Question
Which of the following is not a step in Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer Technology (MOET)? [NEET 2021]
(a) Cow is administered hormone having LH like activity for super ovulation
(b) Cow yields about 6-8 eggs at a time
(c) Cow is fertilised by artificial insemination
(d) Fertilised eggs are transferred to surrogate mothers at 8-32 cell stage
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Multiple Ovulation Embryo Transfer Technology (MOET) is a programme for herd improvement.
In this method, cow is administered hormone, having FSH (not LH) like activity to induce follicular maturation and super ovulation.
Question
Inbreeding depression is [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) reduced motility and immunity due to close inbreeding.
(b) decreased productivity due to mating of superior male and inferior female
(c) decrease in body mass of progeny due to continued close inbreeding
(d) reduced fertility and productivity due to continued close inbreeding
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Inbreeding depression is continued inbreeding, especially close breeding which reduces fertility and even productivity in animals. This problem is usually overcome by outbreeding.
Question
By which method was a new breed ‘Hisardale’ of sheep formed by using Bikaneri ewes and Marino rams? [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) Mutational breeding
(b) Cross breeding
(c) Inbreeding
(d) Outcrossing
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Hisardale is a new breed of sheep developed in Punjab by crossing Bikaneri ewes and Marino rams. In cross-breeding, superior male of one breed is mated with superior female of another breed.
Question
Select the incorrect statement regarding inbreeding. [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) Inbreeding helps in the elimination of deleterious alleles from the population
(b) Inbreeding is necessary to evolve a pureline in any animal
(c) Continued inbreeding reduces fertility and leads to inbreeding depression
(d) Inbreeding depression cannot be overcome by outcrossing
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The incorrect statement regarding inbreeding is the option (d). It is because continuous inbreeding among cattle causes inbreeding depression. It decreases the fertility and even productivity of an animal.
It can be overcome by applying outbreeding in which mating is done between different breeds or individuals of the same breed but having no common ancestors. Outbreeding includes outcrossing, cross-breeding and interspecific hybridisation.
Question
Mad cow disease in cattle is caused by an organism which has [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) inert crystalline structure
(b) abnormally folded protein
(c) free RNA without protein coat
(d) free DNA without protein coat
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Mad cow disease in cattle is caused by prions which are abnormally folded proteins. It is also known as Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy (BSE). It is a progressive neurological disorder of cattle.
Question
Which of the following statements about methanogens is not correct? [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) They can be used to produce biogas
(b) They are found in the rumen of cattle and their excreta
(c) They grow aerobically and breakdown cellulose rich food
(d) They produce methane gas
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Statement (c) is incorrect. Correct information about the statement is as follows Certain bacteria, which grow anaerobically on cellulosic material, produce large amount of methane along with $\mathrm{CO}_2$ and $\mathrm{H}_2$. These bacteria are collectively called methanogens and one such example is Methanobacterium. Rest statements are correct.
Question
Homozygous purelines in cattle can be obtained by [NEET 2017]
(a) mating of related individuals of same breed
(b) mating of unrelated individuals of same breed
(c) mating of individuals of different breed
(d) mating of individuals of different species
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
When closely related species of same organisms are crossed continuously for few successive generations, it results in accumulation of recessive characters, thus homozygous purelines are obtained.
Question
Artificial selection to obtain cows yielding high milk output represents [NEET 2017]
(a) stabilising selection as it stabilises this character in the population
(b) directional as it pushes the mean of the character in one direction
(c) disruptive as it splits the population into two, one yielding higher output and the other lower output
(d) stabilising followed by disruptive as stabilises the population of produce higher yielding cows
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
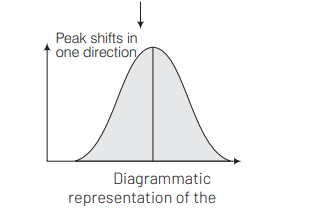
The directional selection leads to change in the phenotypic characters of a population in one direction. In the case of artificial selection, it is intentionally done to increase the milk production, so directional selection operates.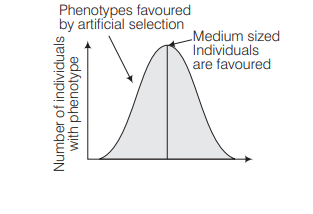
Question
Interspecific hybridisation is the mating of [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) animals within same breed without having common ancestors
(b) two different related species
(c) superior males and females of different breeds
(d) more closely related individuals within same breed for 4-6 generations
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The interspecific hybridisation is the mating or cross between two different related species belonging to same genus.
Question
Among the following edible fishes, which one is a marine fish having rich source of omega-3 fatty acids? [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) Mystus
(b) Mangur
(c) Mrigala
(d) Mackerel
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Mackerel is a marine fish having rich quantity of omega-3 fatty acid.
Question
Outbreeding is an important strategy of animal husbandry because it [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) help in accumulation of superior genes
(b) is useful in producing purelines of animals
(c) is useful in overcoming inbreeding depression
(d) exposes harmful recessive genes that are eliminated by selection
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The breeding of stocks or individuals that are not closely related is called outbreeding. It is an important strategy of animal husbandry because it is useful in overcoming inbreeding depression.
