Question
The QRS complex in a standard ECG represents [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) depolarisation of auricles
(b) depolarisation of ventricles
(c) repolarisation of ventricles
(d) repolarisation of auricles
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Option (b) is correct and can be explained as in an ECG there occurs five consecutive waves: $\mathrm{P}, \mathrm{Q}, \mathrm{R}, \mathrm{S}$ and $T$.
P wave represents depolarisation of atria and leads to contraction of both atria.
QRS complex represents depolarisation of ventricles which leads to initiation of ventricular contraction.
T wave represents return of ventricles from excited to normal state.
Question
All the components of the nodal tissue are autoexcitable. Why does the SA node act as the normal pacemaker? [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) SA node has the lowest rate of depolarisation
(b) SA node is the only component to generate the threshold potential
(c) Only SA node can convey the action potential to the other components
(d) SA node has the highest rate of depolarisation
Answer/Explanation
Ans (d)
The nodal musculature has the ability to generate action potentials without any external stimuli, i.e. it is autoexcitable. However, the number of action potentials that could be generated in a minute vary at different parts of the nodal system.The SAN (Sino-Atrial Node) can generate the maximum number of action potentials, i.e $70-75 \mathrm{~min}$, i.e. the highest rate of depolarisation and is responsible for initiating and maintaining the rhythmic contractile activity of the heart. Therefore, it is called pacemaker.
Question
A specialised nodal tissue embedded in the lower corner of the right atrium, close to atrio-ventricular septum, delays the spreading of impulses to heart apex for about $0.1 \mathrm{sec}$. The delay allows [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) blood to enter aorta
(b) the ventricles to empty completely
(c) blood to enter pulmonary arteries
(d) the atria to empty completely
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Atrio-Ventricular Node (AVN) present in the lower corner of the right atrium, delays the spreading of impulses to heart ventricles for about $0.1$ second. This pause allows the atria to empty completely into the ventricles before the ventricles pump out the blood.
Question
What would be the heart rate of a person if the cardiac output is $5 \mathrm{~L}$, blood volume in the ventricles at the end of diastole is $100 \mathrm{~mL}$ and at the end of ventricular systole is 50 $\mathrm{mL}$ ? [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) 75 beats per minute
(b) 100 beats per minute
(c) 125 beats per minute
(d) 50 beats per minute
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
As per the given data, the heart rate of the person would be 100 beats per minute. It can be calculated as follows Given, Cardiac output $=5 \mathrm{~L}(5000 \mathrm{~mL})$ Blood volume in ventricles at the end of diastole $=100 \mathrm{~mL}$
Blood volume at the end of ventricular systole
$
=50 \mathrm{~mL}
$
So, Stroke volume $=100-50=50 \mathrm{~mL}$
Cardiac output $=$ Stroke volume $\times$ Heart rate, i.e.
$
5000 \mathrm{~mL}=50 \mathrm{~mL} \times \text { Heart rate }
$
Therefore, Heart rate $=100$ beats $/ \mathrm{min}$.
Question
Match the following columns.[NEET (National) 2019]
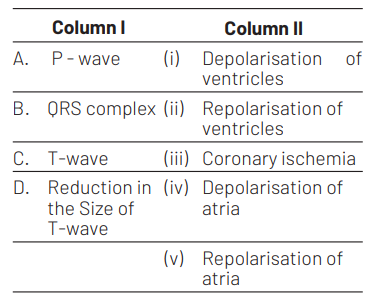
Select the correct option.
A B C D
(a) (iv) (i) (ii) (v)
(b) (ii) (i) (v) (iii)
(c) (ii) (iii) (v) (iv)
(d) (iv) (i) (ii) (iii)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
(A)-(iv), (B)-(i), (C)-(ii), (D)-(iii)
In an Electrocardiograph (ECG), P-wave represents the depolarisation of atria which is caused by the activation of SA node. QRS complex represents depolarisation of ventricles which is caused by the impulse of contraction from AV node.
