Question
Chromosomal theory of inheritance was proposed by [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) Sutton and Boveri
(b) Bateson and Punnett
(c) TH Morgan
(d) Watson and Crick
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Chromosomal theory of inheritance was proposed by Sutton and Boveri independently in 1902.
The two workers found a close similarity between the transmission of hereditary traits and behaviour of chromosomes while passing from one generation to the next through gametes.
Question
Experimental verification of the chromosomal theory of inheritance was done by [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) Sutton
(b) Boveri
(c) Morgan
(d) Mendel
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Experimental verification of the chromosomal theory of inheritance was done by Thomas Hunt Morgan. Sutton and Boveri proposed chromosomal theory of inheritance but it was experimentally verified by TH Morgan. According to this theory, genes are the units of heredity and are found in the chromosomes.
Question
Crossing over takes place between which chromatids and in which stage of the cell cycle? [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) Non-sister chromatids of non-homologous chromosomes at zygotene stage of prophase 1
(b) Non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes at pachytene stage of prophase I
(c) Non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes at zygotene stage of prophase I
(d) Non-sister chromatids of non-homologous chromosomes at pachytene stage of prophase I
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Crossing over takes place between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes at pachytene stage of prophase-1. This stage of prophase-l in meiosis is characterised by the appearance of recombination nodules, the site at which crossing over occurs between non-sister chromatids of the homologous chromosomes.
Question
What map unit (Centimorgan) is adopted in the construction of genetic maps? [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) A unit of distance between two expressed genes representing $100 \%$ cross over
(b) A unit of distance between genes on chromosomes, representing $1 \%$ cross over
(c) A unit of distance between genes on chromosomes, representing $50 \%$ cross over
(d) A unit of distance between two expressed genes representing 10\% cross over
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In the construction of genetic maps, map unit or centimorgan is a unit or distance between genes on chromosomes, representing $1 \%$ crossover.
i. e. 1 map unit $=1 \%$ crossover
Hence, the genetic distance between genes is based on average number of cross over frequency between them.
Question
The frequency of recombination between gene pairs on the same chromosome as a measure of the distance between genes was explained by [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) Gregor J Mendel
(b) Alfred Sturtevant
(c) Sutton-Boveri
(d) TH Morgan
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Alfred Sturtevant was the first to explain the concept of chromosomal mapping. It is drawn on the basis of recombination frequency between gene pairs on the same chromosome. This frequency is directly proportional to the distance between these two genes. It can be used to determine the exact location of a gene on the chromosome.
Question
In a test cross involving $\mathbf{F}_{\mathbf{1}}$ dihybrid flies, more parental-type offspring were produced than the recombinant type offspring. This indicates [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) chromosomes failed to separate during meiosis
(b) the two genes are linked and present on the same chromosome
(c) both of the characters are controlled by more than one gene
(d) the two genes are located on two different chromosomes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
When two genes in a dihybrid cross are situated on the same chromosome, the proportion of parental gene combinations are much higher than the non-parental or recombinant type as linked genes are inherited together in offspring.
Question
The mechanism that causes a gene to move from one linkage group to another is called [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) inversion
(b) duplication
(c) translocation
(d) crossing over
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Translocation is the process causing a gene to move from one linkage group to another. It is the separation of a chromosome segment and its union to a non-homologous chromosome. It is of two types-simple and reciprocal. In simple translocation one chromosome shows deletion or deficiency while a nonhomologous chromosome comes to have an additional segment. In reciprocal translocation two non-homologous chromosomes exchange segments between themselves to create new linkage groups in both the chromosomes. Hence, option (c) is correct.
Question
The term “linkage” was coined by [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) TH Morgan
(b) T Boveri
(c) G Mendel
(d) W Sutton
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The term linkage was coined by TH Morgan. He carried out several dihybrid crosses in Drosophila to study genes that were sex-linked. He described the physical association of genes on a chromosome.
Question
Which of the following statements is not true of two genes that show $50 \%$ recombination frequency? [NEET 2013]
(a) The genes may be on different chromosomes
(b) The genes are tightly linked
(c) The genes show independent assortment
(d) If the genes are present on the same chromosome, they undergo more than one crossovers in every meiosis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Out of the given statements (b) is incorrect because the tightly linked genes on chromosomes show $100 \%$ parental types and $0 \%$ recombinants. Two genes that undergo independent assortment indicated by a recombinant frequency of $50 \%$ are either on non-homologous chromosomes or located far apart in a single chromosome.
