Question
Select the correct option of haploid cells from the following groups. [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) Primary oocyte, secondary oocyte, spermatid
(b) Secondary spermatocyte, first polar body, ovum
(c) Spermatogonia, primary spermatocyte, spermatid
(d) Primary spermatocyte, secondary spermatocyte, second polar body
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Out of the given the option, the haploid cells are secondary spermatocyte, first polar body, ovum, secondary oocyte, spermatids and second polar body. The diploid cells are primary oocyte and
primary spermatocyte. Thus, option (b) is correct.
Question
Match the following columns and select the correct option from the codes given belows [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
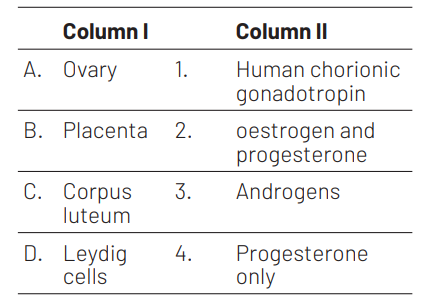
Codes
A B C D
(a) 4 3 2 1
(b) 1 2 3 4
(c) 1 3 2 4
(d) 2 1 4 3
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The option (d) is the correct match which is as follows Ovary produces oestrogen and progesterone. Placenta produces Human Chorionic Gonadotropin (hCG). Corpus luteum produces progesterone
only. Leydig cells produce androgens.
Question
Which of the following hormone levels will cause release of ovum (ovulation) from the Graafian follicle? [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) High concentration of progesterone
(b) Low concentration of LH
(c) Low concentration of FSH
(d) High concentration of oestrogen
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
High level of oestrogen will send positive feedback to anterior pituitary for release of ovum from Graafian follicle. FSH, LH and oestrogen are at peak level during mid of menstrual cycle (28 day cycle). LH surge leads to ovulation.
Question
Meiotic division of the secondary oocyte completed [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) at the time of copulation
(b) after zygote formation
(c) at the time of fusion of a sperm with an ovum
(d) prior to ovulation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Meiotic division of secondary oocyte is completed after the entry of sperm in secondary oocyte which lead to the formation of a large ovum and a tiny llnd polar body.
Question
No new follicles develop in the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle because [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) follicles do not remain in the ovary after ovulation
(b) FSH levels are high in the luteal phase
(c) LH levels are high in the luteal phase
(d) both FSH and LH levels are low in the luteal phase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
No new follicles develop in the luteal phase of menstrual cycle. It is because during this phase, Luteinising Hormone (LH) and Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) levels decrease. Instead, the already ruptured follicle closes after releasing the egg and forms a corpus luteum during luteal phase, which produces progesterone.
Question
What is the fate of the male gametes discharged in the synergid? [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) All fuse with the egg
(b) One fuses with the egg, other(s) fuse(s) with synergid nucleus
(c) One fuses with the egg and other fuses with central cell nuclei
(d) One fuses with the egg other(s) degenerate (s) in the synergid
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Out of the male gametes discharged in the synergid, one fuses with the egg and other fuses with central cell nuclei. The fusion between male gamete and egg is called syngamy or true fertilisation which forms zygote $(2 \mathrm{~h}$. The fusion between male gamete and central cell nuclei is called triple fusion and it results in the formation of a triploid primary endosperm nucleus $(3)$.
Question
Extrusion of second polar body from egg nucleus occurs [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) after fertilisation
(b) before the entry of sperm into ovum
(c) simultaneously with first cleavage
(d) after the entry of sperm but before fertilisation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Extrusion of second polar body from egg nucleus occurs after the entry of sperm but before fertilisation. The entry of sperm into female egg causes the breakdown of Metaphase Promoting Factor (MPF) and turns on Anaphase Promoting Factor (APF). Hence, the secondary oocyte completes its meiotic division after fertilisation and is said to be activated.
