Question
The Adenosine deaminase deficiency results into [NEET 2021]
(a) dysfunction of immune system
(b) Parkinson’s disease
(c) digestive disorder
(d) Addison’s disease
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Adenosine deaminase is an enzyme. The deficiency of this particular enzyme results in severe combined immuno deficiency (SCID). During the deficiency of adenosine deaminase the patient lacks functional T- lymphocytes and thus the immune system does not work properly.
Question
The yellowish fluid ‘colostrum’ secreted by mammary glands of mother during the initial days of lactation has abundant antibodies $(\lg A)$ to protect the infant. This type of immunity is called as [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) passive immunity
(b)active immunity
(c) acquired immunity
(d) autoimmunity
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Passive immunity is when readymade antibodies are directly given to protect the body against foreign agents. For example, the yellowish fluid colostrum secreted by mother during the initial days of lactation has abundant antibodies ( $(g A)$ to protect the infant. Also the foetus receives some antibodies from their mother through the placenta during pregnancy.
Question
Identify the wrong statement with reference to immunity. [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) When readymade antibodies are directly given, it is called ‘passive immunity’
(b)Active immunity is quick and gives full response
(c) Foetus receives some antibodies from mother, it is an example for passive immunity
(d) When exposed to antigen (living or dead) antibodies are produced in the host’s body. It is called ‘active immunity
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The statement in option is (b) incorrect because active immunity is slow and takes time to give its full effective response in comparison to passive immunity where pre-formed antibodies are administered.
Question
Humans have acquired immune system that produces antibodies to neutralise pathogens. Still innate immune system is present at the time of birth because it [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) is very specific and uses different macrophages
(b) produces memory cells for mounting fast secondary response
(c) has natural killer cells which can phagocytose and destroy microbes
(d) provides passive immunity
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Innate immunity is non-specific type of defence that is present at the time of birth because it has natural killer cells which can phagocytose and destroy microbes (cellular barriers). Other forms of innate immunity are physical barriers, physiological and cytokine barriers.
Question
Which of the following diseases is an autoimmune disorder? [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) Myasthenia gravis
(b) Arthritis
(c) Osteoporosis
(d) Gout
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Myasthenia gravis is a chronic autoimmune neuromuscular disorder that causes weakness in the skeletal muscles. This is responsible for breathing and moving parts of the body including the arms and legs.
Question
Concanavalin $A$ is [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) an essential oil
(b) a lectin
(c) a pigment
(d) an alkaloid
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Concanavalin $\mathrm{A}$ is a lectin or a carbohydrate binding protein. It is a T-cell mitogen that can activate the immune system, recruit lymphocytes and elicit cytokine production. It can also induce programmed cell death via mitochondria-mediated apoptosis.
Question
Which of the following immune responses is responsible for rejection of kidney graft? [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) Humoral immune response
(b) Inflammatory immune response
(c) Cell-mediated immune response
(d) Auto-immune response
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Cell-mediated immune response is responsible for the rejection of kidney graft. Cell-mediated immune response is conferred by sensitised T-lymphocytes and here, antibodies are not produced.
T-cells confer a long term memory and they are able to discriminate between self and non-self. These cells sometimes consider graft as non-self and attack the same which causes its rejection.
Question
Which of the following is not an autoimmune disease? [NEET 2018]
(a) Alzheimer’s disease
(b) Rheumatoid arthritis
(c) Psoriasis
(d) Vitiligo
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Alzheimer’s disease is not an automimmune disease. It is caused due to the destruction of vast number of neurons in the Hippocampus. It occurs due to a combination of genetic factors, environmental or lifestyle factors and the ageing process. There is loss of neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Individuals with this disease have trouble remembering recent events. Rheumatoid arthritis, vitiligo and psoriasis all are autoimmune diseases. In rheumatoid arthritis, antibodies are produced against the synovial membrane and cartilage.
Vitiligo causes white patches on skin while psoriasis causes itch-skin.
Question
MALT constitutes about . per cent of the lymphoid tissue in human body. [NEET 2017]
(a) $50 \%$
(b) $20 \%$
(c) $70 \%$
(d) $10 \%$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
MALT is mucosa associated lymphoid tissue located within the linning of the major tracts including respiratory, digestive and urinogenital tracts. It is nearly $50 \%$ of the total lymphoid tissue in the human body.
Question
Transplantation of tissues/organs fails often due to non-acceptance by the patient’s body. Which type of immune-response is responsible for such rejections ? [NEET 2017]
(a) Autoimmune response
(b) Cell-mediated immune response
(c) Hormonal immune response
(d) Physiological immune response
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Transplantation of tissue/organs may fail, when that tissue is rejected by the recipient’s immune system leading to its destruction. Tissue rejection is a function of cell-mediated immune response that involves T-cells. These cells have the ability to distinguish between self and non-self. After the recognition of non-self tissue, the killer T-cells induces apoptosis of the target tissue.
