Question
Match the following columns and select the correct option from the codes given below. [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
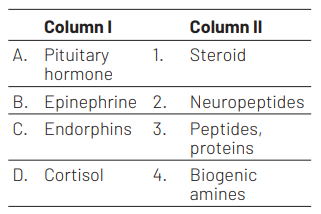
A B C D
(a) 4 1 2 3
(b) 3 4 2 1
(c) 4 3 1 2
(d) 3 4 1 2
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Option (b) is correct match which is as followsPituitary hormones are chemically peptides and proteins. Epinephrine is a biogenic amine. Endorphins are neuropeptides. Cortisol is a steroid hormone.
Question
Hormones stored and released from neurohypophysis are [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) thyroid stimulating hormone and oxytocin
(b) oxytocin and vasopressin
(c) follicle stimulating hormone and leutinizing hormone
(d) prolactin and vasopressin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Neurohypophysis (pars nervosa) is also known as posterior pituitary which stores and releases two hormones called oxytocin and vasopressin, which are actually synthesised by the hypothalamus and are transported axonally to neurohypophysis.
Question
GnRH, a hypothalamic hormone, needed in reproduction, acts on [NEET 2017]
(a) anterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of $\mathrm{LH}$ and oxytocin
(b) anterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of $\mathrm{LH}$ and $\mathrm{FSH}$
(c) posterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of oxytocin and FSH
(d) posterior pituitary gland and stimulates secretion of $\mathrm{LH}$ and relaxin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
GnRH is a hypothalamic hormone. It stimulates the anterior lobe of pituitary gland to secrete $\mathrm{LH}$ and FSH.
Question
Hypersecretion of growth hormone in adults does not cause further increase in height because [NEET 2017]
(a) growth hormone becomes inactive in adults
(b) epiphyseal plates close after adolescence
(c) bones loose their sensitivity to growth hormone in adults
(d) muscle fibres do not grow in size after birth
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Chronic hypersecretion of Growth Hormone (GH) leads to gigantism or acromegally depending on the age of the individual. If its hypersecretion occurs before the ossification of epiphyseal plates, it causes exaggerated and prolonged growth in long bones. It results in gigantism. In adults, hypersecretion of GH leads to accromegaly. No increase in height occurs because of the ossified epiphyseal plate.
Question
The amino acid, tryptophan is the precursor for the synthesis of [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) thyroxine and tri-iodothyronine
(b) oestrogen and progesterone
(c) cortisol and cortisone
(d) melatonin and serotonin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Melatonin and serotonin are derivatives of tryptophan amino acid while thyroxine and tri-iodothyronine are iodinated tyrosine amino acid derivatives.
Question
Which of the following pairs of hormones are not antagonistic (having opposite effects) to each other? [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) Insulin Glucagon
(b) Aldosterone Atrial Natriuretic Factor
(c) Relaxin Inhibin
(d) Parathormone Calcitonin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Relaxin hormone which is secreted by posterior pituitary gland relaxes the pubic symphysis during parturition while inhibin decreases the secretion of FSH from anterior pituitary.
Question
Name a peptide hormone which acts mainly on hepatocytes, adipocytes and enhances cellular glucose uptake and utilisation. [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) Insulin
(b) Glucagon
(c) Secretin
(d) Gastrin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Insulin is the peptide hormone which enhances the uptake of glucose molecules by liver cells (hepatocytes) and fat cells (adipocytes) for its cellular utilisation. Such an activity of insulin brings down the level of glucose in the blood.
Question
Which one the following hormones is not involved in sugar metabolism? [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) Cortisone
(b) Aldosterone
(c) Insulin
(d) Glucagon
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Aldosterone is not involved in sugar metabolism. It is a steroid hormone (mineralocorticoid) produced by the outer section (zona glomerulosa) of the adrenal cortex in the adrenal gland. It plays a central role in the regulation of blood pressure mainly by acting on the distal tubules and collecting ducts of the nephron, increasing reabsorption of ions and water in the kidney, to cause the conservation of sodium, secretion of potassium, increase in water retention and decrease in blood pressure and blood volume.
Question
Which one of the following hormones though synthesised elsewhere, is stored and released by the master gland?[CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) Antidiuretic hormone
(b) Luteinising hormone
(c) Prolactin
(d) Melanocyte stimulating hormone
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) or vasopressin is a peptide hormone synthesised in the hypothalamus, but stored and released from the posterior pituitary lobe.