Question
The difference between spermiogenesis and spermiation is [NEET 2018]
(a) In spermiogenesis, spermatozoa from Sertoli cells are released into the cavity of seminiferous tubules, while in spermiation spermatozoa are formed
(b) In spermiogenesis, spermatozoa are formed, while in spermiation spermatids are formed
(c) In spermiogenesis, spermatids are formed, while in spermiation spermatozoa are formed
(d) In spermiogenesis, spermatozoa are formed, while in spermiation spermatozoa are released from Sertoli cells into the cavity of seminiferous tubules
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Spermiogenesis is the process of transformation of spermatids $(n)$ into spermatozoa $(n)$ or sperms. It involves the differentiation phase in which one spermatid develops into one spermatozoan.
Spermiation involves the release of sperms from seminiferous tubules through Sertoli cells.
Question
Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II and select the correct option given below. [NEET 2018]
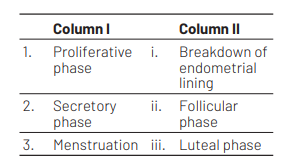
1 2 3
(a) ii iii i
(b) i iii ii
(c) iii ii i
(d) iii i ii
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
During proliferative phase, the follicles start growing in size under the influence of Follicle stimulating Hormone (FSH). Hence, this phase is also called follicular phase.
During secretory phase, corpus luteum secretes progesterone that helps to thicken the endometrial lining. Due to the persistence of corpus luteum, this phase is also called luteal phase.
Menstruation or bleeding occurs due to the breakdown of endometrial lining in the absence of pregnancy. During this phase, corpus luteum regresses and progesterone level decreases.
Question
A temporary endocrine gland in the human body is [NEET 2017]
(a) pineal gland
(b) corpus cardiacum
(c) corpus luteum
(d) corpus allatum
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Corpus luteum is a temporary endocrine gland in the human body. It secretes small amount of estradiol and significant amount of progesterone hormone. In the absence of fertilisation, the corpus luteum degenerates.
Question
Select the incorrect statement. [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) $\mathrm{LH}$ and FSH triggers ovulation in ovary
(b) LH and FSH decrease gradually during the follicular phase
(c) $\mathrm{LH}$ triggers secretion of androgens from the Leydig cells
(d) FSH stimulates the Sertoli cells which help in spermiogenesis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In follicular phase of menstrual cycle, $\mathrm{LH}$ and FSH increase gradually and stimulate follicular development as well as secretion of oestrogens by the growing follicles.
Question
Identify the correct statement on ‘inhibin’. [NEET 2016, Phase 1]
(a) Is produced by granulosa cells in ovary and inhibits the secretion of $\mathrm{FSH}$
(b) Is produced by granulosa cells in ovary and inhibits the secretion of LH
(c) Is produced by nurse cells in testes and inhibits the secretion of $\mathrm{LH}$
(d) Inhibits the secretion of LH, FSH and prolactin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Inhibin is produced by granulosa cells of ovarian follicles in the ovary and has negative feedback effect on the secretion of FSH.
Question
Changes in GnRH pulse frequency in females is controlled by circulating levels of [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) oestrogen and inhibin
(b) progesterone only
(c) progesterone and inhibin
(d) oestrogen and progesterone
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
High levels of oestrogen and progesterone give negative feedback to hypothalamus for the release of GnRH. Thus, inhibiting the gonadotropin release.
Question
Which of the following layers in an antral follicle is acellular? [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) Granulosa
(b) Theca interna
(c) Stroma
(d) Zona pellucida
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Follicles that form an antrum during maturation are called antral follicle or Graafian follicle. During the development of the follicle, a glycoprotein polymer capsule called the zona pellucida which is acellular, forms around the oocyte, separating it from the surrounding granulosa cells. This layer remains with the oocyte after ovulation, and contains enzymes that catalyse with sperm to allow penetration.