Question
In higher vertebrates, the immune system can distinguish self-cells and non-self. If this property is lost due to genetic abnormality and it attacks self-cells, then it leads to [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) graft rejection
(b)auto-immune disease
(c) active immunity
(d)allergic response
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In auto-immune disease, the immune cells are unable to distinguish between self-cells and non-self cells and attack self-cells which may lead to auto-immune disorders like interstitial lung disease in humans.
Question
Antivenom injection contains preformed antibodies while polio drops that are administered into the body contain [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) harvested antibodies
(b) gamma globulin
(c)attenuated pathogens
(d) activated pathogens
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Oral polio vaccine consists of attenuated pathogens. Attenuated pathogens are living microorganisms or viruses cultured under adverse condition, leading to loss of their virulance. But these organisms have the ability to induce protective immunity. The oral vaccine of polio contains three live polio strains in attenuated forms.
Question
If you suspect major deficiency of antibodies in a person, to which of the following would you look for confirmatory evidence? [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) Fibrinogin in plasma
(b)Serum albumins
(c) Haemocytes
(d) Serum globulins
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Globulin is one of the protein found in serum and it includes proteins, enzymes, complement and immunoglobulins (antibody). That’s why, if major deficiency of antibodies is suspected in a person, the globulins in serum is tested as the confirmatory evidence.
Question
Grafted kidney may be rejected in a patient due to [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) humoral immune response
(b) cell-mediated immune response
(c) passive immune response
(d) innate immune response
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Grafted kidney may be rejected in a patient due to the cell-mediated immune response that is mediated by T-lymphocytes. The body is able to differentiate ‘self’ and ‘non-self’. Therefore, tissue matching, blood group matching are essential before undertaking any graft/transplant and even after this the patient has to take immuno-suppressants all his/her life.
Question
Which of the following immunoglobulins does constitute the largest percentage in human milk? [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) $\lg D$
(b) $\lg M$
(c) $\lg \mathrm{A}$
(d) $\lg G$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
All types of immunoglobulin are found in human milk. Out of these secretory IgA, a type of immunoglobulin that protects the ears, nose, throat and the gastrointestinal tract, is found in largest amount.
Question
The cell-mediated immunity inside the human body is carried out by [NEET 2013]
(a) T-lymphocytes
(b) B-lymphocytes
(c) thrombocytes
(d) erythrocytes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
T-lymphocyte receptors can recognise only antigen that bound to cell membrane proteins. These lymphocytes mediate CMI (Cell Mediated Immunity).
B-lymphocytes are the major effector molecules of humoral immunity. Erythrocytes are red blood cells. Thrombocytes or platelets secrete factors that are involved in vascular repair.
Question
Which one the following statements is correct with respect to immunity? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) Preformed antibodies need to be injected to treat the bite by a viper snake
(b) The antibodies against smallpox pathogen are produced by T-lymphocytes
(c) Antibodies are protein molecules, each of which has four light chains
(d) Rejection of a kidney graft is the function of B-lymphocytes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In artificially acquired passive immunity, preformed antibody in an immune serum of some other animal is introduced into the body. As the antivenum used to treat snake bites. In this case, the body does not produce any antibodies. Antibody is a protein molecule having two light chain and two heavy chain. B-cells recognise and bind antigens and may differentiate to memory cell or plasma cells (produce antibody). T-cells causes transplant rejection.
Question
In which one of the following options the two examples are correctly matched with their particular type of immunity? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
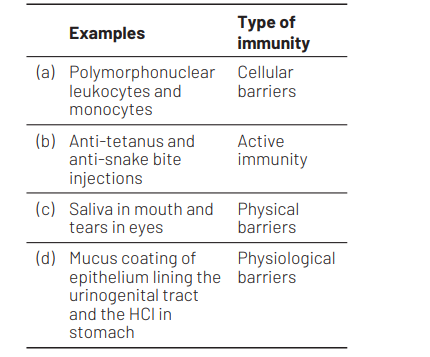
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Phagocytosis is an important feature of cellular innate immunity, performed by cells called phagocytes that engulf or eat pathogens or foreign particles. Common examples of these phagocytes are monocytes, macrophages, neutrophil granulocytes (often referred to as polymorphonuclear leukocytes or $\mathrm{PMN}$ or PML, because of the varying shapes of nucleus), tissue dendritic cells, mast cells etc. Anti-tetanus and anti snake bite injections are examples of passive immunity.
Question
Consider the following four statements (I-IV) regarding kidney transplant and select the two correct ones out of these.
l. Even if a kidney transplant is proper the recipient may need to take immuno-suppresants for a long time.
