Question
Match the items in Column-I with those in Column II [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
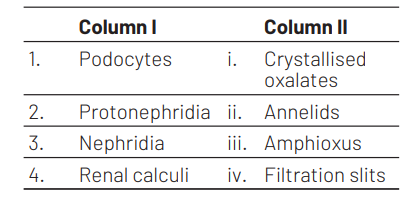
Select the correct option from the following
1 2 3 4
(a) (iii) (iv) (ii) (i)
(b) (iii) (ii) (iv) (i)
(c) (iv) (iii) (ii) (i)
(d) (iv) (ii) (iii) (i)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The correct matches are
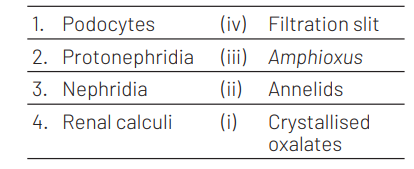
Podocytes are cells in Bowman’s capsule in kidneys. They have filtration slits through which the blood is filtered. Protonephridia help in osmoregulation. Nephridia in annelids help in osmoregulation and excretion. Renal calculi are kidney stones which mainly consist of crystallised oxalates.
Question
Uricotelic mode of passing out nitrogenous wastes is found in [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) birds and annelids
(b)amphibians and reptiles
(c) insects and amphibians
(d) reptiles and birds
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Reptile, birds, land snails and insects excrete nitrogenous waste as uric acid in the form of pellet of paste with a minimum loss of water and are called uricotelic animals.
Question
Which one of the following is not a part of a renal pyramid? [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) Convoluted tubules
(b) Collecting ducts
(c) Loop of Henle
(d) Peritubular capillaries
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Convoluted tubule is the highly convoluted segments of nephron in the renal labyrinth of the kidney.
It is made up of the proximal tubule leading from the Bowmans capsule to the descending limb of Henle’s loop and the distal tubule leading from the ascending limb of Henle’s loop to a collecting tubule.
Question
Uric acid is the chief nitrogenous component of the excretory products of [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) man
(b) earthworm
(c) cockroach
(d) frog
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Cockroach excretes uric acid as the chief nitrogenous excretory product. Man excretes urea as the chief nitrogenous excretory product. Earthworm excretes 40\% urea, 20\% ammonia and $40 \%$ amino acids. Frog excretes urea as the chief nitrogenous product.
Question
05 Consider the following four statements (A-D) about certain desert animals such as kangaroo rat
A. They have dark colour and high rate of reproduction and excrete solid urine.
B. They do not drink water, breathe at a slow rate to conserve water and have their body covered with thick hairs.
C. They feed on dry seeds and do not require drinking water.
D. They excrete very concentrated urine and do not use water to regulate body temperature.
Which two of the above statements for such animals are true? [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) $C$ and $D$
(b) $B$ and $C$
(c) $C$ and $A$
(d) A and B
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Kangaroo rat is a desert rodent. Its body is covered by hairs. Its urine is more than 20 times concentrated as its plasma. This concentrated waste enables it to live in dry or desert environment where little water is available for him to drink.Most of its water is metabolically produced from the oxidation of carbohydrates, fats and proteins in the seeds that it eat. The animal remains in cool burrow during day time and the respiratory moisture condensed in nasal passages.
Question
In Ornithine cycle which one pair of the following wastes are removed from the blood? [CBSE AIPMT 2005, 06]
(a) $\mathrm{CO}_2$ and urea
(b) $\mathrm{CO}_2$ and ammonia
(c) Ammonia and urea
(d) Urea and sodium salts
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
$\mathrm{CO}_2$ and ammonia are the pair of wastes removed from the blood in Ornithine cycle. Urea is formed in Ornithine cycle or urea cycle and urea is fomed of two molecules of ammonia and one molecule of $\mathrm{CO}_2$. Urea cycle is represented as follows
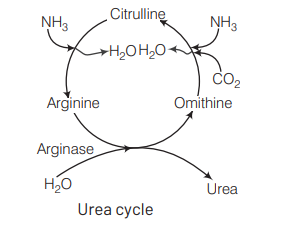
Most of the urea is produced in the liver. The liver cells continuously release urea into the blood and kidneys withdraw it from the blood to excrete it in urine.