Inbreeding depression is the condition in which the fertility and the productivity of animals is reduced due to the continuous breeding in same species.
Question
In cloning of cattle a fertilised egg is taken out of the mother’s womb and [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) in the eight cell stage, cells are separated and cultured until small embryos are formed which are implanted into the womb of other cows
(b) in the eight cell stage the individual cells are separated under electrical field for further development in culture media
(c) from this up to eight identical twins can be produced
(d) the egg is divided into 4 pairs of cells which are implanted into the womb of other cows
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
During cloning of a cattle a fertilised egg is taken out of the mother’s womb and in the eight cell stage, cells are separated and cultured until small embryos are formed which are implanted into the womb of other cows.
Question
Compared to a bull a bullock is docile because of[CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) higher levels of cortisone
(b) lower levels of blood testosterone
(c) lower levels of adrenaline/noradrenaline in its blood
(d) higher levels of thyroxine
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Compared to a bull a bullock is docile because of lower levels of blood testosterone. A bullock is a castrated bull. Bulls are castrated to make them more meek and docile.
Castration is the removal or destruction of one or both testicles and results in sterility, decreased sexual desire and inhibition of secondary sex characteristics. It is performed for the purpose of improving the quality of meat and decreasing the aggressiveness of farm animals; in pet animals it prevents unwanted mating behaviour, reproduction and wandering.
Question
Which one the following is a viral disease of poultry? [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) Coryza
(b) New castle disease
(c) Pasteurellosis
(d) Salmonellosis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
New castle disease is a viral disease of poultry. It is a highly contagious zoonotic bird disease affecting many domestic and wild avian species. Its effects are most notable in domestic poultry due to their high susceptibility and the potential for severe impacts of an epidemic on the poultry industries. It is endemic to many countries.
Question
Which one of the following pair is mismatched? [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) Pilaglobosa – Pearl
(b) Apis indica – Honey
(c) Kenia lacca – Lac
(d) Bombyxmori – Silk
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Out of the following the option (a) is mismatched because pearl is obtained from pearl oyster (Pinctada vulgaris) while, honey from Apis indica, lac from Kenia locca and silk from Bombyx mori.
Question
The world’s highly prized wool yielding ‘Pashmina’ breed is [CBSE AIPMT 2005]
(a) goat
(b) sheep
(c) goat-sheep cross
(d) Kashmir sheep-Afghan sheep cross
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Pashmina refers to a type of Kashmir wool and textiles made from it. This wool comes from a special breed of goat indigenous to high altitudes of the Himalayan mountains. The Himalayan mountain goat, sheds its winter coat every spring and the fleece is caught on thorn bushes. One goat sheds approximately 3-8 ounces of the wool fibre.
Question
Honey is [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) acidic
(b) neutral
(c) alkaline
(d) basic after some days
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Honey is acidic as its $p \mathrm{H}$ is 2.5-4.0.Honey is a byproduct of bee keeping. It is sweet in taste and white to black in colour. Smell of honey varies according to juices collected from different flowers.
Question
High milk yielding varieties of cows are obtained by [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) super ovulation
(b) artificial insemination
(c) use of surrogate mother
(d) All of the above
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In superovulation, a high milk yielding cow is induced to shed 4-6 eggs every 6-8 weeks (instead of $20-21$ days).
The superovulated donor is artificially inseminated with semen from a quality bull. the embryos developing from the eggs so fertilised are flushed out. These good quality embryos are now transferred to surrogate mother for delivery.
Question
Pebrine is a disease of [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) honeybee
(b) fish
(c) silkworm
(d) lac insect
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Pebrine disease is one of the most damaging disease of silkworm. It is caused by Nosema bombycis nageli. The other diseases of silk worm are Flacherie which is an infectious viral disease marked by body flaccidity and digestive disorders. Muscaridine, which is a fungal disease caused by Spicaria or Botrytis.
Question
Pasteurisation of milk involve heating for [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) 60 min at about $90^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$
(b) 30 min at about $50^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$
(c) 30 min at about $65^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$
(d) 60 min at $100^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Pasteurisation of milk involves heating of milk at $60-70^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ for about $30 \mathrm{~min}$ so as to kill the pathogens.
Question
The earliest animal to have been domesticated by man was most likely the [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) horse
(b) cow
(c) dog
(d) pig
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Dog was one of the earliest animals to be domesticated by man.
Question
The long-term prospects for a truly human civilisation depend in a large measure on [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) the ability of humanity to moderate its fecundity
(b) increasing the food production
(c) colonisation of under populated areas
(d) control of human diseases
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The long term prospects for a truly human civilisation depend on a large measure on control of human disease.
Question
The silkworm silk is the product of [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) cuticle of the larva
(b) cuticle of the adult
(c) salivary gland of the larva
(d) salivary gland of the adult
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Caterpillar larva of Bombyx mori secretes liquid silk from its salivary glands.
