Question
Which one of the following statements about histones is wrong? [NEET 2021]
(a) Histones are organised to form a unit of 8 molecules.
(b) The $\mathrm{pH}$ of histones is slightly acidic
(c) Histones are rich in amino acids lysine and arginine
(d) Histones carry positive charge in the side chain
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Statement in option (a), (c) and (d) are correct. Histone proteins are composed of basic amino acid. These proteins attach to the DNA to form the nucleosome. Histones are organised to form a unit of eight molecules called as histone octamer. Histones are rich in basic amino acid residues lysine and arginine. It carries positive charges in their side chains and negatively charge DNA wrap around it. Statement in option (b) is incorrect and can be corrected as The $\mathrm{pH}$ of histones is slightly basic.
Question
Which is the “only enzyme” that has “capability” to catalyse initiation, elongation and termination in the process of transcription in prokaryotes? [NEET 2021]
(a) DNA-dependent DNA polymerase
(b) DNA-dependent RNA polymerase
(c) DNA ligase
(d) DNase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Prokaryotes utilize one RNA polymerase for transcription of all types of RNA. The enzyme RNA polymerase is needed for RNA formation from DNA, i.e. DNA dependent RNA polymerase. It occurs in the cytoplasm of prokaryotic cells. RNA polymerase is the only enzyme which, has the capability to catalyse all initiation, elongation and termination in prokaryotes.
Question
Which of the following RNAs is not required for the synthesis of protein ? [NEET 2021]
(a) mRNA
(b) tRNA
(c) rRNA
(d) siRNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
siRNA mainly protect the cell from exogenous mRNA attacks. It degrades the growing mRNA and stop gene expression. It is highly specific and reduces the synthesis of particular proteins by reducing the translation of specific messenger RNAs. Hence, siRNA is not required for protein synthesis but is used to reduce its synthesis. Whereas rRNA, mRNA and tRNA are required for synthesis of protein.
Question
If adenine makes $30 \%$ of the DNA molecule, what will be the percentage of thymine, guanine and cytosine in it? [NEET 2021]
(a) T:20, G:30, C:20
(b) T:20, G:20, C:30
(c) $\mathrm{T}: 30, \mathrm{G}: 20, \mathrm{C}: 20$
(d) T: 20, G: 25, C: 25
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Chargaff rule – In DNA there is always equality in quantity between the bases $A$ and $T$ and between the bases $\mathrm{G}$ and $\mathrm{C}$.
According to Chargaff rule
$(\mathrm{A})+(\mathrm{G})+(\mathrm{C})+(\mathrm{T})=100 \%$
$A=30 \%$ therefore $T$ is also $30 \%$
Therefore $\mathrm{G}+\mathrm{C}=100 \%-60 \%=40 \%$
Hence, $G=20 \%$ and $C=20 \%$
Question
Complete the flow chart on central dogma [NEET 2021]
(a) (a)-Replication:
(b)-Transcription;
(c)-Transduction:
(d)-Protein
(b) (a)-Translation: (b)-Replication;
(c)-Transcription: (d)-Transduction
(c) (a)-Replication: (b)-Transcription;
(c)-Translation (d)-Protein
(d) (a)-Transduction; (b)-Translation
(c)-Replication; (d)-Protein
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Central dogma of molecular biology was proposed by Francis Crick which states that the genetic information flows from DNA $\rightarrow$ RNA $\rightarrow$ Protein.
Here, $a, b, c$ and $d$ are
a-Replication, b-Transcription,
c-Translation, $d$-Protein
Question
E. coli has only $4.6 \times 10^6$ base pairs and completes the process of replicaton within 18 minutes, then the average rate of polymerisation is approximately [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) $2000 \mathrm{bp} / \mathrm{s}$
(b) $3000 \mathrm{bp} / \mathrm{s}$
(c) $4000 \mathrm{bp} / \mathrm{s}$
(d) $1000 \mathrm{bp} / \mathrm{s}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
E.coli has $4.6 \times 10^6$ base pairs.
It completes replication process in 18 minutes i.e. $18 \times 60$ seconds.
Rate of polymerisation $=\frac{4.6 \times 10^{\mathrm{R}} \mathrm{bp}}{18 \times 60 \mathrm{~s}}$
$
\begin{aligned}
=\frac{4.6 \times 10^3}{18 \times 6} & =\frac{46 \times 10^4}{108} \\
& =\frac{460000}{108}=42591 \mathrm{bp} / \mathrm{s}
\end{aligned}
$
or approximately $4000 \mathrm{bp} / \mathrm{sec}$
Thus, the correct option is (c).
Question
Name the enzyme that facilitates opening of DNA helix during transcription. [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) DNA helicase
(b) DNA polymerase
(c) RNA polymerase
(d) DNA ligase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The correct option is(c) because RNA polymerase facilitate opening of DNA helix during transcription. RNA polymerase is the main transcription enzyme. Transcription begins when RNA polymerase binds to a promoter sequence near the beginning of a gene. DNA helicases function in other cellular processes where double-stranded DNA must be separated, including DNA repair and transcription. DNA ligases helps in joining breaks in the phosphodiester backbone of DNA that occur during replication. DNA polymerase does not function during transcription.
Question
Who coined the term ‘Kinetin’? [NEET (Oet.) 2020]
(a) Skoog and Miller
(b) Darwin
(c) Went
(d) Kurosawa
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The term kinetin was coined by Skoog and Miller in 1955. Chemically kinetin is 6-furfuryl aminopurine. It was the first cytakinin to be discovered from the degraded auto claved herring sperm DNA. Kinetin does not occur naturally.
