Question
Match the List-I with List-II.
Choose the correct answer from the options given below. [NEET 2021]
A B C D
(a) 4 3 2 1
(b) 1 4 3 2
(c) 3 4 1 2
(d) 2 3 4 1
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
(A)-(3), (B)-(4), (C)-(1), (D)-(2)
The inner membrane of mitochondria forms a number of infolding of the cristae These dramatically increases the surface area available for hosting the enzymes responsible for cellular respiration.
The lamellae, in chloroplast after separation from the inner membrane, usually take the form of closed, flattened, ovoid sacs, the thylakoids, which lie closely packed in piles, the grana.
Primary constriction in the chromosome forms the centromere. A cisternae are series of flattened, curved membrane saccules of the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus.
Question
Which of the following is an incorrect statement? [NEET 2021]
(a) Mature sieve tube elements possess a conspicuous nucleus and usual cytoplasmic organelles
(b) Microbodies are present both in plant and animal cells
(c) The perinuclear space forms a barrier between the materials present inside the nucleus and that of the cytoplasm
(d) Nuclear pores act as passages for proteins and RNA molecules in both directions between nucleus and cytoplasm
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Mature sieve tube elements contain structural phloem specific proteins (P-proteins) mitochondria, ER, and sieve elements plastids but not conspicuous nucleus.
Question
The organelles that are included in the endomembrane system are [NEET 2021]
(a) endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria, ribosomes and lysosomes
(b) endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi complex, lysosomes and vacuoles
(c) Golgi complex, mitochondria, ribosomes and lysosomes
(d) Golgi complex, endoplasmic reticulum, mitochondria and lysosomes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The endomembrane system is a group of membranes and organelles in eukaryotic cells that works together to modify, package and transport protein and lipids.
The endomembrane system include-Nuclear envelop
Endoplasmic reticulum
Golgi apparatus
Lysosomes
Vacuoles
Plasma membrane
Question
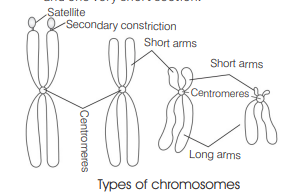
When the centromere is situated in the middle of two equal arms of chromosomes, the chromosome is referred as [NEET 2021]
(a)metacentric
(b) telocentric
(c) sub-metacentric
(d) acrocentric
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Metacentric chromosomes have the centromere in the center, such that both sections are of equal length, e.g. human chromosome 1 and 3 . Other options can be explained as :
Telocentric chromosomes have the centromere at the very end of the chromosome.
Sub-metacentric chromosomes have the centromere slightly offset from the center leading to a slight asymmetry in the length of the two sections.
Acrocentric chromosomes have centromere which is severely offset from the center leading to one very long and one very short section.
Question
Inclusion bodies of blue-green, purple and green photosynthetic bacteria are [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) contractile vacuoles
(b) gas vacuoles
(c) centrioles
(d) microtubules
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Gas vacuoles are the inclusion bodies in many aquatic prokaryotes like blue-green, purple and green photosynthetic bacteria. These are generally small, hollow cylindrical structure which facilitates air permeability. Gas vacuoles are membrane bound inclusion bodies that contain an array of substructures referred to as gas vesicles. The membrane of gas vacuoles is rigid, impermeable to water and freely permeable to all gases.
Question
The biosynthesis of ribosomal RNA occurs in [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a)ribosomes
(b)Golgi apparatus
(c)microbodies
(d) nucleolus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The biosynthesis of ribosomal RNA occurs in nucleolus of nucleus. It helps the nucleus of the cell to control cell metabolism and other activities. The other two types of RNA, i.e. mRNA and tRNA are also synthesised here.
Question
Match the following columns and select the correct option from the codes given below. [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
Codes
A B C D
(a) 2 1 3 4
(b) 3 1 2 4
(c) 4 2 1 3
(d) 1 2 3 4
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The option (a) is the correct match which is as follows Smooth Endoplasmic reticulum is the major site for synthesis of lipid. Rough Endoplasmic reticulum is actively involved in protein synthesis and secretion. Golgi complex is an important site of formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids, i.e. glycosylation. Centrioles help in spindle formation in the cell.
Question
Which of the following elements helps in maintaining the structure of ribosomes? [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) Magnesium
(b) Zinc
(c) Copper
(d) Molybdenum
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Each ribosome consist of two unequal subunits, a larger and a smaller one.
$\mathrm{Mg}^{2+}$ ions are required for binding the two subunits. Below $0.0001 \mathrm{M} \mathrm{Mg}^{2+}$, the two subunits dissociate while above this strength, the two subunits form the dimer.
Question
Which is the important site of formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids in eukaryotic cells? [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) Peroxisomes
(b) Golgi bodies
(c) Polysomes
(d) Endoplasmic reticulum
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Golgi bodies are site of formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids in eukaryotic cells. Glycoproteins are simply proteins with a sugar attached to them. The sugars can be attached to a protein in two locations in the cell, the endoplasmic reticulum, which produces $\mathrm{N}$-linked sugars, and the Golgi apparatus, which produces 0-linked sugars. Glycolipids are components of cellular membranes comprised of a hydrophobic lipid tail and one or more hydrophilic sugar groups linked by a glycosidic bond. Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane.
Question
Match the Column I with Column II. [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
Select the correct option from the following
1 2 3 4
(a) (iii) (iv) (ii) (i)
(b) (iv) (iii) (i) (ii)
(c) (iii) (ii) (iv) (i)
(d) (i) (ii) (iv) (iii)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The correct matches are
Golgi apparatus – Formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids
Lysosomes – Digesting biomolecules
Vacuoles – Trap waste and excretory products
Ribosomes – Synthesis of protein
Question
Which of the following cell organelles is present in the highest number in secretory cells? [NEET Odisha) 2019]
(a) Mitochondria
(b) Golgi complex
(c) Endoplasmic reticulum
(d) Lysosomes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Golgi complex (Golgi apparatus) is a cell organelle present in highest number in secretory cells. These are the site of modification, packaging and secretions of secretory proteins and glycoproteins outside the cell.
