Question
During the process of gene amplification using PCR, if very high temperature is not maintained in the beginning, then which of the following steps of PCR will be affected first? [NEET 2021]
(a) Annealing
(b) Extension
(c) Denaturation
(d) Ligation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Denaturation is first step of PCR that involves seperation of double-stranded DNA. The DNA is subjected to heating at high temperature $\left(95^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\right.$. This leads to breaking of hydrogen bonds between nucleotides and formation of single-stranded DNA. Thus, if high temperature is not maintained, denaturation will be affected.
Annealing is second step of PCR which involves annealing of primer to DNA strands. In this step, DNA must be cooled to $50^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$.
Extension, is third step in which taq polymerase enzyme extends the primers thus, completing replication of rest of DNA. Ligation is the binding of amplified sequence of interest.
Question
Which of the following is not an application of PCR(Polymerase Chain Reaction)? [NEET 2021]
(a) Molecular diagnosis
(b) Gene amplification
(c) Purification of isolated protein
(d) Detection of gene mutation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Polymerase Chain Reaction or PCR, is a technique to make many copies of a specific DNA region in vitro lin a test tube rather than an organism). Following are the applications of PCR
The amplification of gene fragments (Gene amplification). The modification of DNA fragments. The sensitive detection of pathogenic microorganisms, if desired followed by an accurate genotyping. (Molecular diagnosis) DNA analysis of archaeological specimens. Proof-reading PCR(PR-PCR) is designed to detect known mutations within genomic DNA.
Question
During the purification process for recombinant DNA technology. addition of chilled ethanol precipitates out [NEET 2021]
(a) RNA
(b) DNA
(c) histones
(d) polysaccharides
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The role of chilled ethanol and monovalent cation is to remove the solvation (solvent interface of any chemical compound or biomolecule) shell surrounding the DNA and permitting the precipitation of the DNA in pellet form. Ethanol has a lower dielectric constant than water, making it to promote ionic bond formation the $\mathrm{Na}^{+}$(from the salt) and the $\mathrm{PO}_z^{-}$(from the DNA backbone), further, causing the DNA to precipitate.
Question
Which of the iollowing is a correct sequence of steps in a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)? [NEET 2021]
(a) Denaturation, Annealing, Extension
(b) Denaturation, Extension, Annealing
(c) Extension, Denaturation, Annealing
(d) Annealing, Denaturation, Extension
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
PCR stands for Polymerase Chain Reaction. It is a technique in which multiple copies of gene of interest is synthesised using two sets of primers and the enzyme DNA polymerase. The correct sequence of steps in a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) are Denaturation In which the double-stranded template DNA is heated at $95^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ to separate it into two single strands.
Annealing In which the temperature is lowered to $50^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ which enables the DNA primers to attach to the template DNA. Extension/Extending In which the temperature is raised and the new strand of DNA is made by the taq polymerase enzyme. These three stages are repeated $20-40$ times, doubling the number of DNA copies each time.
Question
Select the correct statement from the following. [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) Gel electrophoresis is used for amplification of a DNA segment
(b) The polymerase enzyme joins the gene of interest and the vector DNA
(c) Restriction enzyme digestions are performed by incubating purified DNA molecules with the restriction enzymes of optimum conditions
(d) PCR is used for isolation and separation of gene of interest
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Statement in option (c) is correct as restriction enzyme digestions are performed by incubating purified DNA molecules with the restriction enzymes of optimum conditions. Other statements are incorrect and can be corrected as Gel eletrophoresis is used for separation and isolation of DNA fragments. The polymerase enzyme uses DNA templates to catalyse polymerisation of deoxynucleotides. PCR is Polymerase Chain Reaction, it is used for amplification of a DNA segment.
Question
In a mixture, DNA fragments are separated by [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) bioprocess engineering
(b) restriction digestion
(c) electrophoresis
(d) polymerase chain reaction
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Electrophoresis is a technique used for the separation of substances of different ionic properties. It is used in RDT to separate the DNA fragments that are being cut by restriction endonuclease. In this technique, DNA fragments are loaded on agarose gel and then electric field is applied. Due to negatively charged, DNA fragments move towards anodes (+ ve charge). The smaller fragments move farther away as compared to larger fragments and thus, these get separated.