Question
In the polynucleotide chain of DNA, a nitrogenous base is linked to the $-\mathrm{OH}$ of [NEET (Oet.) 2020]
(a)2’C pentose sugar
(b) $J^{\prime} C$ pentose sugar
(c) 5’C pentose sugar
(d) YC pentose sugar
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
In a DNA polynucleotide chain, a nitrogenous base is linked to the hydroxy $(-\mathrm{OH})$ of $1^{\prime}$ Cpentose sugar. It is represented in the structure given below
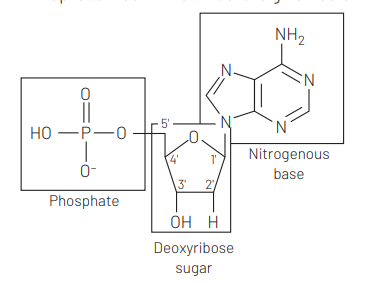
Question
The term ‘Nuclein’ for the genetic material was used by [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) Franklin
(b) Meischer
(c) Chargaff
(d) Mendel
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The nucleic acid was first reported by Friedrich Miescher in 1869 from the nuclei of pus cells and was named nuclein.
Question
Which of the following statements is correct? [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) Adenine pairs with thymine through one $\mathrm{H}$-bond
(b) Adenine pairs with thymine through three $\mathrm{H}$-bonds
(c) Adenine does not pair with thymine
(d) Adenine pairs with thymine through two $\mathrm{H}$-bonds
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The statement in option (d) is correct because Adenine pairs with thymine through two $\mathrm{H}$-bonds, i.e. $\mathrm{A}=\mathrm{T}$ and the cytosine pairs with guanine by three hydrogen bonds . Between the G-C base pairs there are 3 hydrogen bonds which makes this bond pair stronger than the $\mathrm{A}-\mathrm{T}$ base pair.
Question
If the distance between two consecutive base pairs is $0.34 \mathrm{~nm}$ and the total number of base pairs of a DNA double helix in a typical mammalian cell is $6.6 \times 10^9 \mathrm{bp}$, then the length of the DNA is approximately [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) $2.5$ meters
(b) $2.2$ meters
(c) $2.7$ meters
(d) $2.0$ meters
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The distance between two consecutive base pairs is $0.34 \mathrm{~nm}\left(0.34 \times 10^{-2} \mathrm{~m}\right)$ The length of DNA double helix in a typical mammalian cell can be calculated by multiplying the total number of be with distance between the two consecutive bp, i.e. 6. $6 \times 10^5$ bp $\times 0.34 \times 10^{-4} \mathrm{~m} / \mathrm{bp}$ $=2.2$ metres (the length of DNA). Thus, option(b) is carrect.
Question
In RNAi, the genes are silenced using [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) dsRNA
(b) SSDNA
(c) ssRNA
(d) dsDNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In RNAi, the genes are silenced using dsRNA. RNA interference [RNAI] takes place in all eukaryotic organisms as a method of cellular defence. This method involves silencing of a specific mRNA due to a complementary dsRNA molecule that binds to and prevents translation of the mRNA(silencing).
Question
What initiation and termination factors are involved in transcription in eukaryotes? [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) $\sigma$ and $\rho$, respectively
(b) $\alpha$ and $\beta$, respectively
(c) $\beta$ and $\gamma$, respectively
(d) $\alpha$ and $\sigma$, respectively
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
This question is not carrect because out of the given initiation and termination tactors, none is imwalved in transcription in eukaryotes. Only option(a) gives initiation and termination factars which are involved in transcription. These factors $(\sigma$ and $\rho$ ) initiate and terminate transcription in prokaryotes [not in eukaryotes) Initiation and termination factors involved in transcription in eukaryotes are General Transcription Factors (TF IIA – TF I H) and Transcription Termination Factor-1 (TTF-1) respectively.
Question
Which scientist experimentally proved that DNA is the sole genetic material in bacteriophage? [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) Beadle and Tatum
(b) Meselson and Stahl
(c) Hershey and Chase
(d) Jacob and Monod
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase [1952) experimentally proved that DNA is the sole genetic material in bacteriophage. On the other hand, Beadle and Tatum (1940s) experimentally showed one gene-one enzyme hypothesis using Neurospora. Meselsan and Stahl first showed that DNA replicates semiconservatively through experiments on E.colf. Jacob and Monod were first to explain lac aperon.
Question
What will be the sequence of mRNA produced by the following stretch of DNA?
3’ATGCATGCATGCATGS
TEMPLATE STRAND
5’TACGTACGTACGTACS CODING
STRAND [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) 3′-ALGCAUGCALGCAUG 5 ‘
(b) 5′-UACGUACGUACGUAC 3
(c) 3′-UACGUACGUACGUAC 5 ‘
(d) 5′-AUGCAUGCAUGCAUG 3′
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The mRNA will be camplementary to the DNA strand, but in RNA, uracil will be present in place of thymine. If the template strand is J’A $^{\prime}$ A G C A T GC A T G CA T G – 5 then the base sequence of mRNA for the given DNA strand will be 5 ‘ – UACGUACGUACGUAC – 3.
Question
Which of the following nucleic acids is present in an organism having $70 \mathrm{~s}$ ribosomes only? [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) Single-stranded DNA with protein coat
(b) Double-stranded circular naked DNA
(c) Double-stranded DNA enclosed in nuclear membrane
(d) Double-stranded circular DNA with histone proteins
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Double-stranded circular naked DNA type of nucleic acid is present in an organism having 70 S ribosomes.
