Question
Match the following concerning essential elements and their functions in plants. [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
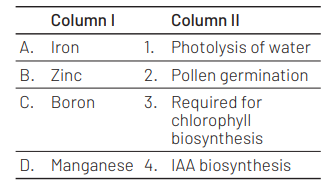
Select the correct option.
A B C D
(a) 4 3 2 1
(b) 3 4 2 1
(c) 4 1 2 3
(d) 2 1 4 3
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The correct option is (b). It can be explained as follows
Iron-essential for the formation of chlorophyll.
Zinc – needed for synthesis of auxin
Boron – have a role in pollen grain germination
Manganese – is involved in the splitting of water to liberate $\mathrm{O}_2$ during photosynthesis.
Question
In which of the following forms is iron absorbed by plants? [NEET 2018]
(a) Free element
(b) Ferrous
(c) Ferric
(d) Both ferric and ferrous
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
According to NCERT, plants absorb iron mostly in the form of ferric $\left(\mathrm{Fe}^{3 *}\right)$ ions. However, plants in acidic soil can absorb iron in ferrous $\left(\mathrm{Fe}^{2+}\right)$ as well as ferric $\left(\mathrm{Fe}^{3+}\right)$ form. It is an important. constituent of proteins involved in the transfer of electrons like ferredoxin and cytochromes. It is reversibly oxidised from $\mathrm{Fe}^{2+}$ to $\mathrm{Fe}^{3+}$ during electron transfer. It activates catalase enzyme. It is essential for the formation of chlorophyl.
Question
In which of the following, all three are macronutrients? [NEET 2016, Phase 1]
(a) Iron, copper, molybdenum
(b) Molybdenum, magnesium, manganese
(c) Nitrogen, nickel, phosphorus
(d) Boron, zinc, manganese
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
None of the option is correct w.r.t. question. The option (a) seems to be more appropriate.
None of the option consist of all three macronutrients, But option (c) have nitrogen and phosphorus which are macronutrients, but nickel is a micronutrients.
Question
Which is essential for the growth of root tip? [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) $Z n$
(b) $\mathrm{Fe}$
(c) $\mathrm{Ca}$
(d) $M \cap$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Calcium is needed to the growing root. tip. It is required in the formation of middle lamella of the cell wall present in the form of calcium pectate. Thus, correct answer is (c).
Question
Deficiency symptoms of nitrogen and potassium are visible first in [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) senescent leaves
(b) young leaves
(c) roots
(d) buds
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Deficiency of both nitrogen and (N) potassium $(K)$ is first visible in senescent. (older)leaves, due to the deficiency symptoms of $\mathrm{N}$ chlorosis occurs while, the deficiency of $K$ causes the inhibition of protein synthesis and scorching of older leaves.
Question
Which one of the following is correctly matched? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) Passive transport of nutrients ATP
(b) Apoplast – Plasmodesmata
(c) Potassium – Readily immobilisation
(d) Bakane of rice seedlings – F Skoog
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Active transport of nutrients require ATP. Symplast includes translocation through plasmodesmata. Bakane disease of rice was found by Hori (1918) to be caused due to Gibberelia fujikuroi. None of the options is correct. Option (c) may be correct if statement be read as “Potassium readily mobilisation” instead of “potassium readily immobilisation.
Question
Which one of the following elements in plants is not remobilised? [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) Calcium
(b) Potassium
(c) Sulphur
(d) Phosphorus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Element like calcium are a part of structural component of the cell and hence, are not released. The deficiency symptoms tend to appear first in the young tissues whenever. the elements are not demobilised.
Question
Which one of the following is not a micronutrient? [CBSE AIPMT 2010, 03]
(a) Molybdenum
(b) Magnesium
(c) Zinc
(d) Boron
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Magnisium is an essential macrountrient found from $0.2-0.4 \%$ dry matter and is necessary for normal plant growth. Magnesium has an important role in photosynthesis because it forms the central atom of chlorophyll.