As the distance between two genes increases, crossover frequency increases. More recombinant gametes, fewer parental gametes.
Question
Select the correct statement from the ones given below with respect to dihybrid cross. [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) Tightly linked genes on the same chromosome show higher recombinations
(b) Genes far apart on the same chromosome show very few recombinations
(c) Genes loosely linked on the same chromosome show similar recombinations as the tightly linked ones
(d) Tightly linked genes on the same chromosome show very few recombinations
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Morgan and his group found that when genes were grouped on the same chromosome, some genes were very tightly linked (showed very low recombination), while others were loosely linked (showed higher recombination).
Recombination is a process of rearrangement of genes during meiosis so that a gamete contains a haploid genotype with a new gene combination.
Question
Two genes $R$ and $Y$ are located very close on the chromosomal linkage map of maize plant. When RRYY and rryy genotypes are hybridised, then $\mathbf{F}_2$ segregation will show
[CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) higher number of the recombinant types
(b) segregation in the expected $9: 3: 3: 1$ ratio
(c) segregation in $3: 1$ ratio
(d) higher number of the parental types
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Higher number of the parental types formed when RRYY and rryy genotypes are hybridised giving the condition that $R$ and $Y$ genes are closely linked. Law of independent assortment does not applicable when the gene of different character occupy the same homologous chromosome i.e. are linked gene.
Question
In which mode of inheritance do you expect more maternal influence among the offspring? [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) Autosomal
(b) Cytoplasmic
(c) Y-linked
(d) X-linked
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The more maternal influence can be expected in the cytoplasmic inheritance, i.e. the inheritance of genes contained in the cytoplasm of a cell, rather than the nucleus.
The reason is that the female reproductive cell or the egg has a large amount of cytoplasm containing many such organelles which contain their own genes and can reproduce independently, e.g. mitochondria and chloroplast and which are consequently incorporated into the cytoplasm of all the cells of the embryo.
The male reproductive cells (sperm or pollen) consist almost solely of a nucleus. Cytoplasmic organelles are thus, not inherited from the male parent. This is why, the cytoplasmic inheritance is also called maternal inheritance. A gene located in the X-chromosome is said to be X-linked and its inheritance is called X-linked inheritance. In this, a male transmits his X-chromosome only to his daughters while a female transmits one of her X-chromosomes to the offspring of both sexes.
Question
The recessive genes located on $\mathrm{X}$-chromosome in humans are always [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) lethal
(b) sublethal
(c) expressed in males
(d) expressed in females
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The recessive genes located on X-chromosome in humans are always expressed in males because a female may be homozygous or heterozygous while male is always hemizygous (i.e. only one allele is present). Haemophilia, colour blindness are some human diseases which are frequently found in males.
Question
Extranuclear inheritance is a consequence of presence of genes [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) mitochondria and chloroplasts
(b) endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria
(c) ribosomes and chloroplast
(d) lysosomes and ribosomes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Extranuclear or extrachromosomal or cytoplasmic or organellar inheritance is a consequence of presence of genes in mitochondria and chloroplast. Extrachromosomal units function either independently or in collaboration with nuclear genetic system.
Question
Lack of independent assortment of two genes $A$ and $B$ in fruit fly Drosophila is due to [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) repulsion
(b) recombination
(c) linkage
(d) crossing over
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
TH Morgan (1910) explained the lack of independent assortment in Drosophila due to the linkage. When genes closely present adhere or link together in a group and transmitted as a single unit, the phenomenon is called linkage. It stops the process of independent assortment. Incomplete linkage is broken down due to the crossing over.
Question
Pattern baldness, moustaches and beard in human males are examples of [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) sex differentiating traits
(b) sex determining traits
(c) sex linked traits
(d) sex limited traits
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Sex limited traits are those which are limited to one sex only. Moustaches, beard are found in human males only: It was suggested on the basis of statistical analysis that premature baldness is controlled by a dominant gene, which expresses only in the presence of a certain level of male hormone (androgen).