These are present in prokaryotic organisms ar cells. All prokaryotic cells have a single double-stranded (double hellax), circular DNA molecule for their genetic material. This DNA is attached to the inner cell membrane where the DNA replicating machinery is located. The DNA is “naked”, it does not have proteins associated with it as eukaryotic DNA does.
Question
Purines found both in DNA and RNA are [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) adenine and guanine
(b) guanine and cytosine
(c) cytosine and thymine
(d) adenine and thymine
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Adenine and guanine are the purines which are found both in DNA and RNA. Cytosine and thymine are the pyrimidines which are found in DNA. In case of RNA, thymine is replaced by uracil.
Question
The experimental proof for semiconservative replication of DNA was first shown in a [NEET 2018]
(a) plant
(b) bacterium
(c) fungus
(d) virus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The experimental proof for semiconservative replication of DNA was first shown in a bacterium, Escherichia coli. It was discovered by Meselson and Stahl (1958).
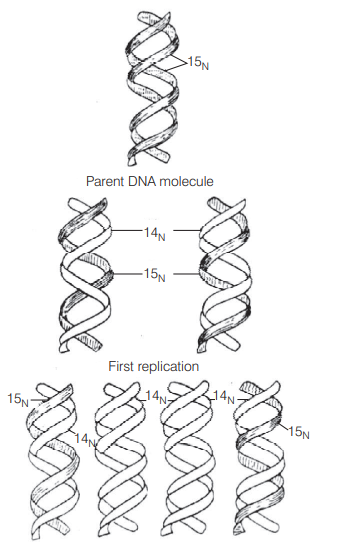
Interpretation of results of experiment of Meselson and Stahl (1958) to prove semi-conservative replication of DNA In this mode of replication, one strand of parent DNA is conserved in the progeny while the second is freshly synthesised. Meselson and Stahl proved this by using heavy isotope of Nitrogen $\left(\mathrm{N}^{15}\right)$.
Question
The final proof for DNA as the genetic material came from the experiments of [NEET 2017]
(a) Griffith
(b) Hershey and Chase
(c) Avery, MacLeod and McCarty
(d) Hargobind Khorana
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The final proof that DNA is the genetic material came from the experiments of Alfred Hershey and Martha Chase (1952). Griffith’s experiment proved the existance of genetic material while Avery, MacLeod and McCarty worked to determine the biochemical nature of transforming principle.
Concept Enhancer Hershey and Chase during their experiment, grew viruses in two mediums, one containing ${ }^{32} \mathrm{P}$ and other ${ }^{35} \mathrm{~S}$, when these were allowed to infect bacteria, they observed that viruses containing ${ }^{32}$ PDNA were radioactive while those with ${ }^{35}$ Sprotein were not radioactive. Hence, DNA not protein coat entered bacterial cells from viruses.
Question
The association of histone $\mathrm{H} 1$ with a nucleosome indicates [NEET 2017]
(a) transcription is occurring
(b) DNA replication is occurring
(c) the DNA is condensed into chromatin fibre
(d) the DNA double helix is exposed
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The association of $\mathrm{H}_1$ histone with nucleosome indicates that DNA remains in its condensed form. Concept Enhancer In eukaryotes, DNA packaging is carried out with the help of histone proteins. Nucleosome is the unit of compaction. Its core consists of four pairs of histones $\left(\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~A}_1 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~B}, \mathrm{H}_3\right.$ and $\left.\mathrm{H}_4\right)$. The linker DNA, consisting of $\mathrm{H}_1$ histone connects two adjacent nucleosomes. They together constitute chromatosome. It gives rise to a chromatin fibre after further condensation.
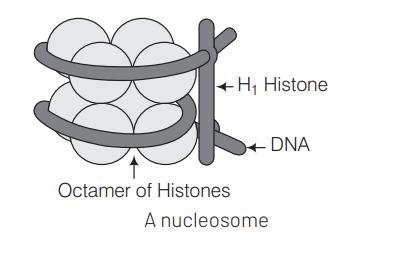
Question
Spliceosomes are not found in cells of [NEET 2017]
(a) plants
(b) fungi
(c) animals
(d) bacteria
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Spliceosome is a large molecular complex found in nucleus of eukaryotic cells of plants, animals and fungi, etc. It is assembled from snRNAs and protein complexes that plays an important role in splicing of introns. Spliceosome is absent in cells of bacteria.
Question
DNA replication in bacteria occurs[NEET 2017]
(a) during S-phase
(b) within nucleolus
(c) prior to fission
(d) just before transcription
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Bacteria lack a cell nucleus. Due to their primitive nature they lack a well marked S-phase. In bacteria DNA replication occurs before fission. Concept Enhancer: Bacterial cell cycle is divided into the $B, C$ and $D$ periods. The $B$ period extends from the end of cell division to the beginning of DNA replication. DNA replication occurs during the $C$ period. The $D$ period refers to the stage between the end of DNA replication and the division of bacterial cell into two daughter cells.
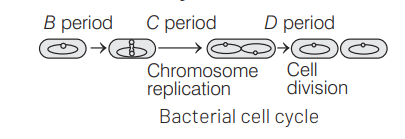
Question
Which of the following RNAs should be most abundant in animals cell? [NEET 2017]
(a) rRNA
(b) tRNA
(c) mRNA
(d) miRNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
There are three main types of RNA, i.e. $r R N A, t R N A$ and mRNA. rRNA is the most abundant form of RNA; because it is responsible for coding and protein synthesis in the cell and associated with ribosomes. mRNA provides the template for translation. tRNA brings amino acids and reads the genetic code.
Question
A complex of ribosomes attached to a single strand of RNA is known as [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) polymer
(b) polypeptide
(c) okazaki fragment
(d) polysome
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
In prokaryotes, several ribosomes may attach to single mRNA and form a chain called polyribosomes or polysomes.