Question
Manganese is required in [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) nucleic acid synthesis
(b) plant cell wall formation
(c) photolysis of water during photosynthesis
(d) chlorophyll synthesis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
In plants, manganese is absorbed in the form of manganous ions $\left(\mathrm{Mn}^{2+}\right]$. It activates many enzymes involved in photosynthesis, respiration and nitrogen metabolism. The best defined function of manganese is in the splitting of water or photolysis of water to liberate oxygen during photosynthesis.
Question
Which one of the following elements is not an essential micronutrient for plant growth? [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) $\mathrm{Mn}$
(b) $Z n$
(c) $\mathrm{Cu}$
(d) $\mathrm{Ca}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Ca is essential macronutrient for plant growth. It is constituent of middle lamella, activator of enzymes, connected with chromosome formation and many aspects of metabolism.
Question
A plant requires magnesium for [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) holding cells together
(b)protein synthesis
(c) chlorophyll synthesis
(d) cell wall develonment.
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Magnesium is an important constituent of chlorophyll molecule. Thus, a plant. requires magnesium for chlorophyll synthesis.
Question
12 The deficiencies of micronutrients, not only affects growth of plants but also vital functions such as photosynthetic and mitochondrial electron flow. Among the list given below, which group of three elements shall affect most, both photosynthetic and mitochondrial electron transport? [CBSE AIPMT 2005]
(a) $\mathrm{Co}, \mathrm{Ni}, \mathrm{Mo}$
(b) $\mathrm{Ca}, \mathrm{K}, \mathrm{Na}$
(c) $\mathrm{Mn}, \mathrm{Co}, \mathrm{Ca}$
(d) $\mathrm{Cu}, \mathrm{Mn}, \mathrm{Fe}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Micronutrients are minerals obtained from the soil and present in plant tissues at concentrations usually less than $3 \mu \mathrm{molg}^{-1}$ dry matter. Cu (copperl, $\mathrm{Mn}$ (manganese) and $\mathrm{Fe}$ (iron) are those micronutrients which affect both photosynthesis and mitochondrial electron transport because they are the main constituents of various electron carriers.
Question
Boron in green plants assists in [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) sugar transport
(b) activation of enzymes
(c) acting as enzyme cofactor
(d) photosynthesis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Boron is required by plants for (i) uptake and utilisation of $\mathrm{Ca}^{2+}$, (ii) pollen germination and cell differentiation (iii) carbohydrate translocation.
Question
Grey spots of oat are caused by deficiency of [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) $\mathrm{Fe}$
(b) $\mathrm{Cu}$
(c) $\mathrm{Zn}$
(d) $\mathrm{Mn}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Grey spots of oat are caused by the deficiency of manganese (Mn). It is a trace element, required in very small amount. Manganese exists in the soil in the form of bivalents, trivalents.
Question
The major portion of the dry weight of plants comprises of [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) carbon, hydrogen and oxygen
(b) nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium
(c) calcium, magnesium and sulphur
(d) carbon, nitrogen and hydrogen
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The four most common elements in living organisms are $\mathrm{H}, \mathrm{C}, \mathrm{O}, \mathrm{N}$. These are also called as framework element.
Question
Passive absorption of minerals depend on [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) temperature
(b) temperature and metabolic inhibitor
(c) metabolic inhibitor
(d) humidity
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Metabolic inhibitors affect active absorption. Humidity does not affect absorption of minerals as much as temperature. The movement of mineral ions into the root cells by the process of simple diffusion is called as passive absorption. This is spontaneous process and does not require energy.
Question
Zinc as a nutrient is used by the plants in the form of [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) $Z n$
(b) $\mathrm{Zn}^{2+}$
(c) $\mathrm{ZnO}$
(d) $\mathrm{ZnSO}_4$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Zinc is taken up by the plants in the form of $\mathrm{Zn}^2$. It is required for biosynthesis of chlorophyll in some plants. Deficiency of $\mathrm{Zn}$ is shown by a reduction in internodal growth as a result plants display a rosette habit of growth in which the leaves form a circular cluster radiating at or close to the ground.
