Topic 3 : Genetics
3.5 Genetic modification and biotechnology
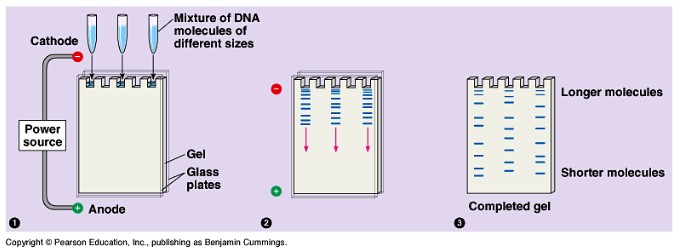
Gel electrophoresis:
- Before gel electrophoresis takes place, restriction enzymes are used to cut DNA into fragments of various lengths and different charges.
- Restriction enzyme: cut DNA into fragments at specific base sequences in each sample.
- These fragments are placed into small depression or wells at one end of the gel.
- An electrical current is applied to the gel (positive on one side and negative on the other).
- The fragments of DNA will fall out and embed in the gel based on their size and charge.
- The smallest particles that are charged go the farthest in the gel, while the large non-charged particles fall out and embed in the gel the
quickest
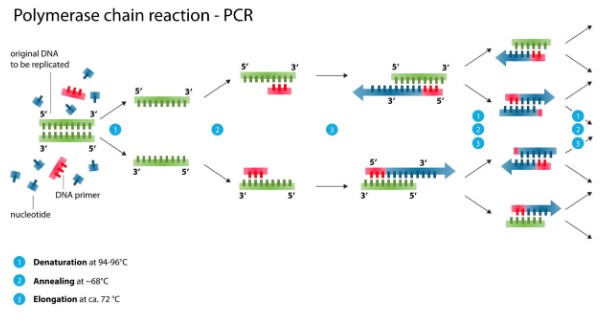
PCR (polymerase chain reaction):
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction) is a laboratory technique that takes a single or few copies of DNA and amplifies them to generate millions
or more copies of a particular DNA sequence. - When you collect DNA from different sources such as sperm samples or small drops of blood, there are usually very little usable cells to collect DNA.
- Therefore, PCR is used to create enough DNA to be analyzed for investigations such as forensics or custody cases.
- Once large quantities of the DNA have been created, other methods such as gel electrophoresis are used to analyze the DNA.
- Denaturation: DNA sample is heated to separate it into two strands
- Annealing: DNA primers attach to the opposite ends of the target gene sequence
- Elongation: A heat-tolerant DNA polymerase (Taq polymerase) copies the strand
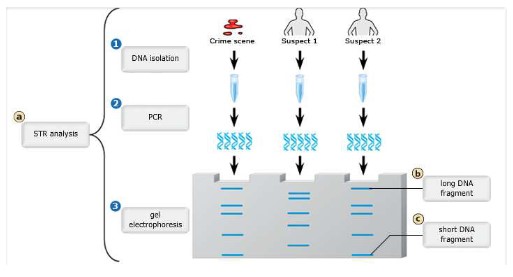
DNA profiling:
- DNA profiling is a method or technique used to identify individuals on the basis of their DNA profiles in comparison to an unknown sample of DNA.
- DNA profiling can be used in paternity test to identify the biological father of a child. Scientists can take a blood sample which contains a
father’s DNA and a blood sample from a child which contains the child’s DNA. They can then run a gel electrophoresis to compare the
banding patterns between the father and the child. - DNA profiling can also be used in criminal investigations where a small sample of blood, semen, hair or other cells where DNA is present is collected.
- PCR can be applied to these small samples of DNA to amplify the DNA into millions of copies to create enough DNA to be analyzed for the investigation.
- Using restriction enzyme to cut the DNA into fragments that are separated through gel electrophoresis and DNA profiling, the DNA sample can be compared to a suspect’s DNA to prove if they are innocent or guilty.
- DNA profiling can also be used to support ancestral relationships between organisms for evolutionary studies.
- Fluorescent marker may be added to show the colour.
Genetic modification:
- A gene produces a certain polypeptide in an organism.
- Since the genetic code is universal, when a gene is removed from one species and transferred to another the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide produced remains unchanged.
Gene tansfer:
- Gene transfer is taking one gene from an organism and inserting it into another organism.