Question
DNA-dependent RNA polymerase catalyses transcription on one strand of the DNA which is called the [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) template strand
(b) coding strand
(c) alpha strand
(d) anti strand
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
DNA dependent RNA polymerase catalyses transcription on one strand of the DNA called a template strand. template can be considered as one of those strands of DNA which decodes its information directly through RNA polymerase. This information is then restored within the RNA molecule and transferred outside the nucleus for protein synthesis within the cytoplasm.
Question
A molecule that can act as a genetic material must fulfill the traits given below, except [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) it should be able to express itself in the form of ‘Mendelian characters’
(b) it should be able to generate its replica
(c) it should be unstable structurally and chemically
(d) it should provide the scope for slow changes that are required for evolution
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
A molecule that can act as a genetic material must be unstable structurally and chemically. The criteria that a molecule must fulfil to act as a genetic material are as following
(i) It should be able to replicate.
(ii) It should be chemically and structurally stable.
(iii) It should provide the scope for slow changes, i.e. mutations which are required for evolution.
(iv) It should be able to express itself in the form of ‘Mendelian characters’.
Question
Which of the following $r$ RNAs act as structural RNA as well as ribozyme in bacteria? [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) 5 srRNA
(b) 18 srRNA
(c) 23 srRNA
(d) 58 srRNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Bacterial cells use their 23 srRNA as an enzyme during protein synthesis. This is the only non-proteinaceous enzyme known so far.
Question
Taylor conducted the experiments to prove semiconservative mode of chromosome replication on [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) Vinca rosea
(b) Vicia faba
(c) Drosophila melanogaster
(d) E. coli
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The use of radioactive thymidine to detect the semiconservative mode of replication of newly synthesised DNA in the chromosomes was performed on Vicia faba by Taylor and colleagues in 1958. This experiment proved that the DNA in chromosomes replicates semiconservatively. Hence, the option (b) is correct.
Question
The equivalent of a structural gene is [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) muton
(b) cistron
(c) operon
(d) recon
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Cistron is the segment of DNA which determines the synthesis of complete polypeptide. Thus, it is considered as equivalent to a structural gene. Therefore, option (b) is correct and others are incorrect. Concept Enhancer Eukaryotic structural gene is monocistronic whereas prokaryotic structural gene is polycistronic. Muton Smallest unit of DNA in which mutation occurs. Operon Functional unit of genomic DNA containing a cluster of genes under control of single promoter.
Recon Smallest unit of DNA for recombination.
Question
Which one of the following is not applicable to RNA? [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) Complementary base pairing
(b) 5′ phosphoryl and 3 hydroxyl ends
(c) Heterocyclic nitrogenous bases
(d) Chargaff’s rule
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Chargaff’s rule is not applicable to RNA. $\mathrm{He}$ is the generalisations formulated about DNA structure. The rule states that DNA from any cell of all organisms should have a 1:1 ratio (base pair rule) of pyrimidine and purine bases, i.e. the amount of guanine is equal to cytosine and the amount of adenine is equal to thymine. Further complementary base pairing is sometimes, visible in RNA as well (in doubled stranded RNAs of viruses) hence option (a) is not taken into consideration.
Question
Identify the correct order of organisation of genetic material from largest to smallest. [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a)Chromosome, gene, genome, nucleotide
(b) Genome, chromosome, nucleotide, gene
(c) Genome, chromosome, gene, nucleotide
(d) Chromosome, genome, nucleotide, gene
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The correct order of organisation of genetic material from largest to smallest is as follows Genome, chromosome, gene, nucleotide. Genome It is the total genetic material of an individual.
Chromosome It is a packed and organised structure containing most of the DNA of a living organism. Gene It is a segment of DNA that encodes for a protein. Nucleotide It is one of the structural components, or building blocks, of DNA and RNA.
Question
Transformation was discovered by [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) Meselson and Stahl
(b) Hershey and Chase
(c) Griffith
(d) Watson and Crick
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Transformation was discovered by $\mathrm{F}$ Griffith [1928]. He isolated the DNA as genetic material that inherit the genetic information between two generations by using two strain of Pneumococcus bacteria which infect mice. i.e. a type III S(smooth) and type II R(rough) strain.
Question
Removal of RNA polymerase-III from nucleoplasm will affect the synthesis of [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) tRNA
(b) hnRNA
(c) mRNA
(d) rRNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
RNA polymerase III transcribes tRNA, therefore tRNA synthesis will be affected. RNA polymerase-Il synthesises mRNA while, RNA polymerase-1 synthesis rRNA in eukaryotes.
Question
Which one of the following is not a part of a transcription unit in DNA? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) The inducer
(b) A terminator
(c) A promoter
(d) The structural gene
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Transcription unit consists of promoter, structural gene and terminator. The inducer (lactose/allolactose) is not a component of transcription unit.
Question
Ribosomal RNA is actively synthesised in [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) lysosomes
(b) nucleolus
(c) nucleoplasm
(d) ribosomes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Nucleolus is the centre for synthesis of ribosomal RNA (rRNA). Ribosomal proteins migrate to the nucleolus from their assembly sites in the cytoplasm and are packaged into ribonucleoproteins. These return to the cytoplasm where they become mature ribosome particles.
Question
Removal of introns and joining of exons in a defined order during transcription is called [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) looping
(b) inducing
(c) slicing
(d) splicing
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The primary transcript from a typical eukaryotic gene contains introns as well as exons. During RNA splicing, introns are removed and exons are joined in a defined order, to produce functional RNA.
