Question
The centriole undergoes duplication during [NEET 2021]
(a) S-phase
(b) prophase
(c) metaphase
(d) $G_2$ -phase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
During S phase or synthesis phase of interphase replication of DNA and synthesis of histone protein, centromere and centrioles occur. During the S phase, DNA replication begins in the nucleus, and the centriole duplicates in the cytoplasm of the cell.
Question
Match the List-I with List-II.
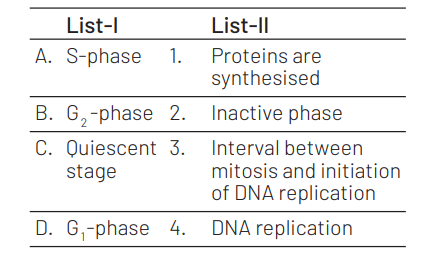
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
$\begin{array}{llll}\text { A } & \text { B } & \text { C } & \text { D }\end{array}$
(a) 3 2 1 4
(b) 4 2 3 1
(c) 4 1 2 3
(d) 2 4 3 1
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
(A) (4), (BH H1), (C)-(2), (D)-(3)
During DNA replication, the unwinding of strands leaves a single strand vulnerable. In the eukaryotic cell cycle, chromosome duplication occurs during ‘S phase’ (the phase of DNA synthesis) and chromosome segregation occurs during ‘M phase’ (the mitosis phase). During the $\mathrm{G}_2$ phase, extra protein is often synthesised, and the organelles multiply until there are enough for two cells. Other cell materials such as lipids for the membrane may also be produced.
The cell is in a quiescent (inactive) stage that occurs when cells exit the cell cycle. Some cells enter $G_0$ temporarily until an external signal triggers the onset of $G_1$. Other cells that never or rarely divide, such as mature cardiac muscle and nerve cells, remain in $\mathrm{G}_a$ permanently.
$G_1$ phase corresponds to the interval between mitosis and initiation of DNA replication. During $G_1$ phase the cell is metabolically active and continuously grows but does not replicate its DNA.
Question
Attachment of spindle fibres to kinetochores of chromosomes becomes evident in [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) anaphase
(b) telophase
(c) prophase
(d) metaphase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
During the metaphase stage of cell cycle, spindle fibres originating from the centrosomes attaches to the kinetochore of chromosomes. Kinetochore is a disc-shaped structure at the surface of centromere through which the sister chromatids are held together. During metaphase, the chromosomes arrange themselves at the equator on metaphasic plate. Due to this arrangement, the attachment of spindle fibres to kinetochore is clearly visible.
Question
Identify the correct statement with regard to $G_1$-phase (Gap 1) of interphase. [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) Reorganisation of all cell components, takes place.
(b) Cell is metabolically active, grows but does not replicate its DNA
(c) Nuclear division takes place
(d) DNA synthesis or replication takes place
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The statement in option (b) is correct with regard to $G_1$ – phase of interphase because during $G$-phase the cell is metabolically active and continuously grows but does not replicate its DNA. DNA synthesis takes place in S-phase. Nuclear division occurs during karyokinesis.
Reorganisation of all cell components takes place in M-phase.
Question
Some dividing cells exist the cell cycle and enter vegetative inactive stage. This is called quiescent stage $\left(G_0\right)$ This process occurs at the end of [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) $G_1$-phase
(b) S-phase
(c) $G_2$-phase
(d) M-phase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Some dividing cells exit the cell cycle and enter vegetative inactive stage, called quiescent stage $\left(G_0\right)$. This process occurs at the end of $M$-phase and beginning of $G_1$-phase. Cells enter $\mathrm{G}_0$ for varying amounts of time, and some cells enter the $G_0$-phase and stay there forever. This is because once they reach maturity, like nerve and heart cells they do not divide again, so they stay in the $\mathrm{G}_0$-phase.
Question
Cells in $\mathrm{G}_0$ phase [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) enter the cell cycle
(b) suspend the cell cycle
(c) terminate the cell cycle
(d) exit the cell cycle
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
$G_0$ phase is the stage in which the cells exit the cell cycle. It is the resting or quiescent phase in which the cells do not divide. It is the permanent state for some cells, e.g., neurons.
Question
The correct sequence of phases of cell cycle is [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) $\mathrm{G}_1 \rightarrow \mathrm{G}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{S} \rightarrow \mathrm{M}$
(b) $\mathrm{S} \rightarrow \mathrm{G}_1 \rightarrow \mathrm{G}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{M}$
(c) $\mathrm{G}_1 \rightarrow \mathrm{S} \rightarrow \mathrm{G}_2 \rightarrow \mathrm{M}$
(d) $M \rightarrow G_1 \rightarrow G_2 \rightarrow S$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The correct sequence of phases of cell cycle is
$
G_1 \rightarrow S \rightarrow G_2 \rightarrow M
$
Here $G_1$ and $G_2$ represent first and second growth phase, respectively.
S-phase represents synthesis phase during which DNA replicates. M-phase is mitotic phase during which cell begins to divide.