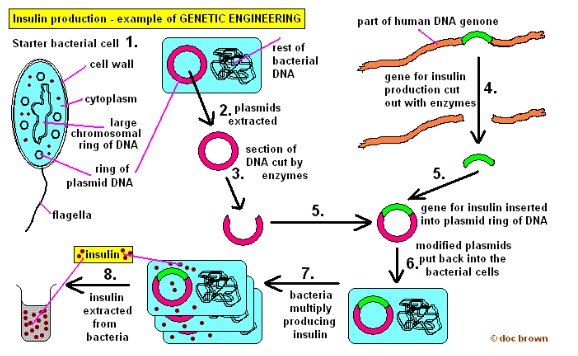
- An example of gene transfer is for the production of human insulin produced by the pancreatic cells.
- First, insulin production genes are cut off using restriction enzyme.
- Use the same restriction enzyme to cut the bacteria plasmid open
- Place the gene into the plasmid using DNA ligase. (antibiotic resistance may also be put in to make the plasmid attractive)
- Put the plasmid back in the bacteria.
- Bacteria go through replication and production of human insulin.
- Harvest and purify the insulin.
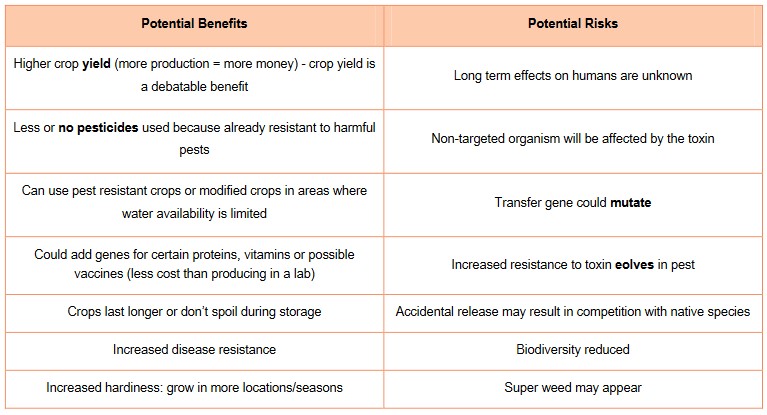
Potential risks and benefits of genetic modified crops:
- Bt corn: combine with soil bacterium that produces insecticidal toxin – give resistance to insects
Clone:
- Clone: a group of genetically identical organisms or a group of cells derived from a single parent cell.
- Organisms that reproduce asexually, produce genetically identical offspring
- Identical twins in humans are also clones (monozygotic twin)
- Bacteria uses binary fission to clone itself
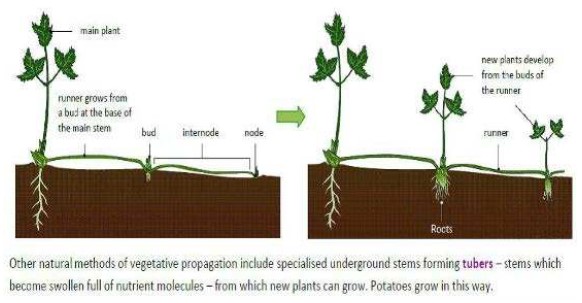
- Underground stems called tubers in potatoes can form new potato plants which are clones of the original parent potato plant
- Runner: growing stems used to reproduce asexually
Embryonic stage cloning:
- At the very early embryo stage, cells are still pluripotent (meaning they can become any type of tissue)
- These cells can be separated artificially in a laboratory in order to create more than one of the same organism
- The separated pluripotent cells can then be inserted into the uterus of a surrogate mother or mothers in order to produce genetically identical offspring
- The separation of cells has to happen early in development, preferably the 8 cell stage
Cloning differentiated cells:
- Once cells start to differentiate and embryos develop into a fetus and eventually an adult cloning becomes much more difficult
- Therapeutic cloning is an example of cloning using differentiated cells
- This type of cloning can be used to create a specific tissue or organ
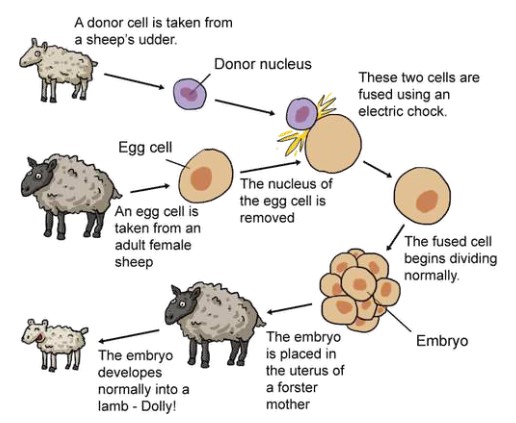
Cloning using differentiated cells can also be used to reproduce organisms like dolly the sheep. This is done through somatic-cell nuclear transfer.
1. Remove a differentiated cell nucleus
2. Enucleate a donor egg cell
3. Insert nucleus into the cell
4. Treat with electricity and put in back to the womb
5. Produce genetically indentical organism