Question
What are the structures called that give an appearance as beads on string’ in the chromosomes when viewed under electron microscope? [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) Genes
(b) Nucleotides
(c) Nucleosomes
(d) Base pairs
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Nucleosome appear as “beads-on-string” in the chromosones. Nucleosome is sub-microscopic sub-unit of chromatin which is formed by wrapping of DNA over a core of histone proteins. The term was coined by Oudet, et. al [1975). It is oblate structure with a length of $10 \mathrm{~nm}$ and a thickness of $5-5.7 \mathrm{~nm}$. Its core is called nu-body. The latter is formed of four pairs of histone molecules $\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~A}_{,} \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{~B}, \mathrm{H}_{\Sigma}$ and $\mathrm{H}_4$. DNA makes $1.75$ turns over the octamer to form a nucleosome.
Two adjacent nucleosomes are connected by a short segment of unbound DNA called linker DNA. A fifth type of histone called $\mathrm{H}_1$ is attached over the linker DNA.
Question
Whose experiments cracked the DNA and discovered unequivocally that a genetic code is a triplet? [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) Nirenberg and Matthaei
(b) Hershey and Chase
(c) Morgan and Sturtevant.
(d) Beadle and Tatum
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The existence of triplet code was simply an assumption till 1961, when Nirenberg and Matthaei proved its existence by experiments. They were able to synthesise artificial mRNA, which contained only one nitrogenous base, i.e. uracil. This synthetic poly U sequence was then placed in a cell free system containing protein synthesising enzymes (extracted from bacterium E. coli) and 20 amino acids together with necessary ATP. During the process, a small polypeptide molecule was produced which was formed by the linking of phenylalanine.This suggested that UUU is the code for phenyl alanine. Nirenberg got Nobel Prize for his contributions.
Question
Polysome is formed by [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) several ribosomes attached to a single mRNA
(b) many ribosomes attached to a strand of endoplasmic reticulum
(c) a ribosome with several subunits
(d) ribosomes attached to each other in a linear arrangement
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The group of ribosomes together with the single mRNA molecules, they are translating is called polysome. They are formed by several ribosomes attached to a single mRNA. In eukaryotic cells the ribosomes are attached to rough endoplasmic reticulum by ribophorin protein. Electron microscopy reveals that membranes of homogenised endoplasmic reticulum disrupt to form closed vesicles called microsomes. Microsomes derived from rough endoplasmic reticulum are studied with ribosomes and are called rough ribosomes.
Question
The Okazaki fragments in DNA chain growth [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) result in transcription
(b) polymerise in the $3^{\prime}$ to $5^{\prime}$ direction and forms replication fork
(c) prove semi-conservative nature of DNA replication
(d) polymerise in the $5^{\prime}$ to $3^{\prime}$ direction and explain 3′ to 5’DNA replication
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The Okazaki fragments in DNA chain growth polymerise in the $5^{\prime}$ to $3^{\prime}$ direction. The replicated DNA results in transcription.
Question
The length of DNA molecule greatly exceeds the dimensions of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells. How is this DNA accommodated? [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) Deletion of non-essential genes
(b) Super-coiling in nucleosomes
(c) DNAse digestion
(d) Through elimination of repetitive DNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In eukaryotic cells, DNA is accommodated by super-coiling in nucleosomes.
Question
Molecular basis of organ differentiation depends on the modulation in transcription by [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) RNA polymerase
(b) ribosome
(c) transcription factor
(d) anticodon
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Transcription factor is molecular basis of organ differentiation.
Question
Telomere repetitive DNA sequences control the function of eukaryotic chromosomes because they [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) act as replicons
(b) are RNA transcription initiator
(c) help chromosome pairing
(d) prevent chromosome loss
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Telomeres, i.e. the ends of chromosome, have repetitive DNA sequences and are stable and resistant to exonuclease digestion hence, prevent chromosome loss.
Question
Which one of the following makes use of RNA as a template to synthesise DNA? [CBSE AIPMT 2005]
(a) Reverse transcriptase
(b) DNA dependant RNA polymerase
(c) DNA polymerase
(d) RNA polymerase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In $1970 \mathrm{H}$ Temin and D Baltimore independently discovered the enzyme reverse transcriptase. This enzyme uses RNA as template for the synthesis of cDNA (complementary DNA).
Question
Which one of the following hydrolyses internal phosphodiester bonds in a polynucleotide chain? [CBSE AIPMT 2005]
(a) Lipase
(b) Exonuclease
(c) Endonuclease
(d) Protease
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Endonuclease hydrolyses internal phosphodiester bonds in a polynucleotide chain.
Question
During transcription holoenzyme RNA polymerase binds to a DNA sequence and the DNA assumes a saddle like structure at that point. What is that sequence called? [CBSE AIPMT 2005]
(a) CAAT box
(b) GGTT box
(c) AAAT bOX
(d) TATA box
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
TATA box is present in eukaryotic promoter region. It has a resemblance with Pribnow box of prokaryotes. TATA box was identified by Dr. Hogness and so, it is also called as Hogness box. It is a $7 \mathrm{bp}$ long region located $20 \mathrm{bp}$ upstream to the start point.
During the process of transcription the RNA polymerase (a holoenzyme which has a core unit and a sigma factor for proper initiation of transcription) binds to TATA box due to which DNA assumes a saddle like structure at this place.
Question
Telomerase is an enzyme which is a [CBSE AIPMT 2005]
(a) repetitive DNA
(b) RNA
(c) simple protein
(d) ribonucleoprotein
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Ends of an eukaryotic chromosome are known as telomeres. Telomerase, which is a special ribonucleoprotein molecule (enzymatic in nature) is responsible for the synthesis of these telomeres.