Question
The plants grown in magnesium deficient but urea sprayed soil would show [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) deep green foliage
(b) early flowering
(c) yellowing of leaves
(d) loss of pigments in petals
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Nitrogen is the constituent of amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids, nucleotides, coenzymes, hexosamines etc. Deficiency of nitrogen rapidly inhibits the plant growth and yellowing of the leaves (chlorosis) magnesium has the specific role in the activation of enzymes, taking part in photosynthesis and respiration. It also forms a part of the ring structure of the chlorophyll molecule. Deficiency of Mg causes chlorosis, i.e. yellowing of leaves.
Thus a plant growing in magnesium-deficient soil would show chlorosis inspite of being sprayed with urea (nitrogen).
Question
Which of the following is not caused by deficiency of mineral nutrition? [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) Necrosis
(b) Chlorosis
(c) Etiolation
(d) Shortening of internodes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The plants grown in dark are said to be etiolated. They lack chlorophyll and, therefore, appear yellow. Thus, it is not caused by deficiency of mineral nutrient.
Chlorosis is resulted due to the partial failure of development of chlorophyll which causes an abnormal colour to plant tissues.
Uncontrolled death of tissues/cells is called as necrosis.
Shortening of internodes is due to the deficiency of $\mathrm{Zn}^{2+}$ ions.
Question
The core metal of chlorophyll is [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) iron
(b) magnesium
(c) nickel
(d) copper
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Chlorophyll molecule, is made up of porphyrin ring which is a structure with alternating single and double bonds containing four small pyrrole rings. It has magnesium atom at the centre.
Question
Which one of the following is not an essential element for plants? [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) Potassium
(b) Iron
(c) lodine
(d) Zinc
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Essential elements are those element which are absolutely necessary for supporting normal growth and reproduction of plants, the elements are specific in their action and are directly involved in the nutrition of the plant. Potassium is macroelement, zinc and iron are microelement. lodine and sodium are essential for animais and are not required by most of the plants however, iodine is found in certain marine algae.
Question
Which one of the following is a micronutrient for plants? [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) Calcium
(b) Magnesium
(c) Manganese
(d) Nitrogen
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Micronutrients are needed in very small amounts by plants, e.g. Manganese, copper, molybdenum, zinc, boron and chlorine.
Question
Phosphorus and nitrogen ions generally get depleted in soil because they usually occur as [CBSE AIPMT 1989]
(a) neutral ions
(b) negatively charged ions
(c) positively charged ions
(d) both positively and negatively charged but disproportionate mixture
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In the soil, phosphorus and nitrogen are present as negatively charged ions, e.g. $\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{PO}_4^{-}, \mathrm{NO}_2^{-}, \mathrm{NO}_3^{-}$ions. These are usually supplied by fertilisers as urea.
Question
The four elements making $99 \%$ of living system are [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) $\mathrm{CHOS}$
(b) $\mathrm{CHOP}$
(c) $\mathrm{CHON}$
(d) $\mathrm{CNOP}$
Ans. (c)
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and nitrogen are called as big four of the cell. C is $18 \%, 0$ is $65 \%, \mathrm{H}$ is $10 \%$ and $\mathrm{N}$ is $2.5 \%$. These are principal non-metal elements and form $95 \%$ of total cellular materials.
Question
Mineral associated with cytochrome is [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) $ \mathrm{Cu} $
(b) $ \mathrm{Mg}$
(c) Fe and Mg
(d) $\mathrm{Fe}$ and $\mathrm{Cu}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Cytochromes are iron-porphyrin (haem) proteins discovered by Mac Cunn. Cytochromes are infact, the conjugated proteins, composed of a protein molecule and a non-protein group, i.e. inorganic factor iron. It is to be noted, that cell cytochromes have iron only, though cyt- $a_3$ possesses both $\mathrm{Fe}$ and Cu. Fe has a role in picking up of electrons and $C u$ hands over the electrons to oxygen.