Question
Which of the following events in not associated with ovulation in human female? [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) Decrease in oestradiol
(b) Full development of Graafian follicle
(c) Release of secondary oocyte
(d) LH surge
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Destradiol levels fall after ovulation and before menstruation while, its levels peak prior to ovulation. Destradiol are not associated with ovulation. Decrease in oestradiol level result in the cessation of menstruation.
Question
The main function of mammalian corpus luteum is to produce [CBSE AIPMT 2014, 1995]
(a) oestrogen only
(b) progesterone
(c) human chorionic gonadotropin
(d) relaxin only
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The main function of mammalian corpus luteum is the secretion of progesterone which is essential for the maintenance of endometrium. Endometrium is necessary for implantation of the fertilised ovum and other events of pregnancy. Corpus luteum also secretes some amount of estrogen to maintain pregnancy. hCG (human Chorionic Gonadotropin) is secreted by placenta for maintaining the corpus luteum. Relaxin is secreted by corpus luteum during the end of gestation period.
Question
What is the correct sequence of sperm formation? [NEET 2013]
(a) Spermatid, Spermatocyte, Spermatogonia, Spermatozoa
(b) Spermatogonia, Spermatocyte, Spermatozoa, Spermatid
(c) Spermatogonia, Spermatozoa, Spermatocyte, Spermatid
(d) Spermatogonia, Spermatocyte, Spermatid, Spermatozoa
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Spermatogonia $\rightarrow$ Spermatocyte $\rightarrow$ Spermatid $\rightarrow$ Spermatozoa Spermatogonia is present on the inside wall of seminiferous tubule which undergo mitotic division and increase their number. Spermatocytes are some of the spermatogonia, which periodically undergo meiosis. The secondary spermatocyte undergo the second meiotic division to produce four, equal haploid spermatids. The spermatids are transformed into spermatozoa (sperm).
Question
Menstrual flow occurs due to lack of [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) progesterone
(b) FSH
(c) oxytocin
(d) vasopressin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Menstrual flow occurs due to the lack of progesterone. Progesterone is secreted by corpus luteum and is essential for the maintenance of endometrium. This endometrium is responsible for implanation of the festilised ovum, i.e. pregnancy. FSH Stimulates gonadal activity and also called as gonadotrophins.
Oxytocin Stimulates contraction in uterus during childbirth.
Vasopressin Stimulate resorption of water and electrolytes by the distal tubules, also called as Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH).
Question
Which one of the following statements is false in respect of viability of mammalian sperm? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) Sperm is viable for only up to $24 \mathrm{hrs}$
(b) Survival of sperm depends on the $\mathrm{pH}$ of the medium and is more active in alkaline medium
(c) Viability of sperm is determined by its motility
(d) Sperms must be concentrated in a thick suspension
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Viability of a sperm means the capability of a sperm, to fertilise an egg.
Sperms are viable for $24 \mathrm{~h}$ to $48 \mathrm{~h}$, whereas the ovum is viable for only $24 \mathrm{~h}$.
Question
Which one of the following statements about human sperm is correct? [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) Acrosome has a conical pointed structure used for piercing and penetrating the egg, resulting in fertilisation
(b) The sperm lysins in the acrosome dissolve the egg envelope facilitating fertilisation
(c) Acrosome serves as a sensory structure leading the sperm towards the ovum
(d) Acrosome serves no particular function
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Penetration of human sperm is a chemical mechanism. In this, acrosome of sperm undergoes acrosomal reaction and releases certain sperm lysins, which dissolve the egg envelope locally and make the path for the penetration of sperm. Sperm lysins are acidic proteins. These sperm lysins contain a lytic enzyme hyaluronidase (that dissolves the hyaluronic acid polymers in the intercellular spaces, which holds the granulosa cells of corona radiata together) corona penetrating enzyme and acrosin.