Question
Non-membranous nucleoplasmic structures in nucleus are the site for acitive synthesis of [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) protein synthesis
(b) mRNA
(c) rRNA
(d) tRNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Non-membranous nucleoplasmic structure in the nucleus of the cell are the site for active synthesis of rRNA. These structures are called nucleolus. Larger and more numerous nucleoli are present in the cell actively carrying out protein synthesis.
Question
Which of the following pairs of organelles does not contain DNA? [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) Chloroplast and Vacuoles
(b) Lysosomes and Vacuoles
(c) Nuclear envelope and Mitochondria
(d) Mitochondria and Lysosomes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Lysosomes and vacuoles do not contain DNA. Lysosomes are single membrane bound small vesicles which contain hydrolytic enzymes. Vacuoles are a large membranous sac found in the cytoplasm. These contain substances that are not essentially useful for the cell like water, sap, excretory products and other materials. Chloroplast and mitochondria are semi-autonomous organelles because they contain their own DNA and are believed to be prokaryotic symbionts.
Question
Which of the following statements is not correct? [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) The hydrolytic enzymes of lysosomes are active under acidic $\mathrm{pH}$
(b) Lysosomes are membrane bound structures
(c) Lysosomes are formed by the process of packaging in the endoplasmic reticulum
(d) Lysosomes have numerous hydrolytic enzymes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The statement “lysosomes are formed by the process of packaging in the endoplasmic reticulum” is incorrect. The correct form of the statement is lysosomes are actually formed by the budding off from the trans-face of Golgi bodies.
These membrane bound structures contain hydrolytic enzymes whose precursors are synthesised by rough endoplasmic reticulum. Rest statements are correct.
Question
The shorter and longer arms of a submetacentric chromosome are referred to as [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) p-arm and $q$-arm, respectively
(b) $q$-arm and $p$-arm, respectively
(c) $\mathrm{m}$-arm and $\mathrm{n}$-arm, respectively
(d) s-arm and l-arm, respectively
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The shorter and longer arms of submetacentric chromosome are designated as $p$ and $q$ arm, respectively. Here, ‘ $p$ ‘ signifies petite or short. In a submetacentric chromosome, centromere is located near the centre due to which the two arms appear unequal in length.
Question
Which of the following statements regarding mitochondria is incorrect? [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) Enzymes of electron transport are embedded in outer membrane
(b) Inner membrane is convoluted with infoldings
(c) Mitochondrial matrix contains single circular DNA molecule and ribosomes
(d) Outer membrane is permeable to monomers of carbohydrates, fats and proteins
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The statement “enzymes of electron transport are embedded in outer membrane” is incorrect. The correct form of statement is
Enzymes of electron transport are embedded in the inner membrane of mitochondria. An electron transport chain is a series of coenzymes and cytochromes that take part in the passage of electrons from a chemical to its ultimate acceptor. Rest statements are correct.
Question
The Golgi complex participates in [NEET 2018]
(a) respiration in bacteria
(b) formation of secretory vesicles
(c) fatty acid breakdown
(d) activation of amino acid
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Golgi complex participates in the formation of secretory vesicles. It is a cytoplasmic structure found in eukaryotic cells. It is made up of four parts; cisternae, tubules, vesicles and vacuoles.
The forming face or cisternae receives vesicles from endoplasmic reticulum. Their contents pass through various cisternae with the help of coated vesicles and intercisternal connectives. They ultimately reach the maturing face where they are budded off as, coated secretory or Golgian vesicles or vacuoles.
In bacteria, respiration occurs with the help of mesosomes. The breakdown of fatty acid occurs in peroxisomes and mitochondria. Activation of amino acid is an important step of protein synthesis and it occurs in cytoplasm. In this process, amino acids get attached to tRNA molecules.
Question
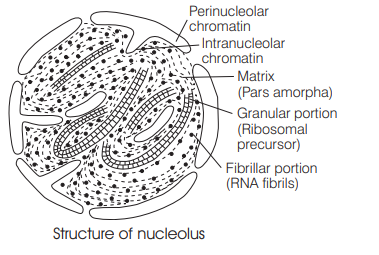
Which of the following is true for nucleolus? [NEET 2018]
(a) It takes part in spindle formation
(b) It is a membrane-bound structure
(c) Larger nucleoli are present in dividing cells
(d) It is a site for active ribosomal RNA synthesis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Nucleolus is a naked, round or slightly irregular structure in nucleus. It lacks a membrane and its contents are in direct. contact with the nucleoplasm. It is a site for active ribosomal RNA (rRNA) synthesis. Microtubules take part in the spindle formation. Mitochondria, vacuoles and plastids, etc. are membrane-bound structures. The dividing cells possess a large number of mitochondria.
Question
Nissl bodies are mainly composed of [NEET 2018]
(a) nucleic acids and SER
(b) DNA and RNA
(c) proteins and lipids
(d) free ribosomes and RER
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Nissl granules are found in the cell-body of neurons. These granules are composed of Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum(RER) that bears free ribosomes. The latter acts as the site of protein synthesis. These granules were named after its discoverer Franz Nissl.