Question
Identify the hormone with its correct matching of source and function. [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) Oxytocin-Posterior pituitary, growth and maintenance of mammary glands
(b) Melatonin-Pineal gland, regulates the normal rhythm of sleepwake cycle
(c) Progesterone-Corpus luteum, stimulation of growth and activities of female secondary sex organs
(d) Atrial natriuretic factor-Ventricular wall increases the blood pressure
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Melatonin is a hormone present in animals, plants and microbes. In animals melatonin allows the regulation of cicarcadian rhythms. Oxytocin is a neurohypophysial hormone which stimulates the muscle contraction (smooth muscle) in the wall of uterus during childbrith.
Progesterone is a female hormone produced by the corpus luteum after ovulation. This hormone maintain the wall of uterus throughout the pregnancy. ANF stimulates the secretion of $\mathrm{Na}$ and $\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$ by the kidneys and helps in regulating blood pressure.
Question
A person entering an empty room suddenly finds a snake right in front on opening the door. Which one of the following is likely to happen in his neurohormonal control system? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) Sympathetic nervous system is activated releasing epinephrine and norepinephrine from adrenal medulla
(b) Neurotransmitters diffuse rapidly across the cleft and transmit a nerve impulse
(c) Hypothalamus activates the parasympathetic division of brain
(d) Sympathetic nervous system is activated releasing epinephrine and norepinephrine from adrenal cortex
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Epinephrine and nor-epinephrine are secreted by adrenal medulla (under the control of sympathetic nervous system) in response to stress of any kind or during emergency situations. These are also called emergency hormones. Thus, they would be released when the person enter an empty room and suddenly finds a snake.
Question
Which one of the following pairs of hormones are the examples of those that can easily pass through the cell membrane of the target cell and bind to a receptor inside it (mostly in the nucleus)? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) Insulin and glucagon
(b) Thyroxin and insulin
(c) Somatostatin and oxytocin
(d) Cortisol and testosterone
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Cortisol and testosterone are lipid soluble hormones, which can directly pass through the cell membrane of the target cell and bind with interacellular receptors.
Question
What is correct to say about the hormone action in humans? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) Glucagon is secreted by $\beta$-cells of islets of Langerhans and stimulates glycogenolysis
(b) Secretion of thymosine is stimulated with ageing
(c) In females, FSH first binds with specific receptors on ovarian cell membrane
(d) FSH stimulates the secretion of oestrogen and progesterone
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
FSH hormone is one of the gonadotropins secreted by anterior lobe of pituitary. It is a proteinaceous hormone, so binds with extra cellular or membrane bound receptors.
Question
Which one of the following pairs is incorrectly matched? [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a)Glucagon $\quad-$ Beta cells (source)
(b) Somatostatin – Delta cells (source)
(c) Corpus luteum- Relaxin (secretion)
(d) Insulin -Diabetes mellitus (disease)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In pancreatic islets, alpha or A-cells constitute about $15 \%$ of pancreatic islets cells and secrete glucagon. Its molecule consists of a single polypeptide chain of 29 amino acid residues. Glucagon intensifies glycogenolysis, deamination and gluconeogenesis and inhibits glycogenesis in liver cells. It also intensifies lipolysis in adipose tissue.
Thus, it is a promoter of catabolic metabolism.
Question
Foetal ejection reflex in human female is induced by [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) pressure exerted by amniotic fluid
(b) release of oxytocin from pituitary
(c) fully developed foetus and placenta
(d) differentiation of mammary glands
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Oxytocin (child birth hormone) secreted by neurohypophysis of pituitary gland stimulates contraction of uterus muscles. It stimulates labour pain for child birth. When secretion of progesterone hormone declines it will result in making the end of pregnancy. As the sensory impulse of increasing labour pain reaches hypothalamus, more and more oxytocin is released from posterior pituitary under a positive feedback regulation, it dilates the cervix (vaginal stretching).
Question
The blood calcium level is lowered by the deficiency of [CBSE AIPMT 2008, 1999]
(a) parathormone
(b) thyroxine
(c) calcitonin
(d) $\operatorname{Both}(a)$ and (c)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The chief cells of the parathyroid secrete parathormone. Its deficiency causes the lowering of blood calcium level. This increases the excitability of nerves and muscles causing cramps and convulsions. This causes parathyroid tetany characterised by sustained contractions of the muscles of larynx, face, hands and feet. Calcitonin is secreted when calcium level is high in blood. It has an opposite action to that of parathyroid hormone and lowers the calcium level by suppressing release of calcium ions from the bones. Thyroxine is secreted from the thyroid gland. It regulates the metabolic rate of the body and thus, maintain basal metabolic rate, stimulate protein synthesis and therefore, promote growth of the body tissues.
Question
In human adult females, oxytocin [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) is secreted by anterior pituitary
(b) stimulates growth of mammary glands
(c) stimulates pituitary to secrete vasopressin
(d) causes strong uterine contractions during parturition
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Oxytocin hormone is secreted from the posterior lobe of pituitary gland. It promotes contraction of uterine muscle during parturition and contraction of myoepithelial cells of lactating breast, sequeezing milk into the large ducts behind the nipple. Because of its role oxytocin is called birth hormone.
