Question
Which of the following is associated with decrease in cardiac output? [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) Sympathetic nerves
(b) Parasympathetic neural signals
(c) Pneumataxic centre
(d) Adrenal medullary hormones
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Parasympathetic neural signals (a component of autonomic nervous system] decreases the rate of heartbeat, speed of conduction of action potential and thereby the cardiac output.
Question
Which of the following statements is not correct? [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) An action potential in an axon does not move backward because the segment behind is in a refractory phase
(b) Depolarisation of hair cells of cochlea results in the opening of the mechanically gated potassium-ion channels
(c) Rods are very sensitive and contribute to daylight vision
(d) In the knee-jerk reflex, stimulus is the stretching of muscle and response is its contraction
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Option (c) is not correct because rods and cones are photoreceptor cells in our eyes. The rod cells contain a purple pigment rhodopsin that is useful in night vision or scotopic vision. Daylight (photopic) vision and colour vision are the functions of cones.
Question
Which part of the brain is responsible for thermoregulation? [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) Hypothalamus
(b) Corpus callosum
(c) Medulla oblongata
(d) Cerebrum
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Hypothalamus is the thermoregulatory centre in the brain and it maintains the constant body temperature of $37^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$. The hypothalamus contains a number of centres, which contral body temperature. Corpus callosum is the thick band of nerve fibres that divide the cerebrum into left and right hemispheres.
Medulla oblongata is the component of hindbrain. It receives and integrates signals from spinal cord and sends them to cerebellum. Cerebrum is the large part of the brain and consists of two hemispheres.
Question
Stimulation of a muscle fibre by a motor neuron occurs at [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) the neuromuscular junction
(b) the transverse tubules
(c) the myofibril
(d) the sarcoplasmic reticulum
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Stimulation of a muscle fibre by a motor neuron accurs at neuromuscular junction (the area of contact between a nerve and muscle fibre). It is also called motor-end plate. At neuromuscular junction a neuron activates a muscle to contract during the excitation contraction coupling of vertebrate skeletal muscles.
Question
Injury localised to the hypothalamus would most likely disrupt [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) short term memory
(b) co-ordination during locomotion
(c) executive function, such as decision making
(d) regulation of body temperature
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The hypothalamus performs many functions which are important for the survival and enjoyment of life. It serves as a link between ‘mind’ and ‘body’ and between the nervous and endocrine system. The hypothalamus is responsible for hormone production. The hormone produced by this area govern body temperature thirst hunger, sleep, circoction rhythm, mood sex drive etc. This area of the brain also controls the functioning of pituitary gland. Thus, if any injury localised to the hypothalamus it will disrupt the complete regulation of body temperature and other activities.
Question
A diagram showing axon terminal and synapse is given. Identify correctly at least two of A-D [NEET 2013]
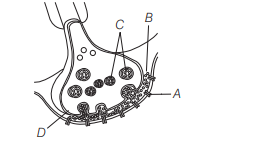
(a) A-Receptor, C-Synaptic vesicles
(b) B-Synaptic connection, D-K
(c) A-Neurotransmitter, B-Synaptic cleft
(d) C-Neurotransmitter, $\mathrm{D}-\mathrm{Ca}^{2+}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
A-Receptor, B-Synaptic cleft, C-Synaptic vesicles, $\mathrm{D}-\mathrm{Ca}^{2+}$.
Question
The human hindbrain comprises three parts, one of which is [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) spinal cord
(b) corpus callosum
(c) cerebellum
(d) hypothalamus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The hindbrain generally has its anterior roof enlarged to form a pair of cerebellar hemispheres. Its floor is thickened to form the pons anteriorly and the medulla oblongata posteriorly.
Question
The nerve centres which control the body temperature and the urge for eating are contained in [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) hypothalamus
(b) pons
(c) cerebellum
(d) thalamus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Hypothalamus is the part of the sides and floor of the brain derived from the forebrain. It lies at the base of thalamus. The hypothalamus contains a number of centres, which control body temperature, urge for eating and drinking. It also contains several groups of neurosecretory cells, which secrete hormones called as hypothalamic hormones.
