
Question
Which one of the following statements is wrong ? [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) Algae increase the level of dissolved oxygen in the immediate environment
(b) Algin is obtained from red algae and carrageenan from brown algae
(c) Agar-agar is obtained from Gelidium and Graciloria
(d) Laminaria and Sargassum are used as food
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Algin extracted from brown algae, e.g. Laminaria, etc. is a hydrocolloid used in shaving creams, jellies, flameproof plastic, etc. Carrageenan is extracted from red algae like Chondrus and used as emulsifier and clearing agent.
Thus, only option (b) is incorrect and all other options are correct.
Question
Which one is a wrong statement? [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) Archegonia are found in Bryophyta, Pteridophyta and Gymnosperms
(b) Mucor has biflagellate zoospores
(c) Haploid endosperm is typical feature of gymnosperms
(d) Brown algae have chlorophyll-a and $c$, and fucoxanthin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
All the statements are correct except the statement (b). Mucor (fungus) belongs to the class-Zygomycetes. The members of Zygomycetes bear non-motile non-flagellated gametes.
Question
Which one of the following shows isogamy with non-flagellated gametes? [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) Sargassum
(b) Ectocarpus
(c) Ulothrix
(d) Spirogyra
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Isogamy with non-flagellated gametes is seen in Spirogyra. It can reproduce both by sexual and asexual (vegetative) means.
They reproduce sexually by conjugation in which two non-flagellated morphologically similar but physiologically different gemetes (isogamous) fuse together. One filament acts as male gamete and passes through the conjugation tube of another filament which acts as female gamete.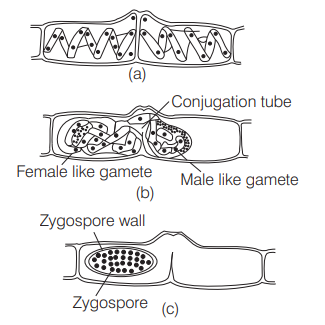
Question
Which one of the following is wrong about Chara? [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) Upper oogonium and lower round antheridium
(b) Globule and nucule present on the same plant
(c) Upper antheridium and lower oogonium
(d) Globule is male reproductive structure
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Both antheridium and oogonium are the male and the female reproductive structures respectively. They have sterile jackets on their surface. In Chara globule (antheridium) is present on lower side, while the nucule (oogonium) is present on upper side of sterile vegetative(leaf-like) structure.
Question
An alga which can be employed as food for human being is [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) Ulothrix
(b) Chiorella
(c) Spirogyra
(d) Polysiphonia
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Chlorella is a potential food source because it is high in protein and other essential nutrients when dried, it contains about $45 \%$ protein, $20 \%$ fat, $20 \%$ carbohydrate, $5 \%$ fibre and $10 \%$ minerals and vitamins.
Question
Select the wrong statement. [NEET 2013]
(a) Isogametes are similar in structure, function and behaviour
(b) Anisogametes differ either in structure, function and behaviour
(c) In oomycetes female gamete is smaller and motile, while male gamete is larger and non-motile
(d) Chlamydomonas exhibits both isogamy and anisogamy and Fucus shows oogamy
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Statement (c) is wrong as oomycetes include water moulds, white rusts and downy mildews. In these, female gamete is large and non-motile, whereas, male gamete is small and non-motile. Isogametes are found in algae like Ulothrix, Chlomydomonas, Spirogyra, etc. which are similar in structure, function and behaviour. Anisogametes are found in Chlamydomonos in which one gamete is larger and non-motile and the other one is motile and smaller.
Oogamy is the fusion of non-motile egg with motile sperm. The gametes, differ both morphologically as well as physiologically. It occurs in Chlamydomonas, Fucus, Chara, Volvox, etc.
Question
Algae have cell wall made up of [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) cellulose, galactans and mannans
(b) hemicellulose, pectins and proteins
(c) pectins, cellulose and proteins
(d)cellulose, hemicellulose and pectins
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Algae have cell wall made up of cellulose, galactans and mannans. Like plants, algae have cell walls containing either polysaccharides such as cellulose (a glucan) or a variety of glycoproteins or both.
The inclusion of additional polysaccharide in algal cell walls is used as a feature for algal taxonomy. Mananas form microfibrils in the cell walls of a number of marine green algae including those from the genera Codium, Acetabuloria as well as in the walls of some red algae like Porphyra.
Question
Mannitol is the stored food in [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) Chara
(b) Porphyra
(c) Fucus
(d) Gracilaria
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Fucus belongs to class-Phaeophyceae, in which reserve food is found in form of laminarin, mannitol and oil.
Chara belongs to class-Chlorophyceae, in which reserve food is found in form of starch and oil.
Porphyra and Gracillaria belongs to class-Rhodophyceae, in which reserve food is found in form of floridean starch and Galactan- $\mathrm{SO}_4$ polymers.