T-wave represents repolarisation of ventricles and reduction in its size signifies coronary ischemic, i.e. when the heart muscles receive insufficient oxygen as in arteriosclerotic heart disease.
Question
Match the items given in Column I with those in Column II and select the correct option given below [NEET 2018]
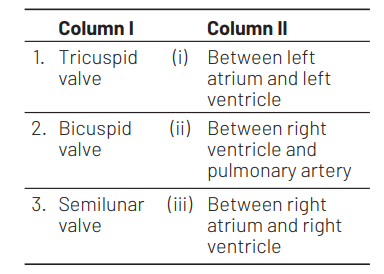
1 2 3
(a) (i) (ii) (iii)
(b) (i) (iii) (ii)
(c) (iii) (i) (ii)
(d) (ii) (i) (iii)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The atrioventricular opening between the left atrium and left ventricle is guarded by the bicuspid valve. It is also called as mitral valve. The right atrioventricular opening is guarded by the tricuspid valve. It has three flaps. Semilunar valve is found in right ventricle and pulmonary artery. Therefore, option (c) is correct.
Question
Doctors use stethoscope to hear the sounds produced during each cardiac cycle. The second sound is heard when [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) AV valves open up
(b) ventricular walls vibrate due to gushing in of blood from atria
(c) semilunar valves close down after the blood flows into vessels from ventricles
(d) AV node receives signal from SA node
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
In healthy adults, there are two normal heart sounds often described as lub and dup. These are the first heart sound and second heart sound produced by the closing of the AV valves and semilunar valves respectively.
Question
Which one of the following animals has two separate circulatory pathways? [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) Frog
(b) Lizard
(c) Whale
(d) Shark
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The circulatory system in which two distinct and separate circulatory pathways for blood flow are involved, is called double circulatory system (also, double-loop circulatory system). It occurs in mammals and birds. Whale is a mammal, so it shows above characteristic.
Question
The diagram given here is the standard ECG of a normal person. The P-wave represents the [NEET, CBSE AIPMT 2013, 2009]
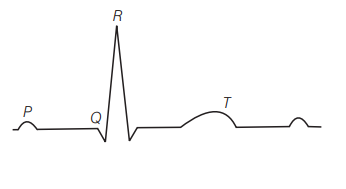
(a) contraction of both the atria
(b) initiation of the ventricular contraction
(c) beginning of the systole
(d) end of systole
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In ECG, P-wave represents the depolarisation of atria which leads to the contraction of both atria. T-wave represents the return of ventricles from excited to normal state. The QRS complex represents the depolarisation of the ventricles which initiates ventricular contraction. The contraction starts shortly after $Q$ and marks the beginning of systole.
Question
‘Bundle of His’ is a part of which one of the following organs in humans? [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) Heart
(b) Kidney
(c) Pancreas
(d) Brain
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The bundle of His, are specialised muscle fibres for electrical conduction present in the heart which were named after the Swiss cardiologist Wilhelm His, Jr., who discovered them in 1893 . These are also known as AV bundle which is a collection of heart muscle cells
Question
If due to some injury the chordae tendinae of the tricuspid valve of the human heart is partially non-functional, what will be the immediate effect? [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) The flow of blood into the aorta will be slowed down
(b) The ‘pacemaker’ will stop working
(c) The blood will tend to flow back into the left atrium
(d) The flow of blood into the pulmonary artery will be reduced
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
If chordae tendinae of the tricuspid valve became partially non-functional due to the injury then the flow of blood into the pulmonary artery will be reduced. Because chordae tendinae, arise from papillary muscles and insert upon the flaps of tricuspid and bicuspid valves and the valves in the heart allow the flow of blood only in one direction, i.e., from the atria to the ventricles and from the ventricles to the pulmonary artery or aorta.
