Question
Which stage of meiotic prophase shows terminalisation of chiasmata as its distinctive feature? [NEET 2021]
(a) Leptotene
(b) Zygotene
(c) Diakinesis
(d) Pachytene
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Diakinesis is the final stage of meiotic prophase 1. In this stage the two homologous chromosomes do not separate completely but remain attached together at one or more points as indicated by ‘X’ arrangement known as chiasmata. The displacement of chiasmata is termed as terminalisation of chiasmata which is completed in diakinesis phase.
Question
Which of the following stages of meiosis involves division of centromere? [NEET 2021]
(a) Metaphase-I
(b) Metaphase-lI
(c) Anaphase-II
(d) Telophase-II
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
During anaphase II, each pair of chromosomes is separated into two identical, independent chromosomes. The chromosomes are separated by a structure called the mitotic spindle made up of many long proteins called microtubules, which are attached to a chromosome at one end and to the pole of a cell at the other end. The sister chromatids are separated simultaneously at their centromeres. The separated chromosomes are then
Question
During meiosis 1, in which stage synapsis takes place? [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) Pachytene
(b) Zygotene
(c) Diplotene
(d) Leptotene
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
During zygotene stage of meiosis-1, chromosomes start pairing together and this process of association is called synapsis. Such paired chromosomes are called homologous chromosomes.
Question
Dissolution of the synaptonemal complex occurs during [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a)zygotene
(b)diplotene
(c) leptotene
(d) pachytene
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Dissolution of the synaptonemal complex occurs during diplotene stage of prophase-1 of meiosis-1. Prophase of meiosis- 1 is long and complex. It is comprised of leptotene, zygotene, pachytene, diplotene and diakinesis. During diplotene, at most places synaptonemal complex dissolves.
Question
Match the following columns with respect to meiosis. [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
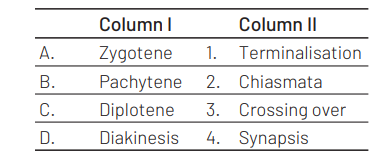
Select the correct option.
A B C D
(a) 4 3 2 1
(b) 1 2 4 3
(c) 2 4 3 1
(d) 3 4 1 2
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The correct option is (a). It can be explained as follows
During zygotene phase the homologous chromosomes pair or come together and forms synapsis.
Crossing over takes place during pachytene stage and at each point of crossing over a chiasma is formed between non-sister chromatids of homologous chromosomes.
Chiasmata is the point of contact between the two non sister chromatids of homologous chromosames, chiasmata becomes visible during diplotene stage.
Terminalisation of chiasmata gets completed during diakinesis phase where chromosomes gets freely distributed in the cytoplasm.
Question
After meiosis-l, the resultant daughter cells have [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) same amount of DNA as in the parent cell in S-phase
(b) twice the amount of DNA in comparison to haploid gamete
(c) same amount of DNA in comparison to haploid gamete
(d) four times the amount of DNA in comparison to haploid gamete
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
After meiosis-l, the resultant daughter cells have twice the amount of DNA in comparison to haploid gamete. Meiosis-l causes segregation of homologous pairs of chromosomes. However, each chromosome is double-stranded, having two sister chromatids due to DNA replication before meiosis began.
Question
In meiosis crossing over is initiated at [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) leptotene
(b) zygotene
(c) diplotene
(d) pachytene
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Leptotene – Condensation of chromatin
Zygatene – Synapsis of homologous chromosomes
Pachytene – Crossing over
Diplotene-Dissolution of synaptonemal complex and appearance of chiasmata
Diakinesis – Terminalisation of chiasmata
Question
Match the stages of meiosis in column I to their characteristic features in column II and select the correct option using the codes given below [NEET 2016, Phase II]
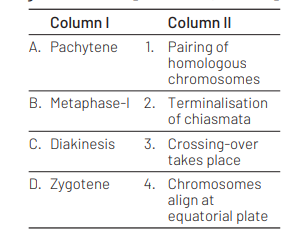
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Various phases of meiosis and their characteristic features are
Pachytene – Crossing-over takes place Metaphase-1 – Chromosomes align at equatorial plate
Diakinesis – Terminalisation of chiasmata
Zygotene – Pairing of homologous chromosomes
Question
Arrange the following events of meiosis in correct sequences. [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
I. Crossing over
II. Synapsis
III. Terminalisation of chiasmata
IV. Disapperance of nucleolus
(a) II, I, IV, III
(b) II, I, III, IV
(c)I, II, III, IV
(d) II, III, IV, I
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The correct sequence of events of meiosis are Synapsis in zygotene $\longrightarrow$ Crossing over in pachytene $\longrightarrow$ Terminalisation of chaismata in diplotene $\longrightarrow$ Disapperance of nucleolus in diakinesis.
Question
The enzyme recombinase is required at which stage of meiosis? [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) Pachytene
(b)Zygotene
(c) Diplotene
(d) Diakinesis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Crossing over is an enzymatic process occurring during the pachytene stage of prophase-l. The enzyme involved in this process is called recombinase which aids in the recombination of genes between homologous chromosomes. During zygotene stage, homologous chromosomes pair up by a process called synapsis and form a complex bivalent structure. Diplotene is marked by the dissolution of synaptonemal complex and chaisma formation. While diakinesis is marked by terminalisation of chiasmata(i.e. chiasmata shifts towards periphery of chromosome).
Question
Meiosis takes place in [NEET 2013]
(a) meiocyte
(b) conidia
(c) gemmule
(d) megaspore
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
In diploid organisms, specialised cells called meiocytes (gamete mother cell) undergo meiosis. Conidia and gemmules are asexual reproductive structures found in Penicillium and sponge respectively. Megaspores are female gametes in plants which undergo sexual reproduction.