Question
When cell has stalled DNA replication fork, which checkpoint should be predominantly activated? [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) G,/S
(b) $G_2 / M$
(c) $M$
(d) Both $G_2 / M$ and $M$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Stalled forks activate checkpoint signaling and pause replication. Since, $\mathrm{G}_1 / S$ checkpoint checks DNA damage, cells size prior to S-phase (i.e. DNA replication phase), this checkpoint would be activated by stalled DNA replication fork.
Question
During cell growth, DNA synthesis takes place in [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) S-phase
(b) $G_1$-phase
(c) $G_2$-phase
(d) M-phase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In the cycle of cell division,interphase is the longest phase consisting of $\mathrm{G}_1, \mathrm{~S}$, $\mathrm{G}_2$-phases. In this phase cell prepares itself for cell division. In S or synthetic phase DNA duplication (synthesis) takes place.
Question
During which phase(s) of cell cycle, amount of DNA in a cell remains at $4 \mathrm{C}$ level if the initial amount is denoted as 2C? [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) $G_0$ and $G_1$
(b) $G_1$ and $S$
(c) Only $\mathrm{G}_2$
(d) $G_2$ and $M$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
During the $S$ or synthetic phase, the DNA content doubles, i.e., from $2 C$ to $4 C$ for all diploid cells. The $G_2$ phase follows the S-phase and is called second growth phase or pre mitotic gap phase. In $G_2$ phase the synthesis of DNA stops therefore, the DNA level remains $4 \mathrm{C}$ if initial was $2 \mathrm{C}$.
However, the formation of RNA and protein continue as they are required for the multiplication of cell organelles, spindle formation and cell growth. This amount becomes half (i.e.) $2 C$ only during anaphase (in mitosis) when chromosomes separate.
Question
In S-phase of the cell cycle [CBSE AIPMT 2014, 2000, 1996]
(a) amount of DNA doubles in each cell
(b) amount of DNA remains same in each cell
(c) chromosome number is increased
(d) amount of DNA is reduced to half in each cell
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
S-phase is the synthesis phase in which the cell synthesise a replica of its genome, i.e. DNA replication occurs by DNA polymerase. DNA replication along with the synthesis of histone proteins results in the duplication of chromosomal material, i.e., amount of DNA doubles in each cell. Amount of DNA remains unchanged during $G_1$-phase or post mitotic gap and/or $\mathrm{G}_2$-phase or pre mitotic phase.
Question
Given below is a schematic break-up of the phases/stages of cell cycle
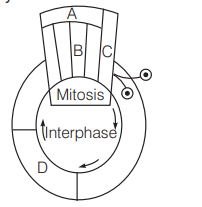
Which one of the following is the correct indication of the stage/phase in the cell cycle? [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) B-metaphase
(b) C-karyokinesis
(c) D-synthetic phase
(d) A-cytokinesis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Cell cycle completes in two steps, i.e. interphase and $M$-phase. Interphase is completed in three successive stages $G_1$-phase (post mitotic phase), S-phase (synthetic phase) and $\mathrm{G}_2$-phase (premitotic or post synthetic phase). In the given figure, $D$ is representing the S-phase (synthetic phase) of cell cycle.
Question
At what stage of the cell cycle are histone proteins synthesised in a eukaryotic cell? [CBSE AIPMT 2005]
(a) During $G_2$-stage of prophase
(b) During S-phase
(c) During entire prophase
(d) During telophase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
During S-phase of cell cycle synthesis of histone proteins takes place because at this stage the amount of DNA per cell get double to that of somatic number. Histone proteins are basic proteins and are used in packing of eukaryotic (absent in prokaryotes) DNA. DNA and histones together comprise chromatin, forming bulk of the eukaryotic chromosomes. Histones are of five major kinds $\mathrm{H} 1, \mathrm{H} 2 \mathrm{~A}, \mathrm{H} 2 \mathrm{~B}, \mathrm{H} 3$ and $\mathrm{H} 4 . \mathrm{H} 1$ histones link neighbouring nucleosomes.
Question
In the somatic cell cycle [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) in $\mathrm{G}_1$-phase DNA content is double the amount of DNA present in the original cell
(b) DNA replication takes place in S-phase
(c) a short interphase is followed by a long mitotic phase
(d) $G_2$-phase follows mitotic phase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
DNA replication occurs during S-phase of the mitotic cycle where it gets doubled as compared to that in the original cell.
Question
Which of the following occurs more than one and less than five in a chromosome? [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a)Chromatid
(b) Chromosome
(c) Centromere
(d) Telomere
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
A chromosome has one centromere, may have many chromomeres, two chromatids; but four telomeres (two each at the opposite ends of each chromatid).
Question
During cell division in apical meristem the nuclear membrane appears in [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) metaphase
(b) anaphase
(c) telophase
(d) cytokinesis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
During telophase, nuclear envelope initially reforms around each chromosome individually which later on fuse to form complete nuclear envelope. Metaphase Chromosomes are arranged on equatorial plate. Anaphase Chromosomes split longitudinally. Chromatids migrate towards opposite poles. Cytokinesis Division of cytoplasm.