Question
Select the incorrect match. [NEET 2018]
(a) Submetacentric – L-shaped chromosomes chromosomes
(b) Allosomes – Sex chromosomes
(c) Lampbrush – Diplotene chromosomes bivalents
(d) Polytene – Oocytes of chromosomes amphibians
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Polytene chromosomes are giant chromosomes that are quite common in the salivary glands of insects therefore they are popularly called as salivary chromosomes.
The Lampbrush chromosomes are highly elongated special kind of synapsed mid-prophase or diplotene chromosome that are bivalents. Sex chromosomes are also called as allosomes. They determine the sex of an organism. Submetacentric chromosomes have a submedian centromere. They appear L-shaped during metaphase. Therefore, except option (d), all are correctly matched.
Question
Which one of the following events does not occur in rough endoplasmic reticulum? [NEET 2018]
(a) Cleavage of signal peptide
(b) Protein glycosylation
(c) Protein folding
(d) Phospholipid synthesis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Phospholipid synthesis does not occur in RER. It occurs inside Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER). A signal peptide is a short peptide present at the $\mathrm{N}$-terminus of the newly synthesised proteins. It targets them to the ER and is then cleaved off. RER synthesises proteins. It bears enzymes for modifying polypeptides synthesised by attached ribosomes, e.g. glycosylation.
Question
Many ribosomes may associate with a single mRNA to form multiple copies of a polypeptide simultaneously. Such strings of ribosomes are termed as [NEET 2018]
(a) plastidome
(b) polyhedral bodies
(c) polysome
(d) nucleosome
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Polysome is a string of ribosomes associated with a single mRNA.
Polysome helps to produce a number of copies of the same polypeptide.
Nucleosome is the unit of eukaryotic DNA that consists of a DNA segment wrapped around a core of eight histone proteins. Nucleosome chain gives a ‘beads on string’ appearance under electron microscope. Plastidome refer to all the plastids of a cell which work as a functional unit.
Question
Which of the following cell organelles is responsible for extracting energy from carbohydrates to form ATP? [NEET 2017]
(a) Lysosome
(b) Ribosome
(c) Chloroplast
(d) Mitochondrion
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Mitochondria is referred as ‘power house of the cell’. It contains the enzymes for cellular respiration. It oxidises carbohydrate to produce ATP molecules in the process of aerobic respiration. Thinking process Mictochondria is a double membrane bound semi-autonomous cell organelles. The number of mitochondria per cell is more in metabolically active cells.
Question
Water soluble pigments found in plant cell vacuoles are [NEET 2016, Phase 1]
(a) chlorophylls
(b) carotenoids
(c) anthocyanins
(d) xanthophylls
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Anthocyanins are water soluble vacuolar pigments that may appear red, purple or blue depending on $\mathrm{pH}$. It is impermeable to cell membranes of plants and can leak out only when membrane is damaged or dead.
Question
Which one of the following cell organelles is enclosed by a single membrane? [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) Chloroplasts
(b) Lysosomes
(c) Nuclei
(d) Mitochondria
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Nuclei, mitochondria and chloroplasts are all double membrane bound organelles. Lysosomes are single membrane bound organelle.
Question
Mitochondria and chloroplast are
I. semi-autonomous organelles.
II. formed by division of pre-existing organelles and they contain DNA but lack protein synthesising machinery. Which one of the following options is correct? [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) Il is true, but $\mathrm{I}$ is false
(b) I is true, but II is false
(c) Both I and II are false
(d) Both $\mathrm{I}$ and II are true
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Mitochondria and chloroplast are semi-autonomous organelles which contains DNA, ribosomes (70S) etc. They are capable of self-replication so called semi-autonomous.
Question
Microtubules are the constituents of [NEET 2016, Phase 1]
(a) spindle fibres, centrioles and cilia
(b) centrioles, spindle fibres and chromatin
(c) centrosome, nucleosome and centrioles
(d) cilia, flagella and peroxisomes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Microtubules are structures present in cilia, flagella, centrioles and spindle fibres. They are also the part of fibres found in cytoskeleton.
Question
A cell organelle containing hydrolytic enzyme is [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) Iysosome
(b) microsome
(c) ribosome
(d) mesosome
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Lysosomes are membrane bound cell organelles. These contain many hydrolytic enzymes which work at high $\mathrm{pH}$. They bring about the intracellular digestion of cell debris and worn and torned cell organelles. These loose their existence while doing so, that is why they are also called as suicidal bags.
Question
Select the mismatch. [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) Gas vacuoles – Green bacteria cells
(b) Large central vacuoles – Animal cells
(c) Protists – Eukaryotes
(d) Methanogens – Prokaryotes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Animal cells do not have large central vacuole. Instead, these have 2-3 small vacuoles. The presence of such large central vacuoles is the characteristics feature of plant cells.
Concept Enhancer The presence of large vacuole is an indication of irregular growth, i.e. growth in cell membrane is synchronised with growth in protoplasmic content.
Question
Match the columns and identify the correct option. [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
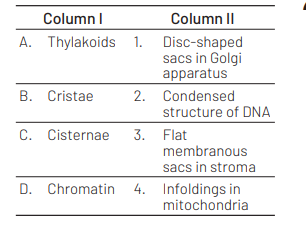
Codes
A B C D
(a) 4 3 1 2
(b) 3 4 1 2
(c) 3 1 4 2
(d) 3 4 2 1
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The columns can be matched correctly as follows
Question
Balbiani rings are sites of [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) lipid synthesis
(b) nucleotide synthesis
(c) polysaccharide synthesis
(d) RNA and protein synthesis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
A Balbiani ring is a large chromosome puff. Balbiani rings are diffused uncoiled regions of the polytene chromosome that are sites of RNA transcription and protein synthesis.
Question
Which of the following are not membrane bound? [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) Vacuoles
(b) Ribosomes
(c) Lysosomes
(d) Mesosomes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Ribosomes are non-membranous particles these are simple aggregations of RNA (rRNA) and proteins.