Question
Which part of human brain is concerned with the regulation of body temperature? [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) Medulla oblongata
(b) Cerebellum
(c) Cerebrum
(d) Hypothalamus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
In human brain, hypothalamus is a centre for hunger, thirst, sweating, sleep, fatigue, temperature, anger, pleasure, love, hate and satisfaction. Medulla oblongata is the centre for heartbeat, respiration, digestion, blood pressure, involuntary functions, and urination etc. Cerebellum regulates posture and balance. Cerebrum is the centre for intelligence, emotion, will power, memory, consciousness, imagination, etc.
Question
Which one of the following statements is correct? [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) Neurons regulate endocrine activity, but not vice versa
(b) Endocrine glands regulate neural activity and nervous system regulates endocrine glands
(c) Neither hormones control neural activity nor the neurons control endocrine activity
(d) Endocrine glands regulate neural activity, but not vice versa
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The autonomous nervous system regulates the secretion of glands whereas, the glands do not regulate the nervous system.
Question
Which one of the following do not act as a neurotransmitter? [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) Acetylcholine
(b) Epinephrine
(c) Norepinephrine
(d) Cortisone
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Cortisone does not act as a neurtransmitter. Cortisone is a corticosteroid that is itself biologically inactive and is formed naturally in the adrenal gland (adrenal cortex) from the active hormone cortisol. Cortisol promotes the synthesis and storage of glucose and is important in the normal response to stress, suppresses inflammation and regulates deposition of fat in body.Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter secreted from the nerve endings. Epinephrine and norepinephrine are secreted from the medulla of adrenal gland and these also act as neurotransmitter.
Question
One of the examples of the action of the autonomous nervous system is [CBSE AIPMT 2005]
(a) knee-jerk response
(b) pupillary reflex
(c) swallowing of food
(d) peristalsis of the intestine
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Peristalsis of the intestine is related with autonomous nervous system whereas, knee-jerk response, pupillary reflex and swallowing of food are related to reflex action.
Question
Four healthy people in their twenties got involved in injuries resulting in damage and death of a few cells of the following. Which of the cells are least likely to be replaced by new cells? [CBSE AIPMT 2005]
(a) Osteocytes
(b) Malpighian layer of the skin
(c) Liver cells
(d) Neurons
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Neuron cells are least likely to be replaced by new cells. These cells are specilalised to conduct electrochemical current. Nerve cells do not have the capability of division as they are restricted at $\mathrm{G}_0$-phase of the cell cycle.
Question
In the resting state of the neural membrane, diffusion due to concentration gradients, if allowed, would drive [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) $\mathrm{K}^{+}$into the cell
(b) $\mathrm{K}^{+}$and $\mathrm{Na}^{+}$out of the cell
(c) $\mathrm{Na}^{+}$into the cell
(d) $\mathrm{Na}^{+}$out of the cell
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
In the resting nerve fibre, the cytoplasm inside the axon has a high concentration of $\mathrm{K}^{+}$and a low concentration of $\mathrm{Na}^{+}$in contrast to the fluid outside the axon. Thus, if diffusion occurs then through concentration gradient $\mathrm{Na}^*$ enters the fibre.
Question
What used to be described as Nissl’s granules in a nerve cell are now identified as [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) ribosomes
(b) mitochondria
(c) cell metabolites
(d) fat granules
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Main cell body of neuron is called as cyton or soma. It contains a large and centrally located nucleus, mitochondria, Golgi bodies, rough endoplasmic reticulum, lysosomes, fat globules. Besides these soma also contains Nissl’s granules or neurofibrils. These are masses of ribosomes and rough endoplasmic reticulum and are engaged in the process of protein synthesis.
Question
Which cells do not form layer and remain structurally separate? [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) Epithelial cells
(b) Muscle cells
(c) Nerve cells
(d) Gland cells
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Only nerve cells do not form layers, they also remain structurally separate from each other (though communicate with each other through synapse). Nerve cells or neurons are the cells specialised to conduct an electrochemical current, nerve tissue is made up of these cells and supporting cells.
Question
An action potential in the nerve fibre is produced when positive and negative charges on the outside and the inside of the axon membrane are reversed, because [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) more potassium ions enter the axon as compared to sodium ions leaving it
(b) more sodium ions enter the axon as compared to potassium ions leaving it
(c) all potassium ions leave the axon
(d) all sodium ions enter the axon
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
When a nerve fibre is stimulated, its membrane becomes more permeable to sodium ions. Hence, more sodium ions enter the axon than potassium ions leaving it. As a result, the positive and negative charges on the outside and inside of the membrane are reversed. The membrane with reversed polarity is called depolarised.