Question
In humans, blood passes from the post caval to the diastolic right atrium of heart due to [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) pushing open of the venous valves
(b) suction pull
(c) stimulation of the sino auricular node
(d) pressure difference between the post caval and atrium
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Due to the pressure difference between the post caval and atrium, the blood passes from the post caval to the diastolic right atrium. Because the action of heart includes contractions and relaxations of the atria and ventricles. The dynamics of blood flow in blood vessels is no exception and blood flows through the blood vessels along a pressure gradient, always moving from higher to lower pressure areas.
Question
Systemic heart refers to [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) enteric heart in lower vertebrates
(b) the two ventricles together in humans
(c) the heart that contracts under stimulation from nervous system
(d) left auricle and left ventricle in higher vertebrates
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Systemic heart refers to enteric heart in lower vertebrates. It pumps the blood to different body parts and not to lungs.
Question
Bundle of His is a network of [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) nerve fibres distributed in ventricles
(b) nerve fibres found throughout the heart
(c) muscle fibres distributed throughout the heart walls
(d) muscle fibres found only in the ventricle wall
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Bundle of His is a network of specialised conducting muscle fibres (Purkinje fibres) which transmit the impulse from AV node to all parts of both the ventricles.
Question
In mammals, histamine is secreted by [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) fibroblasts
(b) histocytes
(c) lymphocytes
(d) mast cells
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Histamine is a potent vasodilator formed by decarboxylation of the amino acid histidine and released by mast cells in response to appropriate antigens.Mast cells are especially prevalent in the connective tissue of the skin, respiratory tract and in surrounding blood vessels.
Question
The correct route through which pulse-making impulse travels in the heart is [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) AV node $\rightarrow$ Bundle of $\mathrm{His} \rightarrow \mathrm{SA}$ node $\rightarrow$ Purkinje fibres $\rightarrow$ Heart muscles
(b) AV node $\rightarrow S A$ node $\rightarrow$ Purkinje fibres $\rightarrow$ Bundle of $\mathrm{His} \rightarrow$ Heart muscles
(c)SA node $\rightarrow$ Purkinje fibres $\rightarrow$ Bundle of His $\rightarrow$ AV node $\rightarrow$ Heart muscles
(d) SA node $\rightarrow$ AV node $\rightarrow$ Bundle of His $\rightarrow$ Purkinje fibres $\rightarrow$ Heart muscles
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The correct route through which pulse-making impulse travels in the heart is : SA node $\rightarrow$ AV node $\rightarrow$ Bundle of His $\rightarrow$ Purkinje fibres $\rightarrow$ Heart muscles.
Question
Pacemaker of heart is [CBSE AIPMT 1994, 99, 2002, 04]
(a) AV node
(b) bundle of $\mathrm{His}$
(c) SA node
(d) Purkinje fibres
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
SA node lies in the right wall af right. auricle below the opening of superior vena cava. It is also called pacemaker as it is first to originate the cardiac impulses and determines the rate of heartbeat.
Question
Dup sound is produced during closure of [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) semilunar valves
(b) bicuspid valve
(c) tricuspid valve
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The period between the end of ane heartbeat to the end of next heartbeat is called cardiac cycle. Cardiac cycle is formed of three phases.
Atrial systole, ventricular systole and joint diastole. During ventricular systole closing of Auriculo ventricular (AV) valves at the start of ventricular systole produces first heart sound called lubb’ or systolic sound. During joint diastole rapid closure of semilunar valves at the beginning of ventricular diastole produces the second heart sound called ‘dup’.
Question
Tricuspid valve is found in between [CBSE AIPMT 1989]
(a) sinus venosus and right auricle
(b) right auricle and right ventricle
(c) left ventricle and left auricle
(d) ventricle and aorta
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Right auricle opens in right ventricle through a wide circular right auriculoventricular aperture guarded by right auriculoventricular valve which is formed of three flaps called cusps, so it
is called tricuspid valve. It regulates the unidirectional flow of blood from right auricle to right ventricle.