Question
In recombinant DNA technology antibiotics are used [NEET Oct.) 2020]
(a) to keep medium bacteria-free
(b) to detect alien DNA
(c) to impart disease-resistance to the host plant
(d) as selectable markers
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
In recombinant DNA technology, antibiotics are used as selectable markers, which help in identifying and eliminating non-transformants and selectively permitting the growth of the transformants. Normally, the genes encoding resistance to antibiotics such as chloramphenicol, ampicillin, tetracycline or kanamycin, etc., are considered useful selectable markers for E.coli.
Question
Match the following columns and select the correct option. [NEET (Sep.) 2020]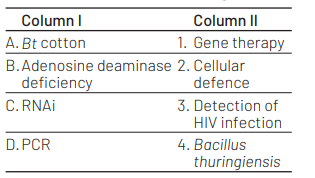
A B C D
(a) 3 2 1 4
(b) 2 3 4 1
(c) 1 2 3 4
(d) 4 1 2 3
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The correct option is (d). It can be explained as follows. In Bt cotton the specific Bt toxin gene was isolated from Bacillus thuringiensis. The first clinical gene therapy was given in 1990 to a 4-year old girl with adenosine deaminase (ADA) deficiency. RNAi (RNA interference) takes place in all eukaryotic organisms as a method of cellular defence. PCR is now routinely used to detect HIV in suspected AIDS patients.
Question
In gel electrophoresis, separated DNA fragments can be visualised with the help of [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) ethidium bromide in UV radiation
(b) acetocarmine in UV radiation
(c) ethidium bromide in infrared radiation
(d) acetocarmine in bright blue light
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In gel electrophoresis, separated DNA fragments can be visualised with the help of ethidium bromide in UV radiation because DNA fragments cannot be seen in visible light without staining.So, they are stained with ethidium bromide and made observable through UV radiation as bright orange coloured bands. The bands are cut out of agarose gel and extracted. The purified DNA fragments are then used in constructing recombinant DNAs by attaching them to claning vectars.
Question
Given below are four statements pertaining to separation of DNA fragments using gel electrophoresis. Identify the incorrect statements.
1. DNA is negatively charged molecule and so it is loaded on gel towards the anode terminal.
2. DNA fragments travel along the surface of the gel whose concentration does not affect. movement of DNA.
3. Smaller the size of DNA fragment larger is the distance it travels through it.
4. Pure DNA can be visualised directly by exposing UV-radiation.
Select the correct option from the following [NEET Odisha) 2019]
(a) 1,3 and 4
(b) 1, 2 and 3
(c) 2,3 and 4
(d) 1,2 and 4
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Statements (1) (2) and (4) are incorrect because DNA fragments are negatively charged molecules they can be separated by torcing them to move towards the anode under an electric field through a medium/matrix. The concentration of gel does affect the resolution of DNA separation. The separated DNA tragments can be visualised anly after staining the DNA with a compound known as ethidium bromide followed by exposure to UV radiation. Only statement 3 is correct. The DNA fragments spearate [resolve] according to their size through sieving effect provided by the agarose gel. Hence, the smaller the fragment size, the farther it moves.
Question
The correct order of steps in Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is [NEET 2018]
(a) Denaturation, Extension, Annealing
(b) Annealing, Extension, Denaturation
(c) Extension, Denaturation, Annealing
(d) Denaturation, Annealing, Extension
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR] involves three basic steps; denaturation, annealing and extension. In the denaturation step. DNA is heated at high temperature $\left[94^{\circ} \mathrm{C}\right.$ to $96^{\circ} \mathrm{Cl}$ to separate the two strands. In the next step lannealingl the two oligo-nucleotide primers anneal to each single-stranded template DNA.