Question
During replication of a bacterial chromosome DNA synthesis starts from a replication origin site and [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) RNA primers are involved
(b) is facilitated by telomerase
(c) moves in one direction of the site
(d) moves in bi-directional way
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The events for initiation of DNA replication in prokaryotes may be classified into (a) pre-priming (occurring only at the origin): (b) priming (recurring with the initiation of each Okazaki fragment during elongation phase. Unwinding of DNA is followed by the synthesis of RNA primers by RNA primase.
Question
The telomeres of eukaryotic chromosomes consist of short sequences of [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) thymine rich repeats
(b) cytosine rich repeats
(c) adenine rich repeats
(d) guanine rich repeats
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Telomeres have been shown to have unique structures that include short nucleotide sequences present as tandemly repeated units. In eukaryotes the telomeres terminate with a single-stranded DNA [12-16 nucleotides long) rich in guanine.
Question
During transcription, the nucleotide sequence of the DNA strand that is being coded is ATACG, then the nucleotide sequence in the mRNA would be [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) TATGC
(b) TCTGG
(c) UAUGC
(d) UATGG
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
If DNA has ATACG nucleotide sequence then the mRNA would contain UAUGC sequence. The formation of mRNA from DNA is termed as transcription. This process takes place in the nucleus (eukaryotes) or in the cytoplasm (prokaryotes). The base sequence of mRNA is complementary copy of the template DNA strand.
Question
Which form of RNA has a structure resembling clover leaf? [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) rRNA
(b) hnRNA
(c) mRNA
(d) tRNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The basic plan of the structure of tRNA assumes the pattern of a clover leaf. The structures of different tRNAs for almost all amino acids are now available and all of these fit the clover leaf model. The tRNA structure can be decomposed into its primary structure and its secondary structure (usually seen as clover leaf structure) and tertiary structure.
Question
During transcription, the DNA site at which RNA polymerase binds is called [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) receptor
(b) enhancer
(c) promoter
(d) regulator
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Promoter is the nucleotide sequence to which RNA polymerase binds and initiates transcription. Formation of a single stranded linear chain of complementary RNA(mRNA) on the template strand of DNA in nucleus (eukaryotes) or in cytoplasm (prokaryotes) is known as transcription.
Question
Chromosomes in a bacterial cell can be 1-3 in number and [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) can be either circular or linear, but never both within the same cell
(b) can be circular as well as linear within the same cell
(c) are always circular
(d) are always linear
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Bacterial chromosomes are circular DNA molecules.
Question
Exon part of mRNAs have code for [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) protein
(b) lipid
(c) carbohydrate
(d) phospholipid
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Exon part of mRNA consists of codons for protein synthesis. Exon is the stretch of bases which codes for amino acids, while the non-coding stretches of bases are called intron.
Question
Which of the following reunites the exon segments after RNA splicing? [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) RNA polymerase
(b) RNA primase
(c) RNA ligase
(d) RNA protease
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
RNA ligase reunites the exon segments after RNA splicing.
Question
Which statements is correct for bacterial transduction? [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) Transfer of some genes from one bacteria to another bacteria through virus
(b) Transfer of genes from one bacteria to another bacteria by conjugation
(c) Bacteria obtained its DNA directly
(d) Bacteria obtained DNA from other external source
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Transduction involves the picking up of DNA by bacteriophage from one bacterial cell and carrying it to another where, the DNA fragment may get incorporated into the bacterial host’s genome.
Question
In a DNA percentage of thymine is 20. What is the percentage of guanine? [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) $20 \%$
(b) $40 \%$
(c) $30 \%$
(d) $60 \%$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Total DNA $[100]=A+T+C+G$
$
\begin{aligned}
A & =20 \% \text { (given) } \\
A & =T \text { (base pairing rule) } \\
100 & =20+20+C+G \\
C+G & =100-40=60 \\
C & =G=30(C=G)
\end{aligned}
$
Question
Sequence of which of the following is used to know the phylogeny? [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) mRNA
(b) rRNA
(c) tRNA
(d) DNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The genes for rRNAs tend to be highly conserved and, are therefore, often employed for phylogenetic studies.
Question
In which direction mRNA is synthesised on DNA template? [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) $5^{\prime} \rightarrow 3^{\prime}$
(b) $3^{\prime} \rightarrow 5^{\prime}$
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Any of above
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
$5^{\prime} \rightarrow 3^{\prime}$ is the direction of synthesis of mRNA on DNA template.
Question
Gene and cistron words are sometimes used synonymously because [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) one cistron contains many genes
(b) one gene contains many cistrons
(c) one gene contains one cistron
(d) one gene contains no cistron
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Cistron is generally accepted as a synonym for gene. Gene (Gr. genos = birth, race) is the basic unit of heredity. It is a sequence of nucleotides on a chromosome that encodes a polypeptide or RNA molecule and so, determines the nature of individual’s inherited traits. Cistron is a segment of DNA that codes for one polypeptide.
Question
E. coli about to replicate was placed in a medium containing radioactive thymidine for five minutes. Then it was made to replicate in a normal medium. Which of the following observation shall be correct? [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) Both the strands of DNA will be radioactive
(b) One strand radioactive
(c) Each strand half radioactive
(d) None is radioactive
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
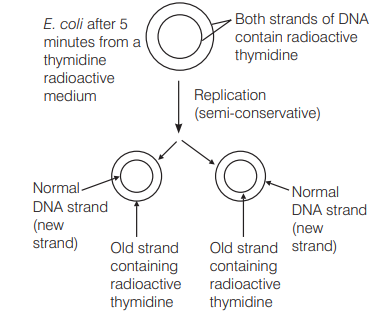
Since, DNA replication is semiconservative, the newly synthesised strand of DNA would be normal while the strand obtained from parent molecule would be radioactive. In the given expreiment
Question
Due to discovery of which of the following in 1980’s the evolution was termed as RNA world? [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) mRNA, tRNA, rRNA synthesise proteins
(b) In some viruses, RNA is genetic material
(c) Some RNAs have enzymatic property
(d) RNA is not found in all cells
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Ribozymes are catalytically active RNA molecules discovered in 1980’s. These are self-splicing introns indicating their possible role as intermediates in the evolution of biological systems from abiotic substances.