Question
Cellular organelles with membranes are [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) nuclei, ribosomes and mitochondria
(b) chromosomes, ribosomes and endoplasmic reticulum
(c) endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes and nuclei
(d) Iysosomes, Golgi apparatus and mitochondria
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Membrane bound organelles include lysosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, vacuoles, nucleus.
Non-membrane bound organelles include ribosomes, centrioles, microtubules.
Question
The solid linear cytoskeletal elements having a diameter of 6 nm and made up of a single type of monomer are known as [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) microtubules
(b) microfilaments
(c) intermediate filaments
(d) lamins
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Microfilaments (actin filament) are the thinnest filaments of the cytoskeleton. They are found in the cytoplasm of the eukaryotic cells.
They constitute the cytoskeleton through which the cells acquire shape their diameter is approximately $6 \mathrm{~nm}$ (avg.) These are the polymer of actin sub-units.
Question
The osmotic expansion of a cell kept in water is chiefly regulated by [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) mitochondria
(b) vacuoles
(c)plastids
(d) ribosomes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The osmotic expansion of a cell kept in water is chiefly regulated by vacuole. It is the single and large organelle which constitutes about $20 \%$ of plant cells and is small and multiple in animal cells. Vacuole store water and macromolecules including ions, sugar, amino acid, protein and carbohydrates. The membrane that surrounds the vacuole is called tonoplast. The vacuole contains cell sap in it. The cell sap has high osmotic pressure which regulate turgor pressure in plant cells.
Question
Match the following and select the correct answer. [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
Codes
A B C D
(a) $4 \quad 2 \quad 1 \quad 3$
(b) $1 \quad 2 \quad 4 \quad 3$
(c) $1 \quad 3 \quad 2 \quad 4$
(d) $4 \quad 3 \quad 1 \quad 2$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
(a) Centriole In organism with flagella and cilia, the position of these organelles is determined by the mother centriole which become the basal body.
(b) Chlorophyll Chlorophyll molecules are specially arranged in and around photosystem that are embedded in the thylakoid membrane of chloroplast.
(c) Cristae These are folds in the inner membrane of mitochondria which provides a large amount of surface area for chemical reaction.
(d) Ribozymes(Ribonucleic acid enzyme) is an RNA molecule that is capable of catalysing specific biochemical reactions of nucleic acids
Question
Which one of the following organelles in the figure correctly matches with its function? [NEET 2013]
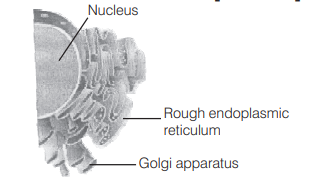
(a) Rough endoplasmic reticulum, formation of glycoproteins
(b) Golgi apparatus, protein synthesis
(c) Golgi apparatus, formation of glycolipids
(d) Rough endoplasmic reticulum, protein synthesis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)Protein synthesis
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)Lipid synthesis.
Golgi apparatus – Important site of formation glycoproteins and glycolipids.
Question
A major site for synthesis of lipids is [NEET 2013]
(a) RER
(b) SER
(c) symplast
(d) nucleoplasm
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER) is the major site for synthesis of lipids. RER is actively involved in protein synthesis and secretion. Nucleoplasm is the site for active ribosomal RNA synthesis. Symplast is the system of interconnected protoplast through which water movement occurs.
Question
The Golgi complex plays a major role [NEET 2013]
(a) in trapping the light and transforming it into chemical energy
(b) in digesting proteins and carbohydrates
(c) as energy transferring organelles
(d) in post translational modification of proteins and glycosidation of lipids
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Golgi complex plays a major role in post translational modification of proteins and glycosidation of lipids.
Chloroplasts contain chlorophyll which traps light and transform into chemical energy. Lysosomes are involved in digesting proteins, fats and carbohydrates. Mitochondria are energy transferring organelles.
Question
Ribosomal RNA is actively synthesised in [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) lysosomes
(b) nucleolus
(c) nucleoplasm
(d) ribosomes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In eukaryotes, the site of synthesis of most of the ribosomal RNA (rRNA) is nucleolus. The nucleolar organiser contains many copies of ribosomal DNA (repetitive DNA). The RNA cistron of nucleolar DNA forms $45 \mathrm{~S}$ precursor with the help of RNA polymerase. This 45S RNA undergoes cleavage with the help of nucleases to give 18S, 28 and 5.8S $r$ RNA units. Out of different rRNAs, the $5 S \mathrm{rRNA}$ is not synthesised in nucleolus. It is synthesised outside it.
Question
What is true about ribosomes? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) The prokaryotic ribosomes are 80 S, where S stands for sedimentation coefficient
(b) These are composed of ribonucleic acid and proteins
(c) These are found only in eukaryotic cells
(d) These are self-splicing introns of some RNAs
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Ribosomes are large, non-membranous, RNA protein complexes which are necessary for protein synthesis. In prokaryotes, $70 S$ type of ribosomes are found while $80 \mathrm{~S}$ type of ribosomes are found in eukaryotes.
Question
Important site for formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids is [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) Golgi apparatus
(b) plastid
(c) lysosome
(d) vacuole
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The Golgi apparatus principally performs the function of packaging materials. Golgi apparatus is the main site of formation of glycoproteins and glycolipids.
Question
Peptide synthesis inside a cell takes place in [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) mitochondria
(b) chromoplast
(c) ribosomes
(d) chloroplast
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The cellular factory responsible for synthesising proteins (peptide synthesis) is the ribosome.