Question
If you are asked to classify the various algae into distinct groups, which of the following characters you should choose? [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) Types of pigments present in the cell
(b) Nature of stored food materials in the cell
(c) Structural organisation of thallus
(d) Chemical composition of the cell wall
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Types of pigments present in the cell of algae is the most important character for classification.
Question
Sexual reproduction in Spirogyra is an advanced feature because it shows [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) physiologically differentiated sex organs
(b) different size of motile sex organs
(c) same size of motile sex organs
(d) morphologically different sex organs
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In Spirogyra, the sexual reproduction involves the fusion of two morphologically identical isogametes and physiologically dissimilar anisogametes. This is a case of primitive anisogamy. In this the active gamete is known as the male and the passive as the female.
Question
A research student collected certain alga and found that its cells contained both chlorophyll-a,b,c and chlorophyll-d as well as phycoerythrin. The alga belongs to [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) Rhodophyceae
(b) Bacillariophyceae
(c) Chlorophyceae
(d)Phaeophyceae
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Members of Rhodophyceae (red algae) contains Chlorophyll-a, $d$, $r$-phycoerythrin, $r$-phycocyanin, $\alpha$ and $\beta$-carotene pigments.
Members of Chlorophyceae (green algae) contain chlorophyll- $a, b$ and $\beta$-carotene pigments.
Members of Bacillariophyceae (diatoms) contain chlorophyll- $\alpha, c$, $\beta$-carotene, $\alpha$-carotene pigments.
Members of Cyanophyceae
(cyanobacteria, blue-green algae) contain chlorophyll-a, c-phycocyanin,
c-phycoerythrin and $\beta$-carotene pigments.
Question
Ulothrix can be described as a [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) non-motile colonial alga lacking zoospores
(b) filamentous alga lacking flagellated reproductive stages
(c) membranous alga producing zoospores
(d) filamentous alga with flagellated reproductive stages
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Ulothrix is a freshwater, filamentous green algae, found in rather cold flowing water. Sexual reproduction in Ulothrix is isogamous type, i.e. it takes place between two morphological similar motile, flagellated male and female gametes which come from different filaments.
Question
Ulothrix filaments produce [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) isogametes
(b) anisogametes
(c) heterogametes
(d) basidiospores
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Ulothrix belongs to green algae.
Sexual reproduction in Ulothrix takes place by the union of isogametes which are motile, biflagellate, morphologically similar gametes. Approximately 8-32 isogametes are produced from a mother cell. Two gametes come from two different filament, fuse and form a diploid zygote.
Question
Brown algae is characterised by the presence of [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) phycocyanin
(b) phycoerythrin
(c) fucoxanthin
(d) haematochrome
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
In addition to chlorophyll-a, brown algae posses special carotenoids and fucoxanthin. It is due to the fucoxanthin (brown pigment) that these algae appear brown.
Phycocyanin and phycoerythrin are phycobilins which are found in red algae (phycocyanin-r, phycoerythrin-r) and blue-green algae(phycocyanin-c, phycoerythrin-c).
Question
An alga very rich in protein is [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) Spirogyra
(b) Ulothrix
(c) Oscillatoria
(d) Chlorella
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Dried Chlorella pyrenoidosa contains approxi- mately $50-55 \%$ crude protein (more than that in dried beef, soyabean meal and dried yeast).
Question
Blue-green algae belong to
(a) eukaryotes
(b) prokaryotes
(c) Rhodophyceae
(d) Chlorophyceae
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Blue-green algae or cyanobacteria are the largest Gram negative, aerobic, photoautotrophic, nitrogen-fixing, simplest chlorophyll containing thallophytes/ prokaryotes. They neither have a definite nucleus nor definite plastid with grana. They also lack flagella, chlorophyll-b, mesosome, meiosis and membrane bound organelles (except ribosame of 70 type).
Question
Agar is commercially obtained from [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) red algae
(b) green algae
(c) brown algae
(d) blue-green algae
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Agar is a gelatinous, sulphated non-nitrogenous, tasteless, odourless mucopolysaccharide obtained from middle lamella of cell wall of marine red algae like Gracillaria, Gelidium, Gigartina, etc. commonly known as agarophytes. It is used as solidifying agent in the culture medium, as luxative stabiliser or thickener in preparing jams, jellies, creams, ice creams, bakery products and as luxative in drug industry.
Question
The absence of chlorophyll, in the lowermost cell of Ulothrix, shows [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) functional fission
(b) tissue formation
(c) cell characteristic
(d) beginning of labour division
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Ulothrix is an advanced alga, with three types of cells-green dome-shaped apical cell, green intercalary cell and basal non-green cell called holdfast. Holdfast or basal cell is for attachment, it has nucleus and cytoplasm, its presence shows the beginning of division of labour.