Question
During replication of DNA, its two strands separate. Each of these serves as a template for the formation of new strands. Such type of replication is called [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) non-conservative
(b) semi-conservative
(c) flexible
(d) conservative
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Since, each daughter DNA molecule contains one strand of the parent DNA double helix (only one strand synthesised afresh) the process of replication is called semi-conservative. Mathew Meselson and Franklin Stahl in 1958 proved experimentally that DNA replication is semi-conservative.
Question
One of the similarities between DNA and RNA is that both [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) are polymers of nucleotides
(b) are capable of replicating
(c) have similar sugars
(d) have similar pyrimidine bases
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
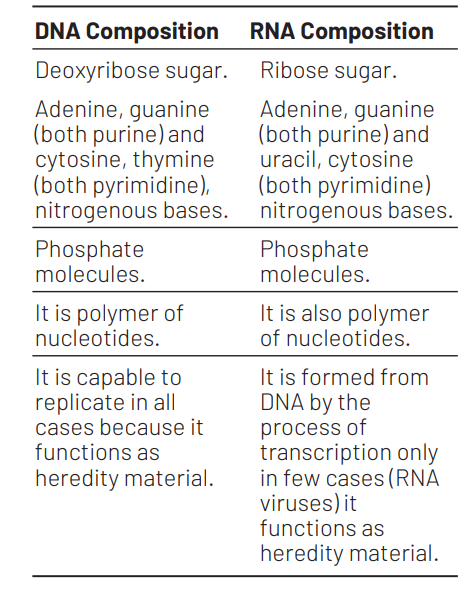
Question
The Pneumococcus experiment proves that [CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) DNA is the genetic material
(b) RNA sometime controls the production of DNA and proteins
(c) bacteria undergo binary fission
(d) bacteria do not reproduce sexually
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The Pneumococcus experiment proves that DNA is the genetic material as Frederick Griffith (1928) found that ‘something’ passed from heat-killed encapsulated forms of Pneumococcus to live non-capsulated forms which caused them to develop capsules and become virulent. Avery et al, (1944) found this transforming agent (hence, genetic material) to be DNA.
Question
DNA elements, which can switch their position, are called [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) exons
(b) introns
(c) cistrons
(d) transposons
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Transposons are genetic elements varying from 750 base pairs to 40 kilo base pairs in length and can move from a site in one genome to another site in the same or in a different genome.
Question
Genes are packaged into a bacterial chromo-some by [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) histones
(b) basic protein
(c)acidic protein
(d) actin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Bacteria are prokaryotic organisms. Polyamines (basic proteins) like spermidine and cadaverine (instead of histones) are associated with DNA packaging in bacteria.
Question
The hereditary material present in the bacterium $E$. coli is [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) single stranded RNA
(b) double stranded RNA
(c) single stranded DNA
(d) double stranded DNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Bacterial chromosome is single, circular double stranded DNA molecule.
Question
An enzyme that joins the ends of two strands of nucleic acid is a [CBSE AIPMT 1996, 2002]
(a) polymerase
(b)synthetase
(c) helicase
(d) ligase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Ligase enzyme joins the ends of two strands of nucleic acid.
Question
Okazaki fragments are seen during [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) transcription
(b) translation
(c) replication
(d)transduction
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
During DNA replication in lagging strand DNA fragments are formed in small pieces these are called Okazaki fragments.
Question
In split genes, the coding sequence are called [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) introns
(b) operons
(c)exons
(d) cistrons
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
In split genes coding region is called exons. In higher organisms (eukaryotes) gene is not continuous, within a single gene there may be four or five silent regions. These regions are called introns (which do not transcribe mRNA). The remaining part is called as exons (transcribe mRNA).
Question
Protein helping in opening of DNA double helix in front of replications fork is
(a) DNA gyrase
(b) DNA polymerase-1
(c) DNA ligase
(d) topoisomeras
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
DNA gyrase helps in opening of DNA double helix in front of replication fork.
Question
Reverse transcriptase is [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) RNA dependent RNA polymerase
(b) DNA dependent RNA polymerase
(c) DNA dependent DNA polymerase
(d) RNA dependent DNA polymerase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Reverse transcriptase is RNA dependent DNA polymerase. H Temin and D Baltimore discovered reverse transcription. Reverse transcriptase has modified central dogma of molecular biology as RNA $\rightarrow$ DNA $\rightarrow$ RNA $\rightarrow$ Protein.
Question
Nucleosome core is made of [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) $\mathrm{H} 1, \mathrm{H} 2 \mathrm{~A}, \mathrm{H} 2 \mathrm{~B}$ and $\mathrm{H} 3$
(b) $\mathrm{H} 1, \mathrm{H} 2 \mathrm{~A}, \mathrm{H} 2 \mathrm{~B}$ and $\mathrm{H} 4$
(c) $\mathrm{H} 1, \mathrm{H} 2 \mathrm{~A}, \mathrm{H} 2 \mathrm{~B}, \mathrm{H} 3$ and $\mathrm{H} 4$
(d) $\mathrm{H} 2 \mathrm{~A}, \mathrm{H} 2 \mathrm{~B}, \mathrm{H} 3$ and $\mathrm{H} 4$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
A nucleosome is an octamer of histone proteins and has a core of 8 molecules of histone proteins (two each of H2A, H2B, $\mathrm{H} 3$ and $\mathrm{H} 4$ lwrapped by two turns of DNA.
