Question
In case of poriferans, the spongocoel is lined with flagellated cells called [NEET 2017]
(a) ostia
(b) oscula
(c) choanocytes
(d) mesenchymal cells
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The body wall of a common sponge consists of three layer, i.e. pinacoderm, choanoderm and mesophyll layer. Choanoderm is inner cellular layer which consists of highly specialised flagellated cells called choanocytes. The beating of their flagella creates water current.
Question
Body having meshwork of cells, internal cavities lined with food filtering flagellated cells and indirect development are the characteristics of phylum [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) Coelenterata
(b) Porifera
(c) Mollusca
(d) Protozoa
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In Porifera (sponges), bodies are asymetrical. Body lacks tissue or organs, but from a meshwork of cells surrounding channels that open to the outside through pores, and that expand into internal cavities lined with food filtering flagellated cells (choanocytes).
Question
Which one of the following statements about all the four Spongilla, leech, dolphin and penguin is correct? [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) Penguin is homiothermic, while the remaining three are poikilothermic
(b) Leech is a freshwater form, while all others are marine
(c) Spongilla has special collared cells called choanocytes, not found in the remaining three
(d) All are bilaterally symmetrical
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Spongilla belongs to phylum-Porifera, in which, choanocytes are the characteristic cells, these are absent in leech, dolphin and pengiun. These distinctive cells line the interior body walls of sponges.
These cells have a central flagellum that is surrounded by a collar of microvilli. Choanocytes are versatile cells.
Their flagella beat to create the active pumping of water through the sponge, while the collars of the choanocytes are the primary areas where nutrients are absorbed into the sponge.
Question
Sycon belongs to a group of animals which are best described as [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) multicellular with a gastrovascular system
(b) multicellular having tissue organisation, but no body cavity
(c) unicellular or acellular
(d) multicellular without any tissue organisation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Sycon belongs to phylum-Porifera. The porifers are most primitive group of multicellular animals. They have no tissue grade of organisation and represent cell aggregated body plan, hence, included in the sub-kingdom-Parazoa.
Question
The canal system is a characteristic feature of [CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) echinoderms
(b) helminthes
(c) coelenterates
(d) sponges
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Sponges possess an extensive system of interconnected cavities called canal system, which typically consists of incurrent canals, radial canals, excurrent canals and spongocoel. The system is useful for nutrition, respiration and excretion.
Question
What is true about all sponges without exception? [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) They are all marine
(b) They have flagellated collar cells
(c) They have a mixed skeleton consisting of spicules and spongin fibres
(d) They reproduce only asexually by budding
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Sponges are all aquatic, mostly marine but few fresh water forms also exist. Choanocytes or collar cells are only present in sponges.
Sponges usually have a skeleton consisting of spicules or spongin fibres. Sponges reproduce asexually by budding, gemmules and reproduce sexually too.
Question
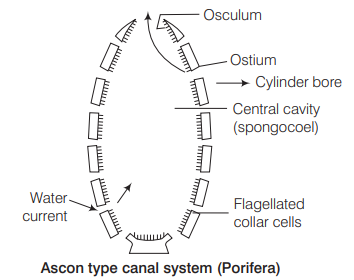
07 The simplest type of canal system in Porifera is [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) ascon type
(b) leucon type
(c) sycon type
(d) radial type
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The simplest type of cana
Question
Classification of Porifera is based on [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) branching
(b) spicules
(c) reproduction
(d) symmetry
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Classification of sponges is primarily based on skeleton which are spicules. These belongs to phylum- Porifera.