This step is carried out at a lower temperature $140^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ to $60^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$. The tinal step is extension, wherein Taq DNA polymerase synthesises the DNA region between the primers, using dNTPs(deoxynucleoside triphosphates) and $\mathrm{Mg}^{2+}$ ions.
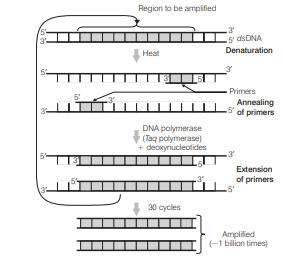
Polymorase Chain Rosction(PCA): Each cycle has three steps: (i) Denaturation; (ii) Primer annealing; and(iii) Extension of primers
Question
The process of separation and purification of expressed protein before marketing is called [NEET 2017]
(a) upstream processing
(b) downstream processing
(c) bioprocessing
(d) postproduction processing.
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The process of separation and purification of expressed protein before marketing is called downstream processing. In this process, a whole range of biochemical separation and purification techniques are used such as drying. chromatography, solvent extraction and distillation. After puritication quality control testings are done.
Question
What is the criterion for DNA fragments movement on agarose gel during gel electrophoresis? [NEET 2017]
(a) The larger the fragment size, the farther it moves
(b) The smaller the fragment size, the farther it moves
(c) Positively charged fragments move to farther end
(d) Negatively charged fragments do not move
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Gel electrophoresis is used for the separation of molecules of similar electric charge on the basis of their size. Hence, smaller the DNA fragment size the farther it moves.
Thinking Process Agarose gel matrix functions as sieve. Smaller DNA fragments easily move and larger fragments take time to move in gel matrix.
Question
The Taq polymerase enzyme is obtained from [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) Thiobacillus ferroxidans
(b) Bacillus subtilis
(c) Pseudomonas subtilis
(d) Thermus aquaticus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Taq polymerase is a thermostable DNA polymerase obtained from Thermus aquaticus. Thermus aquaticus is a bacterium that lives in hot springs and hydrothermal vents.
Question
Which of the following is not a component of downstream processing? [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) Separation
(b) Purification
(c) Preservation
(d) Expression
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Downstream process is the process of separation and purification of products synthesised in bioreactors. After the completion of biosynthetic stage, the product has to be subjected through a series of processes before it is ready for marketing as a finished product. The processes include separation and purification, collectively referred to as downstream processing. The product is then formulated with suitable preservatives. Hence, option (d) is incorrect and all other options are correct.
Question
Stirred-tank bioreactors have been designed for [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) purification of product
(b) addition of preservatives to the product
(c) availability of oxygen throughout the process
(d) ensuring anaerobic conditions in the culture vessel
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
A stirred tank bioreactor is usually cylindrical, possessing a stirrer which facilitates even mixing of the reactor contents and oxygen availability through out the bioreactor.
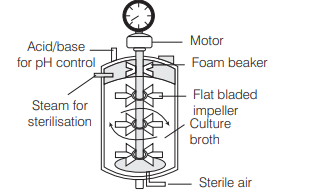
(a) Simple stirred-tank bioreactor
The bioreactor has an agitator system, an oxygen delivery system, foam control, pH and temperature control systems. Hence, option (c) is correct.
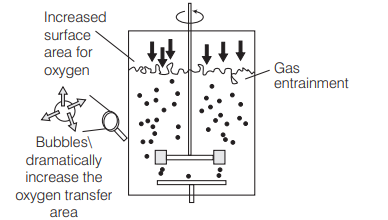
(b) Sparged stirred-tank bioreactor through which sterile air bubbles are sparged
Question
An analysis of chromosomal DNA using the Southern hybridisation technique does not use [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) electrophoresis
(b) blotting
(c) autoradiography
(d) PCR
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Southern hybridisation is a technique used in molecular biology for detection of a specific DNA sequence in DNA samples in which except PCR we use all three methods such as electrophoresis,
blotting and autoradiography. PCR is the method used for the amplification of DNA sample. In vitro clonal propagation is characterised by PCR and RAPD.