Question
A DNA with unequal nitrogen bases would most probably be [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) single stranded
(b) double stranded
(c) triple stranded
(d) four stranded
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
A single stranded DNA do not possess its complementary base pairs so it would have unequal nitrogen bases.
Question
During DNA replication, the strands separate by [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) DNA polymerase
(b) topoisomerase
(c) unwindase/helicase
(d) gyrase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Unwinding of DNA helix is caused by enzyme helicase.
Question
Who proved that DNA is basic genetic material? [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) Griffith
(b) Watson
(c) Boveri and Sutton
(d) Hershey and Chase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Hershey and Chase [1952] proved that DNA is basic genetic material.
Question
Nucleotide arrangement in DNA can be seen by[CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) X-ray crystallography
(b) electron microscope
(c) ultracentrifuge
(d) light microscope
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Astbury by his $\mathrm{X}$-ray diffraction studies suggested $3-D$ configuration for DNA molecules which was confirmed by Wilkins and Franklin in 1952 and then in 1953 Watson and Crick designed the model of DNA molecule.
Question
The transforming principle of Pneumococcus as found out by Avery, Mac Leod and McCarty was [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) MRNA
(b) DNA
(c) protein
(d) polysaccharide
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Avery, Macleod and McCarty [1944] showed the significance of DNA in hereditary transmission in bacteria Pneumococcus. They discovered the biochemical nature of gene.
Question
Experimental material in the study of DNA replication has been [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) Escherichia coll
(b) Neurospora crassa
(c) Pneumococcus
(d) Drosophila melonogaster
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Meselson and Stahl [1958] proved experimentally that in E. coli DNA is replicated by semi-conservative manner.
Question
Escherichia coli fully labelled with $\mathrm{N}^{15}$ is allowed to grow in $\mathrm{N}^{14}$ medium. The two strands of DNA molecule of the first generation bacteria have [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) different density and do not resemble parent DNA
(b) different density but resemble parent DNA
(c)same density and resemble parent DNA
(d) same density but do not resemble parent DNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
When E. coli fully labelled with $\mathrm{N}^5$ is allowed to grow in $\mathrm{N}^2$ medium, then after first generation of replication one of the two strands would have $\mathrm{N}^{\mathrm{s}}$ and the other strand would have $\mathrm{N}^4$. The resulting molecule would have a density which is intermediate between $\mathrm{N}^{\mathrm{E}}$ DNA and $\mathrm{N}^{\mathrm{DF}}$ DNA. These two molecules of DNA will be similar but not same in density.
Question
In RNA, thymine is replaced by [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) adenine
(b) guanine
(c) cytosine
(d) Uracil
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
DNA consists of nitrogenous bases, adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine, whereas in RNA thymine is replaced by uracil. The other nitrogeneous bases, i.e. adenine, guanine, cytosine are present both in RNA and DNA.
Question
A nucleotide is formed of [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) purine, pyrimidine and phosphate
(b) purine, sugar and phosphate
(c) nitrogen base, sugar and phosphate
(d) pyrimidine, sugar and phosphate
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Nucleotide is the basic unit of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). It is composed of nucleoside (nitrogeneous base + pentose sugar) and phosphate group.
Question
The process of transfer of genetic information from DNA to RNA/formation of RNA from DNA is
(a) transversion
(b) transcription
(c) translation
(d) translocation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The transfer of genetic information from DNA to RNA (mRNA) is known as transcription. Both the strands of DNA do not transcribe RNA but only one of them does it which is called as template strand.
Question
Which is not consistent with double helical structure of DNA? [CBSE AIPMT 1990]
(a) $A=T, C=G$
(b) Density of DNA decreases on heating
(c) $A+T / C+G$ is not constant
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
According to Erwin Chargaff, the base ratio $A+T / G+C$ may vary from one species to another, but is constant for a given species. It is rarely equal to one and varies from $0.4$ and $1.9$.
Question
DNA replication is [CBSE AIPMT 1989]
(a) conservative and discontinuous
(b) semi-conservative and semidiscontinuous
(c) semi-conservative and discontinuous
(d) conservative
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
QNA replication is semi-conservative that means DNA formed after replication contains one strand of its parent DNA and this was proved by Meselson and Stahl [ 195B].
During replication the strand formed in leading strand is continuous, while the strand formed in lagging strand is discontinuous in the small pieces (Okazaki fragments).
Question
Which one contains four pyrimidine bases? [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) GATCAATGC
(b) GCUAGACAA
(c) UAGCGGUAA
(d) TGCCTAACG
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Pyrimidines are 6-membered nitrogen bases that contain nitrogen at 1 and 3 positions, e.g. cytosine (C), thymine (T) uracil (U).
Question
A segment of DNA has 120 adenine and 120 cytosine bases. The total number of nucleotides present in the segment is [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) 120
(b) 240
(c) 60
(d) 480
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
According to Chargaff’s rule, molar amount of adenine is equal to that of thymine and cytosine equals to guanine, $A+G=T+C$. So, a segment of DNA with 120 adenine base and 120 cytosine base will have same number of each thymine and guanine base (as, $A=T$ and $C=G$ ), i.e. 120 thymine bases, 120 guanine bases, thus a total of 480 nucleotides.
