Question
Match the organisms in Column I with habitats in Column II [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
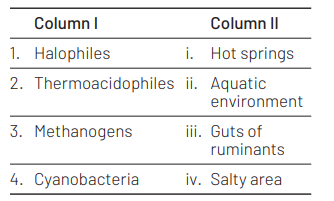
Select the correct option from the following
1 2 3 4
(a) (iv) (i) (iii) (ii)
(b) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
(c) (iii) (iv) (ii) (i)
(d) (ii) (iv) (iii) (i)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The correct match of organisms with their habitats are Halophiles live in salty areas Thermoacidophiles live in hot springs Methanogens live in guts of ruminants Cyanobacteria live in aquatic
environment
Question
It is much easier for a small animal to run uphill than for a large animal, because [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) smaller animals have a higher metabolic rate
(b) small animals have a lower $\mathrm{O}_2$ requirement
(c) the efficiency of muscles in large animals is less than in the small animals
(d) it is easier to carry a small body weight
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Basal metabolic rate is inversely proportional to body size. So, smaller animals have a higher metabolic rate, thus have quick and more energy required to go up the hills.
Question
The figure given below is a diagrammatic representation of response of organisms to abiotic factors. What do (i), (ii) and (iii) represent respectively? [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
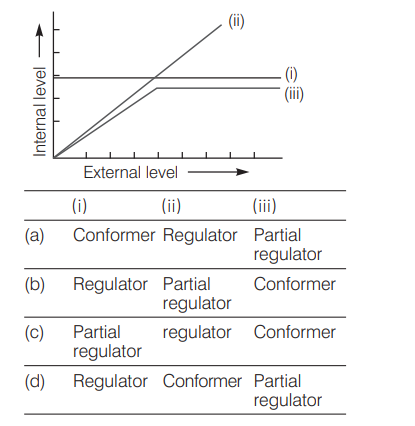
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
In the given diagrammatic representation of response of organisms to abiotic factors
(i) Regulator Some organisms are able to maintain homeostasis by physiological (sometimes behavioural also) means which ensures constant body temperature, constant osmotic concentration, etc. They are known as regulators.
(ii) Conformer Most animals and plants cannot maintain a constant internal environment. Their body temperature changes with the ambient temperature. These animals and plants are simply called conformer.
(iii) Partial regulator During the course of evolution, the costs and benefits of maintaining a constant internal environment are taken into consideration. Some species have evolved the ability to regulate but only over a limited range of environmental conditions, beyond which they simply conform. They are partial regulators.
Question
Consider the following four statements (I-IV) about certain desert animals such as kangaroo rat.
I. They have dark colour and high rate of reproduction and excrete solid urine.
II. They do not drink water, breathe at a slow rate to conserve water and have their body covered with thick hairs.
III. They feed on dry seeds and do not require drinking water.
IV. They excrete very concentrated urine and do not use water to regulate body temperature.
Which two of the above statements for such animals are true? [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) III and I
(b) I and II
(c) III and II
(d) Il and III
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Kangaroo rat feeds an dry seeds. It seldom drinks water. The requirement. of water is met by food(10\%) and metabolic water (90\%). Water loss is prevented by living in burrows during the day, cancentration of urine and solidification of faeces. It has a thick. coat to minimise evaporative desiccation.
Question
Annual migration does not occur in the case of [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) salmon
(b) siberian crane
(c) salamander
(d) arctic fern
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Salamander is semiterrestrial lizard-like talied amphibian that lives under stones, logs and inside cervices. They show hibernation not annual migratian. Salman are anadromous, i.e. they spend their adult lives at sea but feturn. to freshwater to spawn. The pacific species is legandry : after migrating down stream as a smalt a sockeye salman ranges many hundreds ot mile over the pacific for nearly four year and then returns to spewn in the head waters of its parent stream.
Migration is characteristic feature of birds. Arctic tern travels about 1100 miles during winter and returns back during summer.
Question
In which one of the following pair is the specific characteristic of soil not correctly matched? [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) Laterite – Contains aluminium compound
(b) Terra rossa – Most suitable for roses
(c) Chernozems – Richest soil in the world
(d) Black soil – Rich in calcium carbonate
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Black soil is dark ar dark brown in colour. It is formed from basaltic rock under semi-arid condition. Black soil is lagically known as regur ar black cotton soin. Black soil is deficient in nitrogen and phaspharus and rich in patash and lime and not in calcium carbonate.
Question
In which one of the following habitats does the diumal temperature of soil surface vary most? [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) Shrubland
(b) Forest
(c) Desert.
(d) Grassland
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Deserts have a very hot days and very cold nights. Due to the bare plant cover, the soil at desert is much mare exposed to these fluctuations as compared to that of other areas. During day time, the soil becomes hot and in night it frequently, becames cool.
Question
Diffuse porous woods are characteristic of plants growing in [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) temperate climate
(b) tropics
(c) alpine regian
(d) cald winter regians
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In tropics, there is no sharp distinction between the seasons, hence, there is nat much difference in the activity of cambium. In a diffused parcus wood, the large sized vessels are distributed through spring woad and autumn wood, e.g. Syaygium cumin.