Question
Which one of the following has its own DNA? [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) Mitochondria
(b) Dictyosome
(c) Lysosome
(d) Peroxisome
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In mitochondria, the inner membrane space is filled with a matrix which contains dense granules along with ribosomes and mitochondrial DNA. The mitochondrial DNA is circular in nature. Their number varies from 2-6. Besides DNA, a mitochondrion has RNA and its ribosomes (70S) also.
Thus, a complete protein synthesising machinery is present in mitochondria, so mitochondria is semi autonomous organelle in nature. Dictyosome, lysosome and peroxisome do not have their own DNA.
Question
Cytoskeleton is made up of [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) calcium carbonate granules
(b) callose deposits
(c) cellulosic microfibrils
(d) pruteinaceuus filaments
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The cytoplasm of all eukaryotic cells is criss-crossed by a network of protein fibres that support the shape of the cell and here organelles are anchored at fixed locations. It is a dynamic system which includes three types proteinaceous filaments-actin filaments, microtubule and intermediate filament.
Question
The two sub units of ribosome remain united at a critical ion level of [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) copper
(b) manganese
(c) magnesium
(d) calcium
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Magnesium is constituent of chlorophyll, middle lamella, and connected with phosphate transfer in respiration. It is concerned with binding of ribosomes, DNA and RNA synthesis.
Manganese activates enzymes of respiration, photosynthesis and nitrogen metabolism performing oxidation, reduction, decarboxylation, photolysis of water, etc.
Copper is activator of plastocyanin, cytochrome oxidase, RuBP carboxylase and many other enzymes. It functions in electron transfer, maintenance of carbohydrate/nitrogen balance, chlorophyll synthesis, etc.
Calcium is constituent of middle lamella, activator of enzymes connected with chromosome formation and many aspects of metabolism.
Question
Vacuole in a plant cell [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) is membrane-bound and contains storage proteins and lipids
(b) is membrane-bound and contains water and excretory substances
(c) lacks membrane and contains air
(d) lacks membrane and contains water and excretory substances
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The vacuoles of plant cells are bounded by a single semipermeable membrane known as tonoplast. These vacuoles contain water, phenol, flavonols, anthocyanins, alkaloids and storage products such as sugars and proteins. The vacuoles of animal cells are bounded by a lipoproteinaceous membrane and their function is storage, transmission of materials and maintenance of internal pressure of cell.
Question
In germinating seeds, fatty acids are degraded exclusively in the [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) proplastids
(b) glyoxysomes
(c) peroxisomes
(d) mitochondria
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Glyoxysomes are found to occur in the cells of yeast, Neurospora and oil rich seeds of many higher plants. During germination of oily seeds, the stored lipid molecules of glyoxysomes are hydrolysed by the enzyme lipase to glycerol and fatty acids. The long chain fatty acids are then broken down by successive removal of two carbon fragments in the process of $\beta$-oxidation.
Peroxisomes are present in all photosynthetic cells of higher plants in etiolated leaf tissue. It is the site of hydrogen peroxide metabolism and glycolate cycle.
Mitochondria is the site of aerobic respiration in eukaryotic cell. It is called power house of the cell.
Question
Select the wrong statement from the following [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) Both chloroplasts and mitochondria contain an inner and an outer membrane
(b) Both chloroplasts and mitochondria have an internal compartment, the thylakoid space bounded by the thylakoid membrane
(c) Both chloroplasts and mitochondria contain DNA
(d) The chloroplasts are generally much larger than mitochondria
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Thylakoid space which is known as lumen is present only in chloroplasts. The inner membrane of mitochondria is folded to form cristae.
Question
Which of the following statements regarding mitochondrial membrane is not correct? [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) The enzymes of the electron transfer chain are embedded in the outer membrane
(b) The inner membrane is highly convoluted forming a series of infoldings
(c) The outer membrane resembles a sieve
(d) The outer membrane is permeable to all kinds of molecules
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In mitochondria, the enzymes of electron transport chain are found in the inner membrane while outer membrane contains enzymes involved in mitochondrial lipid synthesis and those enzymes that convert lipid substrates into other forms that are subsequently metabolised in the matrix.
The outer membrane resembles a sieve that is permeable to all molecules of 10,000 daltons mole weight or less, including small proteins.
The inner membrane is impermeable and highly convoluted, forming a series of infoldings, known as cristae, in the matrix space.
Question
The main organelle involved in modification and routing of newly synthesised proteins to their destinations is [CBSE AIPMT 2005]
(a) chloroplast
(b) mitochondria
(c) lysosome
(d) endoplasmic reticulum
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Porter coined the name Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER). It is a network of tubules, vesicles and cisternae within an eukaryotic cell (absent in prokaryotic cells). Two types of ER are recognised on the basis of presence/absence of ribosomes on the wall of the ER.
(i) Smooth ER It does not have ribosomes. Smooth ER helps in the synthesis of lipid and glycogen.
(ii) Rough ER Wall of this ER contains ribosomes. Rough ER is involved in protein synthesis and transfer. Protein synthesis takes place in ribosomes attached on wall of ER.
Newly formed protein enters within the cavity of rough ER and follows following path :
Protein $\rightarrow$ Cavity of rough
$\mathrm{ER} \rightarrow$ Cavity of smooth ER $\rightarrow$ Golgi membrane $\rightarrow$ Lysosomes or transport vesicles or secretory granules.
Question
Protein synthesis in an animal cell occurs [CBSE AIPMT 2005, 2000]
(a) only on the ribosomes present in cytosol
(b) only on ribosomes attached to the nuclear envelope and endoplasmic reticulum
(c) on ribosomes present in the nucleolus as well as in cytoplasm
(d) on ribosomes present in cytoplasm as well as in mitochondria
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Protein synthesis is taken place on ribosomes. In an eukaryotic cell ribosomes are present in cytoplasm, mitochondria and chloroplasts. So, in these places protein synthesis also takes place.