Question
Which one of the following is the most likely reason of not occurring regular menstruation cycle in females? [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) Fertilisation of the ovum
(b) Maintenance of the hypertrophical endometrial lining
(c) Maintenance of high concentration of sex-hormones in the blood stream
(d) Retention of well-developed corpus luteum
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
If fertilisation occurs and foetus is implanted in the endometrium, the trophoblast cells of the developing placenta secrete a hormone human Chorionic Gonadotrophic(hCG). This hormone like LH maintains the corpus luteum and the secretion of progesterone and estradiol by it. These two hormones check the breakdown of the endometrium of the uterus. The absence of menstrual bleeding is the earliest sign of pregnancy.
Question
Which one of the following is the correct matching of the events occurring during menstrual cycle? [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) Ovulation $\mathrm{LH}$ and $\mathrm{FSH}$ attain peak level and sharp fall in the secretion of progesterone
(b) Proliferative Rapid regeneration phase of myometrium and maturation of Graafian follicle
(c) Development Secretory phase and of corpus increased secretion luteum of progesterone
(d) Menstruation Breakdown of myometrium and ovum not fertilised
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In secretory phase during ovulation, the follicle breaks and collapes under the continuous influence of Luteinising Hormone (LH). It begins to enlarge and forms a yellowish structure, called the corpus luteum. The corpus luteum plays an important role in the preparation of the endometrium for the implantation of the fertilised egg by secreting oestrogens and progesterone.
Question
Which one of the following statement is incorrect about menstruation? [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) During normal menstruation about 40 $\mathrm{mL}$ blood is lost
(b) The menstrual fluid can easily clot
(c) At menopause in the female, there is especially abrupt increase in gonadotropic hormones
(d) The beginning of the cycle of menstruation is called menarche
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
During normal menstruation approximately $40 \mathrm{~mL}$ of blood and an additional $35 \mathrm{~mL}$ of serous fluid are lost. The menstrual fluid is normally non-clotting because a fibrinolysin is released alongwith necrotic endometrial material.
Question
At the end of first meiotic division, male germ cell differentiates into [CBSE AIPMT 2008, 1994]
(a) secondary spermatocyte
(b) primary spermatocyte
(c) spermatogonium
(d) spermatid
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
First meiotic division takes place in diploid primary spermatocyte and it forms two haploid cells called secondary spermatocytes.
Question
Which part of ovary in mammals acts as an endocrine gland after ovulation? [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) Graafian follicle
(b) Stroma
(c) Germinal epithelium
(d) Vitelline membrane
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
During ovulation, the mature follicle or Graafian follicle bursts and the ovum is released. This is named as corpus luteum which serves as a temporary endocrine gland by releasing progesterone and oestrogen.
Question
If mammalian ovum fails to get fertilised, which one of the following is unlikely?
(a) Corpus luteum will disintegrate
(b) Estrogen secretion further decreases
(c) Primary follicle starts developing
(d) Progesterone secretion rapidly declines
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
If mammalian ovum fails to get fertilized, the estrogen secretion does not decrease further, while corpus luteum will disintegrate. Primary follicle starts developing and progesterone secretion rapidly declines.
Question
Ovulation in the human female normally takes place during the menstrual cycle [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) at the mid secretory phase
(b) just before the end of the secretory phase
(c) at the beginning of the proliferative phase
(d) at the end of the proliferative phase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Ovulation takes place under the influence of LH and FSH. It normally takes place at the end of proliferative ie, $14^{\text {th }}$ day or mid way during menstrual cycle. The LH surge stimulates completion of reduction division of oocyte. Following ovulation, the Graafian follicle changes to corpus luteum.
Question
Which set is similar? [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) Corpus luteum – Graafian follicle
(b) Sebum – Sweat
(c) Bundle of His – Pacemaker
(d) Vit-B $-$ Niacin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Corpus luteum is temporary endocrine tissue developing from ruptured Graafian follicle. Sebum is an oily lipid containing secretion of mammalian sebaceous glands. Sweat is an aqueous secretion of mammalian sweat glands. Bundle of His is a part of conducting system of heart and pace-maker is responsible for initiation of heart beat in right auricle SA node. Vitamin- $B_5$ is also known as niacin.