Question
The linkage map of $X$-chromosome of fruit fly has 66 units, with yellow body gene $(y)$ at one end and bobbed hair (b) gene at the other end. The recombination frequency between these two genes ( $y$ and $b$ ) should be [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) $\leq 50 \%$
(b) $100 \%$
(c) $66 \%$
(d) $>50 \%$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The actual distance between two genes is said to be equivalent to the percentage of crossing over between these two genes. Since, the two genes lie at the ends of the chromosome, there are $100 \%$ chances of their segregation during crossing over.
Question
When a cluster of genes show linkage behaviour they [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) do not show independent assortment
(b) induce cell division
(c) do not show a chromosome map
(d) show recombination during meiosis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Linked genes do not show independent assortment because they are located on the same chromosome. But genes which are located on the same chromosomes (called linked genes) do not assort independently. Such type of genes are called linked genes and this phenomenon is called as linkage.
Question
In recent years, DNA sequences (nucleotide sequence) of mtDNA and $Y$-chromosomes were considered for the study of human evolution, because [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) their structure is known in greater detail
(b) they can be studied from the samples of fossil remains
(c) they are small and therefore, easy to study
(d) they are uniparental in origin and do not take part in recombination
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Wilson and Sarich choose mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) for the study of maternal line inheritance. While Y-chromosomes were considered for the study of human evolution particularly male domain. It is possible because they are uniparental in origin and do not take part in recombination.
Question
Genetic map is one that [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) shows the stages during the cell division
(b) shows the distribution of various species in a region
(c) establishes sites of the genes on a chromosome
(d) establishes the various stages in gene evolution
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Genetic map is a diagram which shows the relative position of genes on a chromosome. Strutevant in 1911 prepared the first genetic map of two chromosomes of fruit fly.
Question
Genes for cytoplasmic male sterility in plants are generally located in [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) nuclear genome
(b) cytosol
(c) chloroplast genome
(d) mitochondrial genome
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Mitochondria are originated from pre-existing mitochondria. These are semi-autonomous, living, organelles present in all eukaryotic cells. These contain DNA (mtDNA). The available evidences show that the genes located in mtDNA control the cytoplasmic male sterility.
Question
There are three genes $a, b, c$, percentage of crossing over between $a$ and $\mathrm{b}$ is $20 \%, \mathrm{~b}$ and $\mathrm{c}$ is $28 \%$ and $a$ and $c$ is $8 \%$. What is the sequence of genes on chromosome? [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) b, a, c
(b) $a, b, c$
(c) $a, c, b$
(d) None of these
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
According to the given question the sequence of gene son chromosome are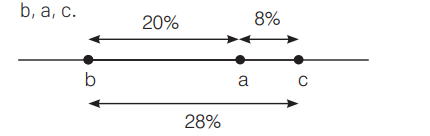
Question
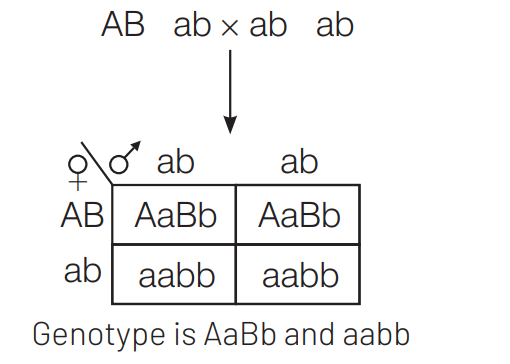
$A$ and $B$ genes are linked. What shall be the genotype of progeny in a cross between $A B / a b$ and $a b / a b$ ? [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) AAbb and aabb
(b) $A a B b$ and aabb
(c) AABB and aabb
(d) None of these
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Linked genes occur on the same chromosome and do not separate during inheritance (complete linkage).
Question
Extranuclear inheritance occurs in [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) Killer Paramecium
(b) Killer Amoebo
(c) Euglena
(d) Hydura
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Extranuclear inheritance or cytoplasmic inheritance is the inheritance of the characters of only one parent (generally the female parent). e.g. some strains of Paramecium called killer strain.
Question
The polytene chromosomes were discovered for the first time in [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) Drosophila
(b) Chironomus
(c) Musca nebulo
(d) Musca domestica
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Polytene chromosomes were first time discovered by the Italian cytologist EG Balbiani(18B1) in the salivary gland cells of Chironomus larva.
Question
Crossing over in diploid organism is responsible for [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) dominance of genes
(b) linkage between genes
(c) segregation of alleles
(d) recombination of linked alleles
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Crossing aver in diploid organism is responsible for recombination of linked alleles.
