Question
Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II and select the correct option given below [NEET 2018]
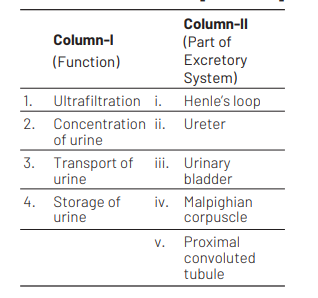
1 2 3 4
(a) v iv i ii
(b) iv i ii iii
(c) iv v ii iii
(d) v iv i iii
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Ultrafiltration or Glomerular filtration is carried out in the glomerular capillaries found in Malpighian corpuscle. This process is carried out under high pressure.
Henle’s loop continuously absorbs the water from glomerular filtrate, because of the hyperosmolarity created by counter-current mechanism. This helps in the concentration of urine and hence, it becomes hypertonic. Ureter are narrow, tubular structures that convey or transport urine from kidney to urinary bladder.
Urinary bladder is pear-shaped, muscular, sac-like structure that temporarily stores urine.
Question
Figure shows human urinary system with structures labelled $A-D$. Select option, which correctly identifies them and gives their characteristics and/of functions [NEET 2013]
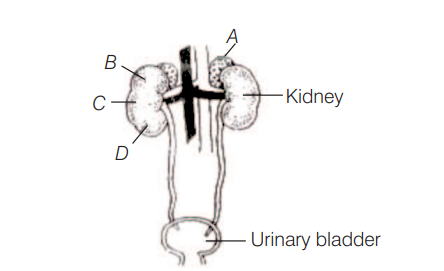
(a) A-Adrenal gland-located at the anterior part of kidney. Secrete catecholamines, which stimulate glycogen break down
(b) B-Pelvis-broad funnel shaped space inner to hilum, directly connected to loops of Henle
(c) C-Medulla-inner zone of kidney and contains complete nephrons
(d) D-Cortex-outer part of kidney and do not contain any part of nephrons
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
A-Adrenal gland it is correctly mentioned. It is located at the anterior part of kidney and secretes catecholamines which stimulate glycogen breakdown.
Question
The principal nitrogenous excretory compound in humans is synthesised [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) in kidneys but eliminated mostly through liver
(b) in kidneys as well as eliminated by kidneys
(c) in liver and also eliminated by the same through bile
(d) in the liver but eliminated mostly through kidneys
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
In humans, the principal nitrogenous excretory compound (i.e. urea) is synthesised in liver by Ornithine cycle and is eliminated mostly through kidney as nitrogeneous excretory product. In liver, one molecule of $\mathrm{CO}_2$ is activated by biotin and combines with two molecules of $\mathrm{NH}_3$ in the presence of carbamyl phosphate synthetase enzyme and 2ATP to form carbamyl phosphate and one molecule of $\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$ is released. Carbamyl phosphate reacts with Ornithine and forms Citrulline. Citrulline combines with another molecule of ammonia and form arginine that is broken into urea and Ornithine in the presence of an enzyme arginase and water.
$
\begin{aligned}
& 2 \mathrm{NH}_3+\mathrm{CO}_2 \stackrel{\text { Arginase }}{\longrightarrow} \mathrm{NH}_2-\mathrm{CO}-\mathrm{NH}_2 \\
& +\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}
\end{aligned}
$
Question
What will happen if the stretch receptors of the urinary bladder wall are totally removed? [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) Urine will not collect in the bladder
(b) Micturition will continue
(c) Urine will continue to collect normally in the bladder
(d) There will be no micturition
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
If stretch receptors of urinary bladder wall are totally removed, the urine will continue to collect normally in the bladder. The urinary bladder is a pear-shaped, hollow muscular organ situated in the pelvic cavity which is made up of smooth and involuntary muscles. The lumen of urinary bladder is lined by transition epithelium which has great power of stretching.
Question
Bowman’s glands are found in [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) olfactory epithelium
(b) external auditory canal
(c) cortical nephrons only
(d) juxtamedullary nephrons
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Bowman’s glands (olfactory glands) occur below the olfactory epithelia.
Their ducts open on the olfactory epithelial surface. These glands secrete watery mucus to protect and keep the epithelium moist.
Question
Part not belonging to uriniferous tubule is [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) glomerulus
(b) Henle’s loop
(c) distal convoluted tubule
(d) collecting tubule
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
From the option given glomerulus do not belong to uriniferous tubule. Each nephron is about $6 \mathrm{~cm}$ long and is divided into two parts : Bowman’s capsule and nephric or uriniferous tubule. Glomerulus is a group of about 50 capillaries. Its capillary wall has numerous minute pores, so the permeability of glomerular membrane increases 100-500 times as high as that of usual capillary.While Henle’s loop, DCT and collecting tubules are part of uriniferous tubule.
Question
Proximal and distal convoluted tubules are parts of [CBSE AIPMT 1990]
(a) seminiferous tubules
(b) nephron
(c) oviduct
(d) vas deferens
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Nephron is the structural and functional unit of kidney. Nephrons are also called renal tubules or uriniferous tubules. Each nephron is formed of two parts.
(i) Bowman’s capsule and (ii) Nephric tubule which is a long and coiled and is formed of proximal convoluted tubule. loop of Henle and distal convoluted tubule.
Question
Brush border is characteristic of [CBSE AIPMT 1990]
(a) neck of nephron
(b) collecting tube
(c) proximal convoluted tubule
(d) All of the above
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Proximal convoluted tubule is present in cortex and is convoluted. It is about $12-24 \mathrm{~mm}$ in length. It is lined by brush bordered cuboidal epithelium with numerous microvilli. These cells have numerous mitochondria for active transport.