Question
Feeling the tremors of an earthquake a scared resident of seventh floor of a multistoryed building starts climbing down the stairs rapidly. Which hormone initiated this action? [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) Thyroxin
(b) Adrenaline
(c) Glucagon
(d) Gastrin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Adrenaline hormone is responsible for this action, as adrenaline hormone is known as $3 \mathrm{~F}$ hormone, i.e. fright, flight and fight.
Question
In the human female, menstruation can be deferred by the administration of [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) $\mathrm{LH}$ only
(b) combination of FSH and LH
(c) combination of estrogen and progesterone
(d) FSH only
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
When the production of progesterone and estrogen hormone stops in blood this leads to shedding of the lining of uterine endometrium. Therefore, by supply of oestrogen and progesterone the menstruation can be deferred.
Question
Compared to a bull a bullock is docile because of [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) higher levels of thyroxin
(b) higher levels of cortisone
(c) lower levels of blood testosterone
(d) lower levels of adrenaline/noradrenaline in its blood
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Testes are degenerated due to which testosterone level in blood is reduced. This hormone promotes the growth of many body tissues such as muscles.
Question
Withdrawl of which of the following hormones is the immediate cause of menstruation? [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) Destrogen
(b) $\mathrm{FSH}$
(c) FSH-RH
(d) Progesterone
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Menstruation is caused by the reduction of oestrogen and progesterone. Hormone level, (especially progesterone) at the end of monthly ovarian cycle. The first effect is decreased stimulation of the endometrial cells by these two hormones followed rapidly by involution of the endometrium itself to about $65 \%$ of its previous thickness.
Question
Which hormone causes dilation of blood vessels, increased oxygen consumption and glucogenesis? [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) $\mathrm{ACTH}$
(b) Insulin
(c) Adrenaline
(d) Glucagon
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Adrenaline (epinephrine) is a hormone produced by adrenal medulla and is secreted in great amounts during emotional states. It elevates the glucose level in blood stream (by glucogenesis) which is accompanied by increase in oxygen consumption, body temperature, heat production. Adrenaline also causes an increase in the flow of blood by dilating the blood vessels.
Insulin regulates the glucose level in blood. ACTH (Adreno Corticotropic Hormone) is secreted by anterior pituitary and stimulates the adrenal cortex.
Glucagon is a polypeptide hormone secreted by the alpha cells of islets of Langerhans of pancreas. It also acts to promote glycogenolysis.
Question
Sertoli cells are regulated by the pituitary hormone known as [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) $\mathrm{FSH}$
(b) $\mathrm{GH}$
(c) prolactin
(d) $\mathrm{LH}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Sertoli cells are the cells that line the seminiferous tubules in the testis. These cells protect the spermatids and convey nutrients to both the developing and mature spermatozoa. Sertoli cells are regulated by FSH (Follicle Stimulating Hormone) as the FSH receptors are confined to the Sertoli cells.FSH stimulates Sertoli cells to produce androgen-binding protein and inhibin and together with testosterone, promotes the proliferation of Sertoli cells.
Question
A steroid hormone which regulates glucose metabolism is [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) cortisol
(b) corticosterone
(c) 11-deoxycorticosterone
(d) cortisone
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Cortisol (a steroid hormone) is the principal glucocorticoid hormone of many mammals including humans (corticosterone is more abundant in some small mammals). It regulates the glucose metabolism and promotes gluconeogenesis, especially during starvation and raises blood pressure. Cortisone is an inactive form of cortisol.
Question
Chemically hormones are [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) biogenic amines only
(b) proteins, steroids and biogenic amines
(c) proteins only
(d) steroids only
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Chemically hormones are of different nature like protein hormones (hypothalmic hormones), steroids (sex hormones) and biogenic amines (like thyroxin hormone).
Question
Which of the following hormones is not a secretion product of human placenta? [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) Human chorionic gonadotropin
(b) Prolactin
(c) Destrogen
(d) Progesterone
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Prolactin is secreted by anterior pituitary gland (not human placenta) which stimulates mammary gland development during pregnancy and lactation after child birth. Placenta is a connection between the uterine wall of mother and the foetus. It helps in exchange of material between these two. Placenta secretes human chorionic gonadotropin, oestrogen and progesterone.
Question
Which one of the following hormones is a modified amino acid? [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) Epinephrine
(b) Progesterone
(c) Prostaglandin
(d) Destrogen
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Epinephrine is synthesised from amino acid tyrosine. While oestrogen and progesterone are modified steroids and prostaglandins are basically fat.