II. The cell-mediated immune response is responsible for the graft rejection.
III. The B-lymphocytes are responsible for rejection of the graft.
IV. The acceptance or rejection of a kidney transplant depends on specific interferons.
The two correct statements are [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) II and III
(b) III and IV
(c) I and III
(d) I and II
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Both statements I and II are correct.
Question
A person likely to develop tetanus is immunised by administering [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) dead germs
(b) preformed antibodies
(c) wide spectrum antibiotics
(d) weakened germs
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In passive immunity, the antibodies are produced in some other organisms (e.g. horse, rabbit, mouse) in response to the given antigen. These antibodies are then injected into the human body at the time of need. This is known as inoculation, e.g. persons infected by tetanus (Clostridium tetani), rabies virus and Salmonella the sufficient amount of antibodies, are given to enhance passive immunity at the time of need.
Question
Globulins contained in human blood plasma are primarily involved in [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) defence mechanisms of body
(b) osmotic balance of body fluids
(c) axygen transport in the blood
(d) clotting of blood
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Globulins are soluble in salt solutions of strong acids and bases and insoluble in pure water and moderately concentrated salt solutions. These are coagulated by heat. Globulins contained in human blood plasma are primarily involved in defense mechanisms of the body. Some examples are i.e. Rabies immune globulin, RhQ(D) immune globulin, specific immune globulin, tetanus immune globulin, etc.
Question
The letter $\mathrm{T}$ in $\mathrm{T}$-lymphocyte refers to [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) thyroid
(b) thalamus
(c) tonsil
(d) thymus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
T-refers to thymus which is haemopoietic as well as an endocrine gland. Thymus is the’seedbed of thymic lymphocytes (T-lymphocytes). Certain stem cells, originating in yolk sac and liver in early embryo, but only in bone marrow in late embryo, migrate into the thymus and proliferate to form a large number of lymphocytes.
Thyroid is an endocrine gland. Thalamus is the part of fore brain in vertebrate lies above the hypothalamus. Tonsil is a mass of lymphoid tissue, several of which are situated at the back of the mouth and throat in higher vertebrates.
Question
Use of anti-histamines and steroids give a quick relief from [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) allergy
(b) nausea
(c) cough
(d) headache
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Allergy is the hypersensitive reaction of a person to some foreign substances coming in contact with or entering the body. The common allergns are dust, pollen mould, spores, fabricates, bacteria, etc. During allergic reaction, there is increased release of histamine from mast cells. Use of anti-histamines and steroids give a quick relief from allergy.
Question
To which type of barriers under innate immunity, do the saliva in the mouth and the tears from the eyes, belong? [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) Cytokine barriers
(b) Cellular barriers
(c) Physiological barriers
(d) Physical barriers
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Innate immunity (inborn) is the resistance to infection, which an individual possesses by virtue of his/her genetic and constitutional make up. Thus it comprises all those defence elements with which an individual is born and, which are always available to protect a living body. Physiological barriers like body temperature, $\mathrm{pH}$ of the body fluid, and various body secretions (saliva, tears) prevent growth of many disease causing micro-organisms. Skin is the physical barrier of the body. Its outer tough layer the stratum corneum prevents the entry of bacteria and viruses.
Question
If you suspect major deficiency of antibodies in a person, to which of the following would you look for confirmatory evidence? [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) Serum albumins
(b) Serum globulins
(c) Fibrinogen in plasma
(d) Haemocytes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Antibodies also called immunoglobulins constitute the gamma globulin which are the part of blood proteins. These are secreted by activated B-cells of plasma cells.
Question
Increased asthmatic attacks in certain seasons are related to [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) hot and humid environment
(b) eating fruits preserved in tin containers
(c) inhalation of seasonal pollen
(d) low temperature
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Asthma is a respiratory disorder. It is caused by foreign allergens and dust particles present in the air passing through the respiratory system, the pollen grains present in air can cause asthmatic attacks in certain seasons as are produced in large number in that particular seasons.
Question
What is true about T-lymphocytes in mammals? [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) They scavenge damaged cells and cellular debris
(b) These are produced in thyroid
(c) There are three main types-cytotoxic T-cells, helper T-cells and suppressor T-cells
(d) These originate in lymphoid tissues
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The function of T-cells is to provide immunity (cellular type) and not to scavenge damaged cells and cell debris. These are produced in bone marrow and get matured in thymus gland. Hence, the only true statement is that there are three types of T-cells, i.e.cytotoxic, helper and suppressor.
Question
The term ‘antibiotic’ was coined by [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) Selman Waksman
(b) Alexander Fleming
(c) Edward Jenner
(d) Louis Pasteur
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The term ‘antibiotics’ was first time used by SA Waksman in 1945. Antibiotics are the substances which are produced by microorganisms such as fungi or bacteria. These substances are harmful to the growth of other microorganisms, example of some of the antibiotics are penicillin, streptomycin. chloramphenicol, etc.
