Question
Match the following columns and select the correct option. [NEET (Sep.) 2020]

A B C D
(a) 1 4 2 3
(b) 3 2 4 1
(c) 2 3 4 1
(d) 4 3 1 2
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The correct option is (c). It can be explained as follows.
Placenta secretes human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG).
Zona pellucida is a primary egg membrane secreted by the secondary oocyte. The secretions of Bulbourethral glands help in lubrication of the penis. Leydig cells synthesise and secrete testicular hormones called androgens.
Question
Select the correct sequence for transport of sperm cells in male reproductive system. [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) Seminiferous tubules $\rightarrow$ Rete testis $\rightarrow$ Vasa efferentia $\rightarrow$ Epididymis $\rightarrow$ Vas deferens $\rightarrow$ Ejaculatory duct $\rightarrow$ Urethra $\rightarrow$ Urethral meatus
(b) Seminiferous tubules $\rightarrow$ Vasa efferentia $\rightarrow$ Epididymis $\rightarrow$ Inguinal canal $\rightarrow$ Urethra
(c) Testis $\rightarrow$ Epididymis $\rightarrow$ Vasa efferentia $\rightarrow$ Vas deferens $\rightarrow$ Ejaculatory duct $\rightarrow$ Inguinal canal $\rightarrow$ Urethra $\rightarrow$ Urethral meatus
(d) Testis $\rightarrow$ Epididymis $\rightarrow$ Vasa efferentia $\rightarrow$ Rete testis $\rightarrow$ Inguinal canal $\rightarrow$ Urethra
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
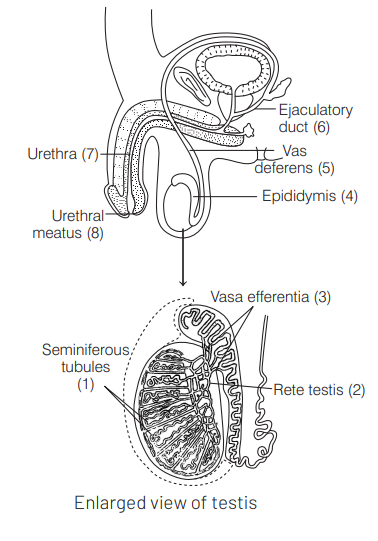
The correct sequence of sperm transport in male reproductive system is seminiferous tubules $\rightarrow$ Rete testis $\rightarrow$ Vasa efferentia $\rightarrow$ Epididymis $\rightarrow$ Vas deferens $\rightarrow$ Ejaculatory duct $\rightarrow$ Urethra $\rightarrow$ Urethral meatus. The pathway of sperm transport is shown in the diagram below
Question
Which of the following depicts the correct pathway of transport of sperms? [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) Rete testis $\rightarrow$ Efferent ductules $\rightarrow$ Epididymis $\rightarrow$ Vas deferens
(b) Rete testis $\rightarrow$ Epididymis $\rightarrow$ Efferent ductules $\rightarrow$ Vas deferens
(c) Rete testis $\rightarrow$ Vas deferens $\rightarrow$ Efferent ductules $\rightarrow$ Epididymis
(d) Efferent ductules $\rightarrow$ Rete testis $\rightarrow$ Vas deferens $\rightarrow$ Epididymis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The sperms are produced in the seminiferous tubules. The rete testis is connected to these tubules at one end and transfers sperms to vasa efferentia (small tubular structures between rete testis and epididymis). The sperms reach to epididymis through vasa efferentia where they are temporarily stored for maturation and then transferred to seminal vesicle through vas deferens.
Thus, the correct route is Rete testis $\rightarrow$ Efferent ductules $\rightarrow$ Epididymis $\rightarrow$ vas deferens.
Question
The shared terminal duct of the reproductive and urinary system in the human male is [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) urethra
(b) ureter
(c) vas deferens
(d) vasa efferentia
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In the human male, urethra provides an exit for urine from the urinary bladder as well as semen from vasa differentia during ejaculation. Thus, it is also known as urogenital duct.
In males, it is about 8 inches $(20 \mathrm{~cm}$ ) long and opens at the end of the penis. Vas deferens and vasa efferentia are the male sex accessory ducts.
Ureters are the tubes that carry urine from the kidney to urinary bladder.
Question
The Leydig cells as found in the human body are the secretory source of [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) progesterone
(b) intestinal mucus
(c) glucagon
(d) androgens
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Interstitial cells or cells of Leydig are present in the connective tissue lying in between seminiferous tubules. These cells secrete oestradiol-steroid androgens, e.g. testosterone.
Androgens stimulate male characters, influence male sexual behaviour (libido) and regulate the development, maturation and functions of male accessory sex organs.
Question
If for some reason, the vasa efferentia in the human reproductive system get blocked, the gametes will not be transported from [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) epididymis to vas deferens
(b) ovary to uterus
(c) vagina to uterus
(d) testes to epididymis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Vasa efferentia (ductuli efference) are 10-20 fine tubules which connect rete testis with an epididymis (ductus epididymis). The latter is a pair of ducts from each testis which is formed by union of its vasa efferentia. If the vasa efferentia get blocked, the sperms will not be transported from testes to epididymis.