Question
Mainly which type of hormones control the menstrual cycle in human beings? [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) $\mathrm{FSH}$
(b) $\mathrm{LH}$
(c) $\mathrm{FSH}, \mathrm{LH}_{\text {, estrogen }}$
(d) Progesterone
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH), Luteinising Hormone (LH) and estrogen all play an important role in controlling the menstrual cycle in human females.
Question
When both ovaries are removed from rat which hormone is decreased in blood? [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) Oxytocin
(b) Prolactin
(c) Estrogen
(d) Gonadotropic releasing factor
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
If both the ovaries are removed from rat then the blood plasma level of oestrogen will be affected as it is produced by theca interna cells of Graafian follicles. Oestrogen regulates growth and development of female accessary reproductive organs, secondary sexual characters and sexual behaviour.
Question
Melanin protects from [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) UV-rays
(b) visible rays
(c) infra-red rays
(d) X-rays
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Melanin is a protective pigment synthesised from tyrosine. Melanocytes under the influence of melanocyte secreting hormone secrete melanin which protects the body from harmful effects of UV rays.
Question
Adrenaline directly affects [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) SA node
(b) $\beta$-cells of Langerhans
(c) dorsal root of spinal cord
(d) epithelial cells of stomach
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The hormone adrenaline (epinephrine) is secreted by adrenal medulla and directly affects SA node thereby increasing heart rate. This hormone is responsible for the alarming reactions. It also increases breathing and blood glucose level.
Question
Which steroid is used for transformation? [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) Cortisol
(b) Cholesterol
(c) Testosterone
(d) Progesterone
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Cholesterol forms a major component of animal cell membranes. Liposomes (artificially created spheres surrounded by a phospholipid bilayer like a membrane) are used for transformation (transgenics).
Question
Secretion of progesterone by corpus luteum is initiated by [CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) thyroxine
(b) $\mathrm{LH}$
(c) $\mathrm{MSH}$
(d) testosterone
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
LH (Luteinising Hormone), secreted by anterior pituitary, stimulates the corpus luteum to secrete the hormone progesterone.
Question
Hormones thyroxine, adrenaline and the pigment melanin are formed from [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) tryptophan
(b) glycine
(c) tyrosine
(d) proline
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Tyrosine is the precursor of : (a) hormone epinephrine (i.e. adrenaline) and thyroid hormones, (b) neurotransmitter dopamine, (c) melanin (the black pigment of skin).
Question
Which one of the following hormones stimulates the ‘let down’ (release) of milk from the mother’s breasts when the baby is sucking? [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) Progesterone
(b) Oxytocin
(c) Prolactin
(d) Relaxin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Oxytocin induces contraction of the mammary gland muscles, helps in the flow of milk from mammary glands to mouth of the child, hence, called’milk ejection hormone’.
Question
$\mathrm{ADH}$ or vasopressin is [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) enzyme that hydrolyses peptides
(b) hormone secreted by pituitary that promotes reabsorption of water from glomerular filtrate
(c) hormone that promotes glycogenolysis
(d) energy rich compound connected with muscle contraction
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
$\mathrm{ADH}$ or vasopressin is synthesised in hypothalamus and stored and released by neurohypophysis or posterior lobe of pituitary gland. It controls the permeability of wall of collecting tubules and DCT of renal tubules to water, which stimulates reabsorption of water so, it controls the osmoregulation.
Question
Insulin is [CBSE AIPMT 1990]
(a) vitamin
(b) lipid
(c) hormone
(d) enzyme
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Insulin is earliest known hormone. It is also called hypoglycemic or antidiabetic factor, as it decreases glucose level in blood and prevents occurrence of diabetes. It is secreted by $\beta$-cells of the islets of Langerhans.
Question
Addition of a trace of thyroxine or iodine in water containing tadpoles will [CBSE AIPMT 1990]
(a) keep them in larval stage
(b) hasten their metamorphosis
(c) slow down their metamorphosis
(d) kill the tadpoles
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Thyroxine controls tissue differentiation and metamorphosis of tadpole larva into frog. Gundernatch (1912) proved that metamorphosis of tadpole into adult frog is controlled by thyroxine. Addition of thyroxine in water will hasten the metamorphosis.
Question
Which hormone possesses anti -insulin effect? [CBSE AIPMT 1988]
(a) Cortisol
(b) Calcitonin
(c) Oxytocin
(d) Aldosterone
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Cortisol is a glucocorticoid, secreted by adrenal cortex. It is primarily meant for carbohydrate metabolism, which increases the rate of gluconeogenesis (conversion of proteins in liver into
sugars) and decreases peripheral utilisation of glucose, thus it possess anti-insulin effect.