Question
Which cranial nerve has the highest number of branches? [CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) Facial nerve
(b) Trigeminal
(c) Vagus nerve
(d) None of these
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Vagus nerve has five branches
(a) Superior laryngeal nerve
(b) Recurrent laryngeal nerve
(c) Cardiac nerve
(d) Pneumogastric nerve
(e) Depresser nerve
Question
The Nissl’s granules of nerve cell are made up of [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) ribosomes
(b) protein
(c) DNA
(d) RNA
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Nissl’s granules (or Nissl’s bodies)are the groups of ribosomes and rough endoplasmic reticulum. These are actively involved in the synthesis of proteins.
Question
The roof of the cranium of frog is formed by [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) parasphenoid
(b) alisphenoid
(c) frontoparietal
(d) orbitosphenoid
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Dorsal part of the cranium is formed of two large and flat frontoparietals which are articulated together by a mid dorsal sagittal suture together and are collectively called frontoparietal. Endo-frontoparietal consists of a frontal bone (in front) and a parietal bone (behind). But now it has been proved that it is only the frontal bone, the parietals are not present in frog due to the absence of neck.
Question
The sympathetic nerves, in mammals arise from [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) sacral nerves
(b) cervical nerves
(c) thoraco-lumbar nerves
(d) III, VII, IX and X cranial nerves
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Sympathetic nerves arise from thoracic and lumbar spinal segments.
Question
Respiratory centre is situated in [CBSE AIPMT 1994, 99]
(a) cerebellum
(b) medulla oblongata
(c) hypothalamus
(d) cerebrum
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Normally, the breathing process (inspiration and expiration) is controlled involuntarily by a breathing centre located in the medulla oblongata. The ventral portion of the breathing centre (inspiratory centre) increases the rate and depth of inspiration while the dorsal and lateral portions of the centre (expiratory centre) inhibit inspiration and stimulate expiration.
Question
CNS is mostly made of [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) motor neurons and sensory neurons
(b) sensory neurons and association neurons
(c)association neurons
(d) motor neurons and association neurons
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Central nervous system is mostly made up of association neurons.
Question
Ivan Pavlov performed experiments on
(a) simple reflexes
(b) conditioned reflexes
(c) cardiac reflexes
(d) origin of life
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Conditional reflexes are those responses which can be initiated to a stimulus other than the one which normally initiates that response. Conditional reflexes were first demonstrated by a Russian physiologist 1 Pavlov (1929). He conducted ‘Bell experiment on dog’. He rang a bell every time he offered food to a dog. finally he noticed that merely ringing bell can substitute sight or smell of food to initiate salivation.
Question
Vagus nerve is [CBSE AIPMT 1992, 97]
(a) $X$
(b) IX
(c) VII
(d) $\mathrm{V}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Vagus nerve is Xth cranial nerve. It is mixed in nature having both sensory and motor fibres.
Question
Third ventricle of brain is also known as [CBSE AIPMT 1990]
(a) metacoel
(b) rhinocoel
(c) paracoel
(d) diacoel
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Inside diencephalon there is a narrow cavity called 3rd ventricle of brain or diacoel, which is connected anteriorly with lateral ventricles (also called paracoel) of cerebral hemisphere (called 1 st and 2 nd ventricle) by a common aperture called foramen of Monro. While it is connected posteriorly with 4 th ventricle of medulla oblongata through a narrow longitudinal canal called iter/aqueduct of Sylvius.
Question
Which of the following cranial nerves can regulate heartbeat? [CBSE AIPMT 1989]
(a) $X$
(b) IX
(c) VIII
(d) VII
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Xth cranial nerve is vagus or pneumogastric nerve which originates from lateral side of medulla oblongata behind IX cranial nerve. It is a mixed nerve, its sensory fibres innervate to receptor present in the wall of visceral organs. Whereas, its motor fibres innervates to muscles in the wall of visceral organs-like heart, alimentary canal, trachea, lungs, kidneys, genital tracts etc. It also regulates heartbeat.