Question
Chlorophyll in chloroplast is located in [CBSE AIPMT 2005]
(a) grana
(b) pyrenoid
(c) stroma
(d) Both (a) and (c)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Chlorophyll is a specialised light absorbing pigment which is found in the inner wall of granum. Each granum is a flat, sac-like structure in which light reaction of photosynthesis takes place.
Question
Extra nuclear inheritance is a consequence of presence of genes in [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) mitochondria and chloroplasts
(b) endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria
(c) ribosomes and chloroplast
(d) lysosomes and ribosomes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Extra nuclear or extra chromosomal or cytoplasmic or organellar inheritance is a consequence of presence of genes in mitochondria and chloroplast. Extra chromosomal units function either independently or in collaboration with nuclear genetic system.
Question
In chloroplasts, chlorophyll is present in the [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) outer membrane
(b) inner membrane
(c) thylakoids
(d) stroma
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The thylakoids of chloroplast are flattened vesicles arranged as a membranous network within the stroma. $50 \%$ of chloroplast proteins and various components involved (namely chlorophyll, carotenoids and plastoquinone)are present in thylakoid membranes that are involved in photosynthesis.
Question
Flagella of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) type of movement and placement in cell
(b) location in cell and mode of functioning
(c) microtubular organisation and type of movement
(d) microtubular organisation and function
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Flagella of prokaryotic and eukaryotic species differ in microtubular organisation and type of movement. In eukaryotes the arrangement is $(9+2)$ and specialised while in prokaryotes arrangement is $(9+0)$ and is simple.
Question
Ribosomes are produced in [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) nucleolus
(b) cytoplasm
(c) mitochondria
(d) Golgi body
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The proteins required for the formation of ribosome are synthesised within the cytoplasm through the process of translation.
These proteins are later shifted to nucleus and then to nucleolus where the RNA and proteins are assembled into ribosomal sub-units. In prokaryotes (bacteria) ribosomes are synthesised in cytoplasm. In eukaryotes, the process takes place both in the cell cytoplasm and in the nucleolus which is a region within the cell nucleus.
Question
Microtubules are absent in [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) mitochondria
(b) centriole
(c) flagella
(d) spindle fibres
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Microtubules are present only in eukaryotes; and are component of cilia and flagella as well as spindle (during cell division). They are straight, hollow rods measuring about $25 \mathrm{~nm}$ in diameter and $200 \mathrm{~nm}$ to $25 \mu \mathrm{m}$ in length. Microtubules give shape and support to the cell.
Question
Lysosomes are reservoirs of [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) RNA and protein
(b) fats
(c) secretory glycoproteins
(d) hydrolytic enzymes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Lysosomes were discovered by Christian de Duve (1955) from rat liver. Matile (1964) discovered lysosomes in plants. Generally, Iysosomes are 0.2-0.8 $\mu$ in size, irregular membranous vesicles filled with hydrolytic enzymes. They are polymorphic. About 40 enzymes (all hydrolytic)are present in lysosomes. These include proteases, nucleases, glycosidases, lipases, phospholipases,
phosphatases and sulphatases.
Question
The cell organelle involved in glycosylation of protein is [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) ribosome
(b) peroxisome
(c) endoplasmic reticulum
(d) mitochondria
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The proteins synthesised by the ribosomes bound to ER are passed into the lumen of $E R$ where an oligosaccharide is added to them, (i.e. these are glycosylated).
Question
Some of the enzymes which are associated in converting fats into carbohydrates, are present in [CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) liposomes
(b) Golgi bodies
(c) microsomes
(d) glyoxysomes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Besides catalase, the glyoxysomes contain enzymes for the glyoxylate cycle through which fats are converted into carbohydrates. Microsomes are product of homogenisation of $E R$.
Liposomes are artificially produced lipid bilayers, $25 \mathrm{~nm}$ or more in diameter. Golgi body is a dynamic eukaryotic organalle, consisted of cisternae, vesicles and tubules.
Question
The proteins are synthesised at [CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) ribosomes
(b) mitochondria
(c) centrosomes
(d) Golgi bodies
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
During protein synthesis, smaller sub-units of ribosomes attach to mRNA. The ribosomes provide space as well as enzyme for the synthesis of proteins. Therefore, these are known as protein factories or workbenches of protein.
Question
Which of the following organ has single membrane? [CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) Nucleus
(b) Cell wall
(c) Mitochondria
(d) Spherosomes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Cell wall does not have a membrane. The mitochondria and nucleus are surrounded by double membraned envelope. Spherosomes are single membrane bound, spherical structures in plant cell cytoplasm. These are apparently centres of lipid synthesis and accumulation.
Question
Microtubule is involved in the [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) cell division
(b) membrane architecture
(c) muscle contraction
(d) DNA recognition
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Microtubules are one of the essential protein filaments of the cytoskeletons of probably all eukaryotic cells and their cilia, flagella, basal bodies, centrioles and mitosis and meiosis spindles. Each microtubule is made up of a hollow cylinder of 13 protofilaments of the tubulin protein. The diameter of each microfibril is $25 \mathrm{~nm}$. The function of microtubule is to guide organelle and chromosome movement in the cell, cause cell elongation and help in movements of cilia/flagella.
Question
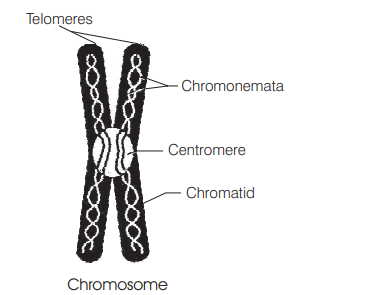
Centromere is a part of [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) ribosomes
(b) chromosome
(c) mitochondria
(d) endoplasmic reticulum
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In every chromosome, there is a small region called primary constriction in which there is a centromere where two sister chromatids are held together and spindle fibres get attached during cell dizvision.