Question
Uricotelism is found in [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) mammals and birds
(b) fishes and freshwater protozoans
(c) birds, reptiles and insects
(d) frogs and toads
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The animals which excrete mainly uric acid are uricotelic and this phenomenon is called uricotelism. Uric acid is excreted by terrestrial reptiles (lizard, snakes, etc) birds and insects to conserve water in their body. Frog and mammals excrete urea and so they are called as ureotelic animals and this phenomenon is known as ureotelism.
Question
In living beings, ammonia is converted into urea through [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) ornithine cycle
(b) citrulline cycle
(c) fumarine cycle
(d) arginine cycle
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Ornithine combines with one molecule of $\mathrm{NH}_3$ and $\mathrm{CO}_2$ to produce citrulline. Citrulline combines with another molecule of $\mathrm{NH}_3$ to form arginine. Arginine is broken down into urea and ornithine which repeats the cycle. This is called Ornithine cycle or urea cycle or Krebs-Henseleit cycle.
Question
The enteronephric nephridia of earthworms are mainly concerned with [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) digestion
(b) respiration
(c) osmoregulation
(d) excretion of nitrogenous wastes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Enteronephridia is concerned with excretion of nitrogenous waste. In annelids, the nephridia are the excretory organs. In earthworm, three types of nephridia are found (a) septal (b) pharyngeal and (c) integumentary. The septal nephridia do not discharge the excretory fluid to the exterior. Instead, these pour it into the intestine. Hence, these are also called enteronephric nephridia.
Question
Aquatic reptiles are [CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) ammonotelic
(b) ureotelic
(c) ureotelic in water
(d) ureotelic over land
Ans. (b)
Ureotelic animals include, Ascaris, earthworm, cartilaginous fishes, semiaquatic amphibians aquatic or semiaquatic reptiles like turtles and alligators.
Question
In ureotelic animals, urea is formed by [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) Ornithine cycle
(b) Cori cycle
(c) Krebs’ cycle
(d) EMP pathway
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Urea is the main nitrogenous excretory product of ureotelic animals. It is produced by liver cells from deaminated excess amino acids via urea cycle, also called Ornithine cycle or Krebs-Henseleit cycle.
Question
The kidney of an adult frog is [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) pronephros
(b) mesonephros
(c) metanephros
(d) opisthonephros
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Mesonephric kidney consists of a large number of tubules which develop internal glomeruli enclosed in capsules forming Malpighian bodies. In amphibians, (e.g. frog) it is functional both in embryo as well as adults.
Question
Uric acid is nitrogenous waste in [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) mammals and molluscs
(b) birds and lizards
(c) frog and cartilaginous fishes
(d) insects and bony fishes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Uric acid is least soluble nitrogenous waste and $1 \mathrm{~g}$ of it needs only $10 \mathrm{~mL}$ of water to be expelled out of body.
Another advantage of it is that it is least toxic among all nitrogenous wastes and can be retained in the body for longer period, so it is of greater advantage to animals which have limited access to water like birds and lizards.
Question
Nitrogenous waste products are eliminated mainly as [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) urea in tadpole and ammonia in adult frog
(b) ammonia in tadpole and urea in adult frog
(c) urea in both tadpole and adult frog
(d) urea in tadpole and uric acid in adult frog
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Ammonia is the main nitrogenous waste. It is soluble in water and highly toxic. A large amount of water is required for its excretion. Tadpole is aquatic and lives in plenty of water so, nitrogenous wastes in tadpole are eliminated as ammonia. Frog being amphibious, excretes its nitrogenous wastes as urea.
