Question
Which of the following statement is not correct? [NEET 2021]
(a) Pyramid of biomass in sea is generally inverted
(b) Pyramid of biomass in sea is generally upright
(c) Pyramid of energy is always upright
(d) Pyramid of numbers in a grassland ecosystem is upright.
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Pyramid of biomass in a sea is generally inverted because the primary producers(phytoplanktons) have a lower biomass than that of succeeding zooplanktons, which further have a lower biomass than that of succeeding small fishes and so on. Pyramid of energy is the only pyramid that can never be inverted and is always upright. This is because some amount of energy in the form of heat is always lost to the environment at every trophic level of the food chain. In a grassland ecosystem, the number of producers is always maximum, followed by reducing number of organisms at second trophic level, third trophic level and other higher level (if present). Thus, the pyramid of number in grassland is upright.
Question
Which of the following ecological pyramids is generally inverted? [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) Pyramid of energy
(b) Pyramid of biomass in a forest
(c) Pyramid of biomass in a sea
(d) Pyramid of numbers in grassland
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Pyramid of biomass in sea is generally inverted because the biomass of a trophic level depends upon reproductive potential and longevity of its members. In a sea, the biomass of phytoplanktons is usually lesser than that of zooplanktons while the biomass of carnivores is greater than small carnivores and zooplanktons. On the other hand, pyramid of energy is always upright. Pyramid of biomass in terrestrial ecosystems (forests, grasslands) is also upright.
Question
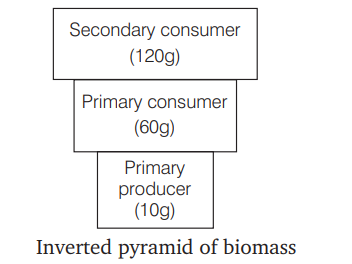
What type of ecological pyramid would be obtained with the following data?
Secondary consumer: $120 \mathrm{~g}$
Primary consumer : $60 \mathrm{~g}$
Primary producer : 10 g[NEET 2018]
(a) Upright pyramid of numbers
(b) Pyramid of energy
(c) Inverted pyramid of biomass
(d) Upright pyramid of biomass
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
An inverted pyramid of biomass will be obtained from the given data. The biomass is continuously decreasing from secondary consumer $(120 \mathrm{~g})$ to primary consumer $(60 \mathrm{~g})$ to primary producer (10 g).
Therefore, upright pyramid of biomass cannot be obtained. The data is given in the form of biomass, therefore pyramid of number and energy cannot be obtained. Further, pyramid of energy is always upright.
Question
During ecological succession [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) the gradual and predictable change in species composition occurs in a given area
(b) the establishment of a new biotic community is very fast in its primary phase
(c) the numbers and types of animals remain constant
(d) the changes lead to a community that is in near equilibrium with the environment and is called pioneer community
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The gradual and fairly predictable change in the species composition of a given area is called ecological succession. During succession some species colonise an area and their populations become more numerous, whereas populations of other species decline and even disappear.
Question
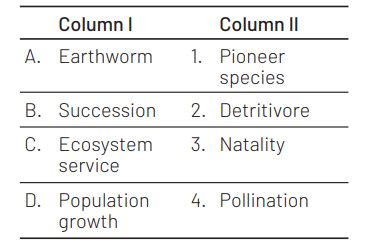
Match the following and select the correct option. [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
Codes
A B C D A B C D
(a) 1 2 3 4 (b) 4 1 3 2
(c) 3 2 4 1 (d) 2 1 4 3
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The species that invade a base area in succession is called pioneer species and earthworm is a detritivore. Ecosystem services are the products of ecosystem process, e.g. biodiversity maintenance, crop pollination, etc. and natality is the term used for population growth or birth rate in population ecology.
Question
Given below is an imaginary pyramid of numbers. What could be one of the possibilities about certain organisms at some of the different levels? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
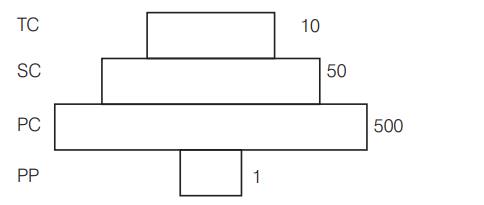
(a) Level PC is insects and level SC is small insectivorous birds
(b) Level PP is phytoplanktons in sea and Whale on top level TC
(c) Level one PP is pipal trees and the level $\mathrm{SC}$ is sheep
(d) Level PC is rats and level SC is cats
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The given figure shows spindle-shaped pyramid of number in single tree ecosystem. Here, a single large sized tree provides food to a large number of herbivores which support a few carnivores and the later are eaten by small number of top carnivores. So, here PP is used for producer, i.e. single tree, PC is Primary Consumers, i.e. large number of insects, $\mathrm{SC}$ is Secondary Consumers, i.e. small insectivorous birds and TC is Top Consumers which may be eagles or falcon, etc.
Question
The upright pyramid of number is absent in [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) pond
(b) forest.