Question
The mechanism of ATP formation both in chloroplast and mitochondria is explained by [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) Relay Pump Theory of Godlewski
(b) Cholodny-Went’s Model
(c) Chemiosmotic Theory
(d) Munch’s Mass Flow Hypothesis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
As per Peter Mitchell’s chemiosmoticcoupling hypothesis, outward pumping of protons across the inner chloroplast or mitochondrial membrane results in accumulation of protons between outer membrane and inner membrane. A proton gradient is thus established. As protons now flow back, passively down the gradient, the proton motive force is utilised to synthesise ATP.
Question
Protein synthesis in an animal cell takes place [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) only in cytoplasm
(b) in the nucleolus as well as in the cytoplasm
(c) in the cytoplasm as well as in mitochondria
(d) only on ribosomes attached to nucleus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Protein synthesis is a complex process, it essentially involves DNA for the synthesis of mRNA(transcription) which contains information for the synthesis of proteins(translation).
The process of translation takes place on ribosomes which are found in cytoplasm (in attached form on ER) and in mitochondria (in the free form).
Question
Genes located on mitochondrial DNA [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) generally show maternal inheritance
(b) are always inherited from the male parent
(c) show biparental inheritance like the nuclear genes
(d) are not inherited
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Mitochondria are found only in eukaryotic cells, they contain a single circular double stranded DNA molecule (mtDNA). Available evidences show that mitochondria of female parent are transferred to progeny during fertilisation. Recent studies have shown that factors responsible for cytoplasmic male sterility are located in mitochondrial DNA.
Question
Lysosomes have a high content of [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) hydrolytic enzymes
(b) lipoproteins
(c) polyribosomes
(d) DNA ligases
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Lysosomes or suicidal bags are filled with about 40 types of acid hydrolases (digestive enzymes) like acid proteases, acid nucleases, acid phosphatases, acid sulphatases, acid lipases, acid glycosidases working at an optimum $\mathrm{pH} \leq 5$ for controlling intracellular digestion of macromolecules.
Question
The function of rough endoplasmic reticulum is [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) fat synthesis
(b) lipid synthesis
(c) protein synthesis
(d) steroid synthesis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER) provides surface for ribosomes for synthesis of secretory (serum proteins), lysosomal and membrane proteins, glycoproteins and helps in packaging of polypeptide chains into enzymes/proteins. It also provides membrane to Golgi bodies for forming vesicles and lysosomes.
Question
The prokaryotic flagella possess [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) unit membrane enclosed fibre
(b) protein membrane enclosed fibre
(c) ‘ $9+2$ ‘ membrane enclosed structure
(d) helically arranged protein molecule
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Prokaryotic (bacterial) flagellum is made up of flagellin protein arranged helically. It do not show $9+2$ organisation and ATPase activity. These flagella do not beat but rotate like a propellar that brings about backward pushing of water. Gram +ve bacteria having two rings in the basal body. Gram-ve bacteria have four rings. The $L, P, M$ and $S$ rings.
Question
The desmosomes are concerned with [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) cytolysis
(b) cell division
(c) cell adherence
(d) cellular excretion
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Desmosomes (macula adherens) consists of intercellular thickening materials, disc-shaped intracellular thickening adjacent to each membrane with tonofibrils. These act as intercellular cementing material, adhere cells together at places like spot welding.
Question
Inner membrane convolutions of a mitochondrion are known as[CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) lamellae
(b) thylakoids
(c) grana
(d) cristae
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Mitochondrial inner membrane is convoluted several times to form cristae.
Question
Mitochondrial cristae are sites of [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) breakdown of macromolecules
(b) protein synthesis
(c) phosphorylation of flavoproteins
(d) oxidation-reduction reactions
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Mitochondrial cristae bear the functional unit, i.e. oxysomes, Fernandes and Moran particles $\left(F_0-F_1\right)$ particles or electron transport particle. Since, inner membrane is impermeable to ATP, thus ATP is synthesised on oxysomes having ATPase in $F_1$ (stalk) and proton channels on $F_0$ (base). ATPase helps in oxidative phosphorylation, synthesise ATP through electron transport system by undergoing oxidation reduction reactions.
Question
Organelle having flattened membrane bound cisternae and lying near the nucleus is [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) Golgi apparatus
(b) mitochondrion
(c) centriole
(d) nucleolus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Golgi body or dictyosome has a stack of single membrane bound cisternae with swollen ends, network of tubules and vesicles. Cisternae are parallel membrane lined narrow sacs which are interconnected. Golgi body has two faces- concave or distal or maturing $(M)$ face or trans face towards cell membrane and cis or convex or proximal or forming $(F)$ face towards rough $\mathrm{ER}$ and nuclear membrane. New cisternae are formed from SER and added from $F$-face.
Question
Cell organelles having hydrolases/digestive enzymes are [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) peroxisomes
(b) lysosomes
(c) ribosomes
(d) mesosomes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Lysosomes (or suicidal bags or cellular house keepers or scavenger of cell) are single membrane bound, spherical microbodies, filled with different types of acid hydrolases (digestive enzymes) working at $\mathrm{pH} \leq 5$ and can digest almost every type of organic matter except cellulose.
Primary lysosome (storage granules) unites with food vacuole (phagosome) forming secondary lysosomes (heterophagosomes or digestive vacuoles) which cause intracellular digestion (heterophagy).