Question
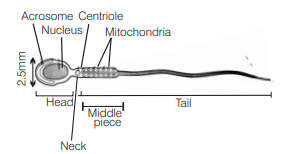
Middle piece of mammalian sperm possesses [CBSE AIPMT 1999, 91]
(a) mitochondria and centriole
(b) mitochondria only
(c) centriole only
(d) nucleus and mitochondria
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The middle piece of human sperm contains mitochondria which are coiled around an axial filament called mitochondrial spiral. These provide energy for the movement of sperm.
Question
After ovulation, Graafian follicle regresses into [CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) corpus luteum
(b) corpus callosum
(c) corpus albicans
(d) corpus artesia
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Just after ovulation, LH(secreted by anterior lobe of pituitary gland) stimulates remaining ovarian follicles to develop into corpus luteum. The corpus luteum plays an important role in the preparation of the endometrium for the implantation of the fertilised egg by secreting oestrogens and progesterone.
Question
In 28 days human ovarian cycle, ovulation occurs on [CBSE AIPMT 1997, 94]
(a) 1 day
(b) 5 day
(c) 14 day
(d) 28 day
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The first phase (proliferative phase) of menstrual cycle ends on $14^{\text {th }}$ day, the ovarian follicles rupture and ovulation occurs.
Question
Fertilisins are emitted by [CBSE AIPMT 1997, 91]
(a) immature eggs
(b) mature eggs
(c) sperms
(d) polar bodies
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Eggs secrete the chemical fertilisin, which is made up of glycoprotein. It interacts with the antifertilisin (protein on sperm surface) of a sperm of same species.
Question
Human eggs are [CBSE AIPMT 1997, 89]
(a) alecithal
(b) microlecithal
(c) mesolecithal
(d) macrolecithal
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The eggs almost free of yolk are called alecithal, e.g. human eggs (ova). In such eggs the cleavage pattern is holoblastic (Gr. holo-whole; blastos-germ) that is the cleavage extends completely through the egg.
Question
Ovulation occurs under the influence of [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) $\mathrm{LH}$
(b) FSH
(c) oestrogen
(d) progesterone
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The Luteinising Hormone (LH) of anterior pituitary regulates the ovulation from the Graafian follicle. This LH surge causes ovulation to occur.
Question
In telolecithal egg the yolk is found [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) all over the egg
(b) on one side
(c) both the sides
(d) at centre
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Yolk is concentrated towards vegetal pole. The nucleus and major part of cytoplasm is displaced to animal pole as in mesolecithal and macrolecithal eggs of vertebrates.
Question
Freshly released human egg has [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) one Y-chromosome
(b) one X-chromosome
(c) two X-chromosomes
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Human female is homozygous, i.e. produces same kind of gametes that carry $X$-chromosome while human male is heterozygous, i.e. produces unlike gametes that carries either X-chromosome orY-chromosome.
Question
Egg is liberated from ovary in [CBSE AIPMT 1989]
(a) secondary oocyte stage
(b) primary oocyte stage
(c)oogonial stage
(d) mature ovum stage
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In most of the organisms including human female the ovulation, i.e., release of ovum from ovary occurs at secondary oocyte stage in which meiosis-1 has been completed and first polar body has been released.
Question
There is no DNA in [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) an enucleated ovum
(b) mature RBCs
(c) a mature spermatozoan
(d) hair root
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The chromatin material inside the nucleus is composed of DNA, some proteins and RNA. Infact it is basically DNA-protein complex. Thus, in an enucleated ovum, DNA will be absent. The mature RBCs, mature spermatozoan and root hair are nucleated which contain DNA.