(c) lake
(d) grassland
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Pyramid of number represents the number of individuals per unit area at various trophic levels. It is always upright in grassland, pond and lake ecosystems. But in forest or single tree ecosystem, it is spindle-shaped and of parasitic food chain is considered then it will be an inverted pyramid.
Question
The second stage of hydrosere is occupied by plants like [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) Azoila
(b) Typha
(c) Salix
(d) Vallisneria
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Vallisneria is at second stage of hydrosere. It starts orginating in a pond with colonisation of some phytoplanktons which forms the pioneer plant community. The stages are
Ist – Bacteria, blue-green algae and algae
Ilnd- Hydrilla, Potamogeton and Vallisneria
Illrd-Nelumbo, Nymphaea, Trapa, Azolla and Wolffia
IVth – Typha and Sagitaria
Vth-Juncus and Cyperus
Vith- Salix and Populus, Almus.
Question
Which one of the following statements is correct for secondary succession? [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) It occurs on a deforested site
(b) It follows primary succession
(c) It is similar to primary succession except that it has a relatively fast pace
(d) It begins on a bare rock
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Secondary succession of subsere is ecological succession that takes place in a recently denuded area which still contains a lot of organic debris, remains and propagules of previous living organisms. It is more common and caused by baring of an area due to the forest fires, deforestation, excessive overgrazing, landslides, earthquakes, repeated floods, etc.
Question
Which one of the following statements for pyramid of energy is incorrect whereas the remaining three are correct? [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) It show energy content of different trophic level of organisms
(b) It is inverted in shape
(c) It is upright in shape
(d) Its base is broad
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Pyramid of energy is graphic representation of energy per unit area sequence-wise in various rising trophic levels with producers at the base and top carnivores at the apex. Pyramid of energy is upright in all cases. It is also more accurate than other types of ecological pyramids.
Question
Which one of the following is not used for constructing of ecological pyramids? [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) Dry weight
(b) Number of individuals
(c) Rate of energy flow
(d) Fresh weight
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Ecological pyramids are the graphical representation of the trophic structure and function at successive trophic levels. Ecological pyramids are of three general types, listed as here under:
(a) Pyramid of numbers, showing the number of organisms at each level.
(b) Pyramid of biomass, showing the total dry weight of living matter.
(c) Pyramid of energy, showing the rate of energy flow/productivity at successive trophic levels.
Thus, fresh weight is not used for the construction of ecological pyramids.
Question
The greatest biomass of autotrophs in the world’s oceans is that of [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) benthic brown algae, coastal red algae and dephnids
(b) benthic diatoms and marine viruses
(c) sea grasses and slime molds
(d) free-floating micro-algae,
cyanobaceria and nanoplankton
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The greatest biomass of autotrophs in the world’s ocean is that of free floating micro-algae, cyanobacteria and nanoplankton. Phytoplanktons, diatoms and dinoflagellates are the dominant producers in the world’s oceans.
Question
In a terrestrial ecosystem such as forest, maximum energy is in which trophic level? [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) $T_1$
(b) $T_2$
(c) $T_3$
(d) $\mathrm{T}_4$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
There is $90 \%$ loss of energy at every trophic level. Therefore, maximum energy is at $\mathrm{T}_1$ level.
Question
In a food chain, the largest population is that of [CBSE AIPMT 1996, 1994]
(a) decomposers
(b) producers
(c) primary consumers
(d) tertiary consumers
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Producers are present in largest number in any food chain.
Question
The nature of climax community ultimately depends on [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) climate
(b) bed rock
(c) soil organisms
(d) pool of available nutrients
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The climax community ultimately depends on the climate such as rain forest in moist tropical area and mixed coniferous or deciduous forest in temperate area.
Question
The primary succession refers to the development of communities on a [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) fleshly cleared crop field
(b) forest clearing after devastating fire
(c) pond, freshly filled with water after a dry phase
(d) newly-exposed habitat with no record of earlier vegetation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Primary succession is the succession in a totally barren area with no record of earlier vegetation. It takes long time of 1000 year or more.
Question
The pyramid which cannot be inverted in a stable ecosystem is that of [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a)biomass
(b) number
(c) energy
(d) All of these
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Pyramid of energy is graphic representation of amount of energy trapped per unit time and area in different trophic levels of a food chain with producers forming the base and top carnivores or consumers the tip. It is always upright in shape.
Question
Pyramid of number deals with number of [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) species in an area
(b) individuals in a community
(c) individuals in a trophic level
(d) sub-species in a community
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Pyramid of number is a graphic representation of the number of organisms per unit area of various trophic levels. It deals with the number of individuals in a trophic level. It deals with the number of individuals in a trophic level.
Question
Pyramid of number in a pond ecosystem is [CBSE AIPMT 1993, 1991, 1990]
(a) irregular
(b) inverted
(c) upright.
(d) spindle-shaped
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Pyramid of number in a pond ecosystem is upright or erect, in which producers are maximum in number and top consumers are least in number.