Question
In Chlorophyceae, sexual reproduction occurs by [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) isogamy and anisogamy
(b) isogamy, anisogamy and oogamy
(c) oogamy only
(d) anisogamy and oogamy
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In Chlorophyceae, three types of sexual reproduction occurs, i.e. isogamy, anisogamy and oogamy.
Isogamy involves the fusion of those gametes which are similar in size, shape and structure, e.g.
Chlamydomonas debaryana.
In anisogamy gametes differ
morphologically and also behave differently, e.g. Chiomydomonas braunii. In oogamy, fusion between motile and non-motile gametes takes place, e.g. Chlamydomonas coccifera.
Question
Which of the following cannot fix nitrogen? [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) Nostoc
(b)Azotobacter
(c) Spirogyra
(d) Anabaena
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Spirogyra is a free floating, filamentous, green, freshwater alga, popularly called pond silk. It has no role in nitrogen fixation. It forms a green slimy mass on the surface of standing and stagnant water of ponds during spring season, hence also called pond scum.
Whereas, blue-green algae like Nostoc, Anaboena are the important nitrogen fixing cyanobacteria, so these are used as biofertiliser. Azotobacter is the aerobic free living/non-symbiotic nitrogen fixer.
Question
Chloroplast of Chlamydomonas is [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) stellate
(b) cup-shaped
(c) collar-shaped
(d)spiral
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In Chlamydomonas, chloroplast is single and cup-shaped. Chloroplasts are the pigment (chl- $a$ and chl-b) containing bodies present in green algae. The green colouration of the members of chlorophyta is due to the presence of excess of chlorophyll in the chloroplasts. The chloroplasts are well defined bodies met within every cell of the members of this class, though number and shape of the chloroplasts varies in different orders of the class.
Question
In Ulothrix/Spirogyra, reduction division (meiosis) occurs at the time of [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) gamete formation
(b) zoospore formation
(c) zygospore germination
(d) vegetative reproduction
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
In Uiothrix/Spirogyro, meiosis takes place at the time of zygospore germination. It takes place when (+) and (-) plants/fillaments results in the formation of diploid zygote (2x). Zygote is tetraflagellated, it secretes a thick wall and becomes non-motile to form diploid zygospore.
Under favourable conditions, zygospore undergoes zygotic meiosis to form motile tetraflagellated zoomeiospores or non-motile aplanomeiospores. Each meiospore (haploid) germinates to new filament of $(+)(-)$ strain.
Question
Pyrenoids are the centres for formation of [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) porphyra
(b) enzymes
(c) fat
(d) starch
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Pyrenoid is a seat of synthesis and storage of starch present in the chloroplast of algae. A pyrenoid has a core of protein around which starch is deposited as layers.
Question
A plant in which sporophytic generation is represented by zygote is [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) Pinus
(b) Selaginella
(c) Chlamydomonas
(d) Dryopteris
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
In Chiamydomonas, the plant body is haploid, and represents gametophyte. It reproduces asexually through the formation of zoospores and sexually through gametes. Gametes(haploid) fuse to produce diploid zygote, representing the sporophytic generation. The zygote secretes a wall around it to become a resting zygospore(diploid). The zygote and zygospore are the only diploid structure which represents the diplophase.
Question
The product of conjugation in Spirogyra or fertilisation of Chlamydomonas is [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) zygospore
(b) zoospore
(c) oospore
(d) carpospore
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Zygospore (zygote) is the fusion product of two gametes. It infact, represents the resting stage formed after withdrawl of flagella and formation of a thick wall around the freshly formed zygote. Zygospore is spherical with thick, smooth or stellate wall and contains fats and reserve food materials other than starch. It can resist unfavourable conditions.
In Chlamydomonas, zygospore is the resultant of isogamy, anisogamy or oogamy. In Spirogyra sexual reproduction occurs through conjugation, which may be scalariform or lateral. The resulting zygote secretes a thick wall called zygospore (having 3 layers thick wall, diploid nucleus and abundant food reserves in the form of oil and starch).
Question
Sexual reproduction involving fusion of two cells in Chlamydomonas is [CBSE AIPMT 1988]
(a) isogamy
(b) homogamy
(c) somatogamy
(d) hologamy
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
In Chlamydomonas, hologamy involves the fusion of two young individuals directly, e.g. C. snowioe and isogamy involves fusion of gametes which are similar in size, structure and physiology. e.g. C. euganetos.
Question
Acetabularia used in Hammerling’s nucleocytoplasmic experiments is [CBSE AIPMT 1988]
(a) unicellular fungus
(b) multicellular fungus
(c) unicellular uninucleate green alga
(d) unicellular multinucleate green alga
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Acetabularia is the largest uninucleated green marine alga popularly called mermaids wine glass umbrella plant. It has a cap, stalk and rhizoidal base and nucleus lies in the base. Danish biologist J Hammerling (1953) by his grafting experiments involving exchange of nucleus in Acetabularia proved the role of nucleus in heredity. growth, morphology, differentiation and morphogenesis.