Question
During gamete formation, the enzyme recombinase participates during [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) metaphase-I
(b)anaphase-II
(c) prophase-1
(d) prophase-II
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The pachytene stage of prophase-l of meiosis-l is characterised by the appearance of recombination nodules, the sites at which crossing over occurs between non-sister chromatids of the homologous chromosomes. Crossing over is the exchange of genetic material between two homologous chromosomes. It is also an enzyme mediated process and the enzyme involved is called recombinase.
Question
Given below is the representation of a certain event at a particular stage of a type of cell division. Which is this stage? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
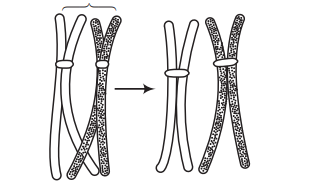
(a) Prophase-l during meiosis
(b) Prophase-ll during meiosis
(c) Prophase of mitosis
(d) Both prophase and metaphase of mitosis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
During zygotene stage of prophase-l of meiosis-l, bivalent chromasomes clearly appear as tetrads. Pachytene stage is characterised by the appearance of recombination nodules, the sites at which crossing over (exchange of genetic material) occurs between non-sister chromatids of the homologous chromosomes.
Question
Synapsis occurs between [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) a male and a female gamete
(b) mRNA and ribosomes
(c) spindle fibres and centromere
(d) two hamolagous chromosomes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
In zygotene of prophase-1, homalogous chromosomes pair up. This process is called synapsis. One chromosome of the pair is from the male parent and one from the female parent.
Question
Crossing over that results in genetic recombination in higher organisms occur between [CBSE AIPMT 2004]
(a) sister chromatids of bivalent.
(b) non-sister chromatids of a bivalent
(c) two daughter nuclei
(d) two different bivalents
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
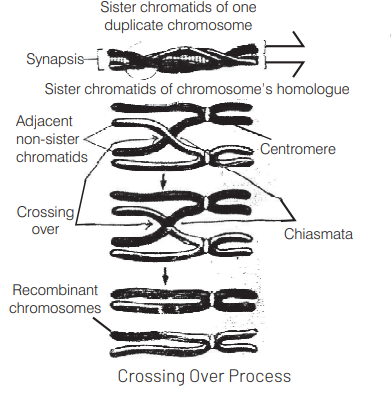
The process of crossing over takes place in pachytene stage of prophase-1 of meiosis-1. In this process some genes of two non-sister chromatids of a bivalent are exchanged.
The process of crossing over is depicted
Question
The exchange of genetic material between chromatids of paired homologous chromosomes during first meiotic division is called [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) transformation
(b) chiasmata
(c) crossing aver
(d) synapsis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
In pachytene stage of prophase-l of meiosis, there is breakage and reunion of chromatids, it results in exchange of segments between nonsister chromatids of a bivalent, known as crossing over. It leads to recombination of linked genes/alleles and is a major source of continuous type of genetic variations in sexually reproducing organisms.
Question
Lampbrush chromosomes occur during [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) prophase of mitosis
(b) diplatene of meiosis
(c) metaphase of meiosis
(d)interphase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Lampbrush chromosames were reparted by W Flemming(1882) and described by Ruchert (1892) from nuclei of yolk rich primary bacytes of newts and frag (amphibians). These are also found in spermatocytes of many animals. These are found in permanent. diplatene stage of meiosis and do not undergo cell cycle.
Each such chromosome has a double main axis made up of DNA and histones. The chromosames are coiled and held at many places forming cross like structure called chiasmata. Loaps arising laterally has uncoiled DNA which helps in rapid transcriptian and yolk synthesis.
Question
Meiosis has evolutionary significance because it results in [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) genetically similar daughters
(b) four daughter cells
(c) eggs and sperms
(d) recambinations
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Recombination takes place in meiosis but still Meiosis maintains the chromosome number canstant. It produces haploid gametes by reducing the chromosome number to haif. Crossing over produces niew cambination of linked genes and is major source of genetic variation. Also, distribution of bivalents which is at random in meraphase-1 provides the secondary source of genetic variation in the organisms and is essential for speciation and evokition.
Question
Meiosis-ll performs [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) separation of sex chromosomes
(b) synthesis of DNA and centromeres
(c) separation of homologous chromosomes
(d) separation of chromatids
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Meiosis-ll is hamatypic or equational division similar to mitosis but occurs in haplaid nuclei. Meiosis-Il is essential to separate out the chromatids of diad chromosames to bring real hapioidy in amount of DNA. It also increases the number of dsughter cells thaugh the chromosame number remains the same in daughter cells as produced after meiosis-l.
Question
In meiosis, the daughter cells differ from parent cell as well as amongst themselves due to [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) segregation, independent assortment and crossing over
(b) segregation and crossing over
(c) independent assortment and crossing over
(d) segregation and independent assortment.
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The daughter cells differ from parent cell as well as amongst themselves due to the segregation and crossing over taking place in them. Meiosis-1 brings gene recombinations and haplaidy of number of chromasomes. Crossing over during pachytene praduces new cambinatian of genes and is the major source of new genetic variations in the sexually reproducing organisms.
Question
Meiosis-l is reductional division. Meiosis-11 is equational division due to [CBSE AIPMT 1988]
(a) pairing of homologous chromosomes
(b)crossing over
(c) separation of chromatids
(d) disjunction of homologous chromosames
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Meiosis-l is called heteratypic division as the two chromatids of a chromosome became geneticaly different due to the crossing over.
Number af chromosomes is reduced to half, hence, called reduction division. Meiosis-llis just like mitasis but accurs in haploid nuclei, it is called homotypic of equational division as the chromosomes are distributed equally into daughter cells and chromasome number remains the same in daughter cells.