Question
Two dominant non-allelic genes are 50 map units apart. The linkage is [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) cis type
(b) trans type
(c) complete
(d) absent/incomplete
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Chromosome mapping is based on two genetic principles
(a) The frequency of crossing over between two genes is directly proportional to the distance between them in the chromosome.
(b) Genes are arranged in a linear order in the chromosome.
50 map unit distance between the genes is quite enough to change the $c i s$ arrangment of dominant genes into trans. So, there is no fixed linkage present.
Question
Two linked genes a and $b$ show $20 \%$ recombination. The individuals of a dihybrid cross between $++/++\times$ ab/ab shall show gametes [CBSE AIPMT 1989]
(a) $++80: a b: 20$
(b) $++50: a b: 50$
(c) $++40: a b$ 40: $+a 10:+b: 10$
(d) $++30: a b 30:+a 20:+b: 20$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The gametes of a dihybrid cross between $++1++\mathrm{x}$ ab/ab will be $++40: a b 40:+a 10:+b: 10$
Question
Crossing over in diploid organism is responsible for [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) dominance of genes
(b) linkage between genes
(c) segregation of alleles
(d) recombination of linked alleles
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The genes present an the same chromosome do not always remain together. These usually get separated and recombine with genes present on homologous chromosomes to form new combinations (recombinants).
Question
A fruit fly heterozygous for sex-linked genes, is mated with normal female fruit fly. Male specific chromosome will enter egg cell in the proportion [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) $1: 1$
(b) $2: 1 $
(c) $3: 1$
(d) $7: 1$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Genes which are present an sex chromosomes are called sex linked genes. Male Drosophila contains XY sex chromosome, while female contains XX-chromosomes. During gamete formation male produces $50 \%$ male specific gametes and $50 \%$ female specific gametes while female produces only one type of gametes, i.e. female specific. As male produces two types of gametes in equal proportion. There is an equal opportunity to getting a male or female offspring.
Question
After crossing two plants, the progenies are found to be male sterile. This phenomenon is found to be maternally inherited and is due to some genes which are present in [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) nucleus
(b) chloroplast
(c) mitochondria
(d) cytoplasm
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Factors responsible for cytoplasmic male sterility are located in mitochondrial DNA. Mitochondria are found only in eukaryotic cells. They contain a single circular double stranded DNA molecule (mtDNA) and mitochondria of female parent are transferred to progeny during fertilisation.
Question
When two genetic loci produce identical phenotypes in cis and trans position, they are considered to be [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) pseudoalleles
(b) different genes.
(c)multiplealleles
(d) parts of same gene
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Pseudoalleles are closely placed genes producing related phenotypic effect which is distinguishable only through a rare crossing over, e.g. dominant star and recessive asteroid eye traits in Drosophila.
Question
Genes located on Y-chromosome are [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a)mutant genes
(b) sex-linked genes
(c) autosomal genes
(d) holandric genes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Holandric genes are those that occur on the $Y$-chromosome only they are not expressed in females. These genes are directly transmitted from father to son. Hairy ears (hypertrichosis) in man is inherited through genes on Y-chromosomes.
Question
Mr. Kapoor has Bb autosomal gene pair and d allele sex-linked. What shall be proportion of $\mathrm{Bd}$ in sperms? [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) 0
(b) $1 / 2$
(c) $1 / 4$
(d) $1 / 8$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Mr. Kapoor will have the genotype Bb, $d$, so $1 / 4$ th af the sperms will have $\mathrm{Bd}$.
Question
When a certain character is inherited only through female parent, it probably represents [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) multiple plastid inheritance
(b) cytoplasmic inheritance
(c) incomplete dominance
(d) Mendelian nuclear inheritance
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The amount of nuclear hereditary material contributed by the two sexes is almost equal but the cytoplasm in egg is always much more than that of the sperm, so when a certain character is inherited only through female parent it represents cytoplasmic inheritance.
Question
Out of 8 ascospores formed in Neurospora the arrangement is $2 a$ : $4 a$ : 2 a showing [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) no crossing over
(b) some meiosis
(c) second generation division
(d) first generation division
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
In Neurospora after crossing over between the gene and centromere, the paired arrangement of ascospores is $A A$ aaaa AA or $2 \mathrm{a}: 4 \mathrm{a}: \mathrm{2a}$. This is known as second division segregation.