Question
Organelle/organoid involved in genetic engineering is [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) plasmid
(b) mitochondrion
(c) Golgi apparatus
(d) lomasome
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Plasmids are small, self-replicating extra chromosomal, non-essential genetic/DNA elements. Plasmid consists of a ring of circular, supercoiled double stranded naked DNA carrying genes for replication and for one or more cellular non-essential functions.
They are ideal vectors for genetic engineering, gene cloning since, they are self-replicating, carry non-essential genes and has a restriction site for one or more restriction endonucleases.
Question
In plant cells, peroxisomes are associated with [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) photorespiration
(b) phototropism
(c) photoperiodism
(d) photosynthesis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Peroxisomes are microbodies arising from ER and containing enzymes for peroxide formation. In plants, they occur in green mesophyll cells of leaves of $\mathrm{C}_3$ plants and are involved in photorespiration through interacting with chloroplast and mitochondria. In animals, they are involved in lipid synthesis, purine catabolism, gluconeogenesis, etc.
Question
Membranous bag with hydrolytic enzymes which is used for controlling intracellular digestion of macromolecules is [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) endoplasmic reticulum
(b) nucleosome
(c) lysosome
(d) phagosome
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The intracellular digestion, i.e. the breakdown of substances within the cytoplasm of a cell is controlled by lysosomes. Intracellular digestion occurs in animals that lack a digestive track. e.g. in Pycnogonida, Mollusca, Cnidaria and Porifera.
Question
Golgi apparatus is absent in [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) higher plants
(b) yeast
(c) bacteria and blue-green algae
(d) None of the above
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Golgi bodies are absent in prokaryotic cells, (i.e. bacteria, cyanobacteria, mycoplasma), in mature RBC, mature sperms, mature eggs, sperms of bryophytes, pteridophytes and mature sieve tubes. In contrast, active eukaryotic cells are rich in Golgi bodies. Maximum number (25000) of Golgi bodies are found in rhizoidal cells of Chara.
Question
All plastids have similar structure because they can [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) store starch, lipids and proteins
(b) get transformed from one type to another
(c) perform same function
(d) be present together
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
All plastids are similar in structure because these are interconvertible and get transformed from one type to another. Leucoplasts are formed from proplastids and leucoplasts; chloroplasts can arise from pre-existing chloroplasts, proplastids and leucoplasts and chromoplasts can develop from proplastids, leucoplasts and chloroplasts.
Question
Oxysomes or $F_0-F_1$ particles occur on [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) thylakoids
(b) mitochondrial surface
(c) inner mitochondrial membrane
(d) chloroplast surface
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Oxysomes are the elementary particles or $F_0-F_1$ or Fernandes-Moran particle present on the inner membrane of mitochondria. They are about $10^4-10^5$ in number and has a base of $F_0$ sub-unit toward C-face $(11 \times 1.5 \mathrm{~nm})$, a stalk $(0.5-3.5 \mathrm{~nm})$ and a head or $F_1$ sub-unit (8.5-10 nm diameter) towards matrix or M-face.
Question
An outer covering membrane is absent over [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) nucleolus
(b) lysosome
(c) mitochondrion
(d) plastids
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Nucleolus was discovered by Fontana (1781) and named by Bowman (1840) is a naked roughly rounded darkly stained structure. It is attached to chromatin at specific spot called nucleolar organiser region or NOR. Nucleolus constitute $35 \%$ mass of nucleus and is the largest part of nucleus.
Question
Ribosomes are the centre for [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) respiration
(b) photosynthesis
(c) protein synthesis
(d) fat synthesis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Ribosomes are smallest, membraneless sub- microscopic organelles, called as protein factories. They act as a template, bringing together different components involved in the protein synthesis.
Question
Which one is apparato reticolare interno? [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) Golgi apparatus
(b) Endoplasmic reticulum
(c) Microfilaments
(d) Microtubules
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Golgi body (dictyosomes, lipochondria) is a stack of flattened membrane bound sac-like body. They form internal reticulare apparatus (apparato reticolare interno).
Question
128 Experiments on Acetabularia by Hammerling proved the role of [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) cytoplasm in controlling differentiation
(b) nucleus in heredity
(c) chromosomes in heredity
(d) nucleocytoplasmic ratio
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
J Hammerling (1953) carried the grafting experiments involving exchange of nucleus (located at the base) in Acetabularia. He proved the role of nucleus in heredity, growth, etc.
Question
Ribosomes were discovered by [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) Golgi
(b) Porter
(c) de Robertis
(d) Palade
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Ribosomes were first observed by Claude (1941), he called them as microsomes. Robinson and Brown (1950) noticed them in plant cells of bean roots and Palade (1955) detected them in animal cells and called these structures as ribosomes.
Question
Polyribosomes are aggregates of [CBSE AIPMT 1989]
(a) ribosomes and rRNA
(b) only rRNA
(c) peroxisomes
(d) several ribosomes held together by string of mRNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Polyribosomes or ergasomes are formed by the combination of 6-8 ribosomes attached on a single-strand of mRNA. MRNA brings about polymerisation of a specific protein molecule, with the help of ribosomes, from amino acid molecules found in the cytosol.
Question
Organelles can be separated from cell homogenate through [CBSE AIPMT 1989]
(a) chromatography
(b) X-rays diffraction
(c) differential centrifugation
(d) auto-radiography
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Differential centrifugation is the mechanical separation of individual sub-cellular components from homogenate in centrifuge at low speed. Depending upon the size, specific gravity, mass, density, different organelles are separated and settled at the bottom of the centrifuge tube at different centrifugal speeds. Ultracentrifuges have 50,000-1,00,000 rpm and are used for the separation of minute cell organelles and constitutents on the basis of different densities.