Question
The figure given below depicts a diagrammatic sectional view of the female reproductive system of humans. Which one set of three parts out of $A-F$ have been correctly identified?
[CBSE AIPMT 2011]
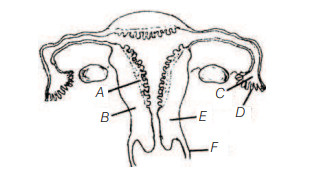
(a) C-Infundibulum, D-Fimbriae, E-Cervix
(b) D-Oviducal funnel, E-Uterus, F-Cervix
(c) A-Perimetrium, B-Myometrium, C-Fallopian tube
(d) B-Endometrium, C-Infundibulum, D-Fimbriae
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The Fallopian tube is about $10-12 \mathrm{~cm}$ long and extends from the periphery of each ovary to the uterus. The part closer to the ovary is funnel shaped and is called infundibulum. The edges of the infundibulum possess finger-like projections called fimbriae, which help in collection of the ovum after ovulation. The uterus opens into vagina through a narrow cervix.
Question
The testes in humans are situated outside the abdominal cavity inside a pouch called scrotum. The purpose served is for [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) escaping any possible compression by the visceral organs
(b) providing more space for the growth of epididymis
(c) providing a secondary sexual feature for exhibiting the male sex
(d) maintaining the scrotal temperature lower than the internal body temperature
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The testes in humans are situated out side the abdominal cavity in scrotal sacs. This is because the temperature of scrotal sacs is $2-2.5^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ which is less than internal body temperature.
Question
Sertoli cells are found in [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) ovaries and secrete progesterone
(b) adrenal cortex and secrete adrenaline
(c) seminiferous tubules and provide nutrition to germ cells
(d) pancreas and secrete cholecystokinin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The epithelium of seminiferous tubule is made up of two types of cells, i.e. Sertoli cells and spermatogenic cells. Sertoli cells are elongated and pyramidal which partially envelope the spermatogenic cells. These nourish spermatozoa, act as nurse cells for differentiating spermatozoa. These secrete a glycoprotein hormone, called inhibin which is involved in the negative feed back control of sperm production.
Question
Vasa efferentia are the ductules leading from [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) testicular lobules to rete testis
(b) rete testis to vas deferens
(c) vas deferens to epididymis
(d) epididymis to urethra
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Rete testis is connected to epididymis by 12-20 fine tubules called vasa efferentia or ductuli efferens. These collect sperms from inside the testis and transfer them to the epididymis. Vasa deferens arises from caudal epididymis, conducts sperms from epididymis to urethra.
Question
Seminal plasma in human males is rich in [CBSE AIPMT 2010, 09]
(a) fructose and calcium
(b) glucose and calcium
(c) DNA and testosterone
(d) ribose and potassium
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Seminal plasma is composed of the fluid and sperms from the vas deferens (about $10 \%$ of the total), fluid from the seminal vesicles(almost 60 percent), fluid from the prostate gland (about 30 percent)and small amount of mucous glands, especially the bulbourethral glands.
Question
The part of Fallopian tube closest to the ovary is [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) isthmus
(b) infundibulum
(c) cervix
(d) ampulla
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The Fallopian tubes, uterus and vagina constitute the female accessory ducts. Each Fallopian tube extends from the periphery of each ovary to the uterus. The part closer to the ovary is funnel-shaped infundibulum, which help in collection of the ovum after ovulation.
Question
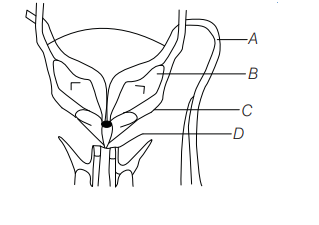
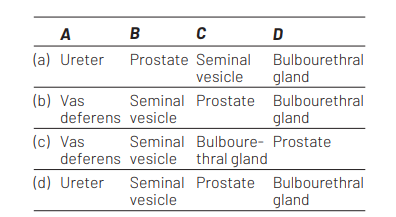
Given below is a diagrammatic sketch of a portion of human male reproductive system. Select the correct set of the names of the parts labelled $A, B, C, D$.
[CBSE AIPMT 2009]
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Option (b) is correct, $A=$ Vas deferens.
$B=$ Seminal vesicle,$C=$ Prostrate and
$D=$ Bulbourethral gland .
Question
Bartholin’s glands are situated [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) on either side of vagina in humans
(b) on either side of vas deference in humans
(c) on the sides of the head of some amphibians
(d) at the reduced tail end of birds
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Bartholin’s glands(Bulbovestibular glands) are one pair, small sized glands find just behind the labia minora, one on either sides of vaginal orifice. These lubricate the vagina during mating and parturition by secretion of mucus.
Question
Location and secretion of Leydig’s cells are [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) liver $\quad-$ cholesterol
(b)ovary – estrogen
(c)testis $\quad-$ testosterone
(d) pancreas – glucagon
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The endocrine part of testis is formed of groups of cells, called interstitial cells or Leydig’s cells, scattered in connective tissue between the sperm producing seminiferous tubules of the testis.
These cells are stimulated to produce male sex hormones, called androgens by ICSH of anterior pituitary. Testosterone is main androgen and is a steroid hormone.