Question
Special kinds of roots called pneumatophores are characteristics of the plants growing in [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) sandy solls
(b) saline solis
(c) marshy places and salt lakes
(d) dryland regions
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Pneumatophores are specialised roats which grow vertically upwards into the air trom roats embedded in the mud. Since, they are loosely constructed. these make gaseous exchange possible for submerged roats. These are found in plants growing in marshes of saline swamps.
Question
Temperature changes in the environment affect most of the animals which are [CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) homeothermic
(b) aquatic
(c)poikilothermic
(d) desert living
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Poikilathermy(cold blaodedness) is a condition of any animal whose body temperature fluctuates considerably with that of its efrironment.Homeathermy, an the other hand, is the quality of maintaining a constant bady temperature.
Question
Extremities, tail and ear are relatively shorter in animals living in cooler regions as compared to those inhabiting warmer zones. This is [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) Bergman’s rule
(b) Jordan’s rule
(c) Gloger’s rule
(d) Allen’s rule
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Accarding to Allen’s rule, extremities; tail and ear are relatively shorter in animals living in coaler regions as compared to those inhabiting warmer zones.
Question
Desert plants are generally[CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) viviparous
(b)succulent.
(c)herbaceous
(d)heterophyllus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Desert plants are generally succulents of fleshy xerophytes, They are referred as drought resisting xerophytes, e.g. Dpuntia, Bryophylum, Euphorbia, Mesembryanthemum [ice plant].
Question
Sunken stomata is the characteristic feature of [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a)hydrophyte
(b)mesophyte
(c) xerophyte
(d) halaphyte
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Sunken stomata is the characteristic feature of xerophytes, these stomata are found generaly on the lower surface af leaves.
Question
Which of the following does not have stomata? [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) Hydrophytes
(b) Mesophytes
(c) Xerophytes
(d) Submerged hydrophytes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Sub-merged hydrophytes are those plants which live completely inside the water, so there is no need of transpiration that’s why these plants da not have stomata, e.g. Utriculario, Ceratophylum.
Question
Animals that can tolerate a narrow range of salinity are [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) stenohaline
(b) euryhaline
(c) anadromous
(d) catadromous
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Animals that can tolerate anly a small range of salinity are stenahaline.
Question
Soil best suited for plant growth is[CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) clay
(b)loamy
(c) sandy
(d) gravel
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Loamy soil containing about 1 part clay: 2 parts silt and 2 parts sand (20\% clay, $40 \%$ silt and $40 \%$ sand) is best for plant. growth because it possesses good aeration, sufficient nutritive salts and gaod water retaining capacity.
Question
Soil particles determine its [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) texture
(b) field capacity
(c) water holding capacity
(d) soil flora
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Soil particles determine its texture. The behaviour of water in the ground is influenced by the type of soil present. Soils are classified according to their particle size as follows:
(i) Gravel $-2 \mathrm{~mm}-75 \mathrm{~mm}$
(ii) Sand $-0.05 \mathrm{~mm}-2 \mathrm{~mm}$
(iii) Sil $-0.002 \mathrm{~mm}-0.05 \mathrm{~mm}$
(iv) Clay – less than $0.002 \mathrm{~mm}$
Question
A fertile agricultural soil appears dark coloured at the surface as compared to soil one metre down. The reason for colour of top soil is [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) more molsture
(b) rich in arganic matter
(c) rich in iron, calclum and magnesium
(d) recent formation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Dark colour of soll is due to accumulation of leached arganic substances and organic matter which serves as a reservoir of nutrients and water in the soil, aids in reducing compacting and surface crusting and increases water infiltration into the sail.
Question
River water deposits [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) loamy soil
(b) alluvial soil
(c) laterite soil
(d) sandy soil
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
River water deposits are found in alluwial soil. It is rich in nutrients and may contain heavy metals. These soils are formed when streams and rivers slow their velocity and suspended soil particles gets deposited on the river bed.
Question
Deep black soil is productive due to high proportion of [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) sand and zinc
(b) gravel and calcium
(c) clay and humus
(d) silt and earthworm
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Black soil is productive due to the high proportion of clay and humus, because most of the minerals are present in it.
Question
CAM helps the plants in [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) secondary growth
(b) disease resistance
(c) reproduction
(d) conserving water
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
CAM plants are mostly succulent. xerophytes. The stomata in these plants remain closed during the day. This helps to check the transpiration. In this way, water is conserved.
Question
Two different species cannot live for long duration in the same niche or habitat. This law is [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) Allen’s law
(b) Gause’s hypothesis
(c) Dollo’s rule
(d) Weismann’s theory
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The principle of competitive exclusion was postulated by Saviet ecolagist G F Gause. It states that if two species are competing with ane another for the same limited resources, then one at the species will be able to use that resource mare efficiently than the other and the farmer will, therefore, eventually eliminate the lattef locally.
Question
In which of the following plant sunken stomata are found? [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) Nerium
(b) Hyanilia
(c) Mango
(d) Guava
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Presence of sunken stomata is an adaptive feature of xerophytic plants. These stomata are partially covered by hairs and cuticle. Sunken stomata are found in Nerium to check the transpiration.
Mango is a mesaphytic plant.
Hydrillo is a hydraphytic plant.
Guava is also a mesaphytic plant.