Question
Interferons are synthesised in response to [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) Mycoplasma
(b) bacteria
(c) viruses
(d) fungi
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Cells infected by virus produce interferons (an antiviral protein) which is antiviral. It spreads to neighbouring cells and makes them resistant to virus infections by inhibiting viral growth.
Question
Small proteins produced by vertebrate cells naturally in response to viral infections and which inhibit mutliplication of viruses are called [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) immunoglobulins
(b) interferons
(c) antitoxins
(d) lipoproteins
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Interferons (INFs) are a group of three vertebrate glycoproteins $(\alpha, \beta, \gamma)$.0ut of these, two $(\alpha$ and $\beta)$ are produced within viral infected cells. Interferon induces, among adjacent cells, as antiviral state by inducing synthesis of the enzymes which inhibit the viral production cycle. Thus, inhibiting multiplication of virus in the body.
Question
If a person shows production of interferons in his body, the chances are that he has got an infection of [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) typhoid
(b) measles
(c) tetanus
(d) malaria
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Interferons are proteins produced by a cell infected by a virus and provide protection to other healthy cells against infection by viruses. Measles is also viral disease. It is caused by paramyxo virus (RNA virus). Interferon was discovered in 1957 by Issacs and Lindenmann. Typhoid and tetanus are bacterial diseases and malaria is a protozoan disease.
Question
Passive immunity was discovered by [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) Edward Jenner
(b) Emil von Behring
(c) Robert Koch
(d) Louis Pasteur
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Passive immunity was first discovered by Edward Jenner against chickenpox. In passive immunity readymade antibodies ( $\gamma$-globulins) obtained from human or animal serum, who already had recovered from an infectious disease, are injected into human body to develop immunity. It is used against measeles, rubella, mumps, diphtheria, tetanus, snake venom, scarlet fever, rabies and Salmonella and many other bacterial infection.
Question
Hypersensitivity to an allergen is associated with [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a)aberrant functioning of the immune mechanism
(b) increase in ambient temperature
(c) age of the individual
(d) food habits
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Allergy is hypersensitivity or inappropriate over reaction or aberrant functioning of the immune system.
Question
Which of the following diseases is due to an allergic reaction? [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) Goitre
(b) Skin cancer
(c) Hay fever
(d) Enteric fever
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Allergy also known as hypersensitivity, is an inappropriate over-reaction of the immune system. Hay fever is an allergic reaction, antigens for such response are pollens grains, dust and SPM in the polluted air.Symptoms of hay fever includes closure of bronchial tubes that results in difficulty in normal breathing, skin rashes and eosinophilia.
Question
Cells involved in immune mechanism are [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) erythrocytes
(b) lymphocytes
(c) eosinophils
(d) thrombocytes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Lymphocytes are agranulocytes and they play a key role in immunological reactions. Lymphocytes are of two types
(i) B-lymphocytes-function in the form of immunity called antibody mediated immunity (humoral immunity).
(ii) T-lymphocytes-function in cell-mediated immunity (cellular immunity).
Question
Small proteins produced by vertebrate cells naturally in response to viral infections and which inhibit multiplication of viruses are called [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) immunoglobulins
(b) interferons
(c) antitoxins
(d) lipoproteins
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
interferons (INFs) are a group of three vertebrate glycoproteins $(\alpha, \beta, \gamma)$. . Out of these, two $(\alpha$ and $\beta)$ are produced within virally infected cells. Interferon act as antiviral protein by inducing synthesis of the enzymes which inhibit the viral production cycle. So, interferons are inhibitors of virus particles.
Question
The antibodies are [CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) germs
(b) carbohydrates
(c) proteins
(d) lipids
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Antibodies are glycoproteins and are secreted by mature vertebrate plasma cells which are modified form of B-cells. These selectively bind to epitopes of antigens and clumping them (agglutination) prior to phagocytic engulfment.
Question
In mammals, histamine is secreted by [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) fibroblasts
(b) histocytes
(c) lymphocytes
(d) mast cells
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Histamine is a potent vasodilator formed by decarboxylation of the amino acid histidine and released by mast cells in response to appropriate antigens. Mast cells are especially prevalent in the connective tissue of the skin, respiratory tract and in surrounding blood vessels.
Question
Interferons are [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) antiviral proteins
(b) antibacterial proteins
(c)anticancer proteins
(d) complex proteins
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Interferons(IFNs)are anti-viral, regulatory glycoproteins, produced in virus infected cells for defence. They are non-antigenic protein of molecular weight 20000 daltons; discovered by Issacs and Lindemann (1957). These IFNs induce formation of certain enzymes that suppress viral multiplication in host cell and protect host from further viral reinfection.