Question
In vitro clonal propagation in plants is characterised by [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) PCR and RAPD
(b) Northern blotting
(c) electrophoresis and HPLC
(d) microscopy
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
RAPD (Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA) is a type of PCR reaction, but the segments of DNA that are amplified are random. Often, PCR is used to amplify a known DNA sequence like in vitro clonal propagation in plants.
Question
DNA fragments generated by the restriction endonucleases in a chemical reaction can be separated by [NEET 2013]
(a) centrifugation
(b) polymerase chain reaction
(c) electrophoresis
(d) restriction mapping
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
DNA fragments generated by the restriction endonucleases in a chemical reaction can be separated by electrophoresis. The polymerase chain reaction is simply DNA replication in a test-tube. Restriction mapping is the process of obtaining structural information on a piece of DNA by the use of restriction enzymes, e.g. endonucleases that recognise specific $4-8$ base regions of DNA.
Question
PCR and restriction fragment length polymorphism are the methods for [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) study of enzymes
(b) genetic transformation
(c) DNA sequencing
(d) genetic fingerprinting
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
PCR and RFLP are methods used for genetic fingerprinting. As Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism(RFLP) is the basis of genetic (or DNA) fingerprinting and is useful in identifying individuals from their semen, blood or tissues or any other DNA sample and resolution of parent hood disputes. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is also useful in genetic fingerprinting as it can amplify the DNA sample even if available in a very small amount.
Question
Which one is a true statement regarding DNA polymerase used in PCR? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) It is used to ligate introduced DNA in recipient cells
(b) It serves a a selectable marker
(c) It is isolated from a virus
(d) It remains active at high temperature
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) is used to amplify a DNA segment or to synthesise in vitro the multiple copies of gene (or DNA) of interest, using two sets of primers and the enzyme DNA polymerase. This enzyme is isolated from a bacterium Thermus aquaticus and it remains active during the high temperature but high temperature induced denaturation of double stranded DNA.
Question
Agarose extracted from sea weeds is used in [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) spectrophotometry
(b) tissue culture
(c) PCR
(d) gel electrophoresis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
For gel electrophoresis the commonly used matrix is agarose which is a natural polymer extracted from seaweeds (e.g. Gelidium, Gracilaria, Gigartina, etc.). Gel electrophoresis is a technique to separate fragments of DNA. Since, DNA fragments are negatively charged molecules they can be separated by forcing them to move towards the anode under an electric field through a medium/matrix.
Question
Stirred-tank bioreactors have been designed for [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) addition of preservatives to the product
(b) purification of the product
(c) ensuring anaerobic conditions in the culture vessel
(d) availability of oxygen throughout the process
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The most common type of aerobic bioreactor in use today is the stirred-tank bioreactor, which may feature a specific internal configuration designed to provide a specific circulation pattern. The stirred tank bioreactor have been designed for availability of oxygen through out the processes.
Question
Polyethylene glycol method is used for [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) biodiesel production
(b) seedless fruit production
(c) energy production from sewage
(d) gene transfer without a vector
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Polyethylene glycol method is used for gene transfer without a vector. Introduction of DNA into plant cells without the involvement of a biological agent and leading to stable
transformation is known as direct gene transfer. There are various methods for direct direct gene transfer, one of which is chemical method.
Certain chemicals, e.g. PEG (Polyethylene Glycol), polyvinyl alcohol and calcium phosphate enhance the uptake of DNA by plant protoplast. PEG and calcium phosphate are thought to precipitate the DNA onto the outer surface of plasmalemma and the precipitate is taken up by the endocytosis.
Question
Gel electrophoresis is used for [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) construction of recombinant DNA by joining with cloning vectors
(b) isolation of DNA molecules
(c) cutting of DNA into fragments
(d) separation of DNA fragments according to their size
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
When genomic DNA extracted from any tissue of a plant or animal species is digested with a restriction enzyme, it is cleaved into segments. The segments of different sizes can be separated through gel electrophoresis. Gel electrophoresis involves movement of fragments or molecules from a well created on one edge of the gel.
