Question
Inspite of interspecific competition in nature, which mechanism the competing species might have evolved for their survival? [NEET 2021]
(a) Resource partitioning
(b) Competitive release
(c) Mutualism
(d) Predation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Resaurce partitioning is the phenomenon where division of limited resources accurs by species to help avoid interspecific competitian in an ecalogical niche. If two species compete for the same resource, they could avoid campetition by choosing. for instance, different times for feeding or different foraging patterns. Thus, we can say inspite of interspecific competition in nature, competing species evalved a mechanism called resource partitioning for their survival. Other options can be explained as: Campetitive release occurs when one or two species campeting for the same resource disappears, thereby allowing the remaining competitor to utilize the rescurce more fully than it could in the presence ot the first species.
Mutualism is the interaction that conters benefits on both the interacting species. Lichens represent an intimate mutualistic relationship between a fungus and photosynthesising algae or cyanobacteria. Both the species benefit in mutualism and both lose in campetition in their interactions with each other. in bath parasitism and predation only one species benefits [parasite and predator, respectivelyl and the interaction.
Question
In the exponential growth equation $N_t=N_0 e^{n t}$, e represents [NEET 2021]
(a) the base of number logarithms
(b) the base of exponential logarithms
(c) the base of natural logarithms
(d) the base of geometric logarithms
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
When resources in the habitat are unlimited, each species has the ability to realise fully its innate potential to grow in number, as Darwin observed while developing his theory of natural selection. Then the papulation grows in an exponential or geametric fashion.
The integral form of the exponential growth can be represented by equation as
where,
$N_4=$ Population density after time $t$
$\mathrm{N}_6=$ Population density at time zero
$t=$ intrinsic rate of natural increase
$e=$ the base of natural logarithms.
In exponential growth, a population’s per capita (per individually growth rate stays the same regardless of papulation size, making the population grow faster and faster as it gets larger.
Question
Amensalism can be represented as [NEET 2021]
(a) species $A(-1)$ species $B(0)$
(b)species $A(+)$ : species $B[+]$
(c) species $A(-1$ : species $B(-]$
(d) species $A(+)$ : species $B$ (0)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Amensalism is the relationship between two arganisms, where one is hurt. A prime example of amensalism is penicilin filling bacteria. The bread mould Penicilium secretes penicillin that ultimately kills bacteria. In this cantact between two organisms, 0ne is destroyed or inhibited, and other remains unaffected. Hence, it is represented as Species A (−); Species B (0).
Question
Match the items in Column I with those in Column II. [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
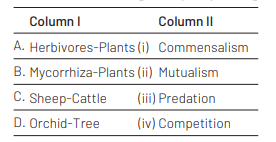
Select the correct option.
A B C D
(a) (iv), (ii), (i), (iii)
(b) (iii), (ii), (iv), (i)
(c) (ii), (i), (iii), (iv)
(d) (i), (iii), (iv), (ii)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Option (b) is correct match, which is as follows The relationship between herbivores and plants is prey-predator type in which herbivores are predators and plants are the prey.
In mycorrhiza plants association, both species are benefited and thus it represents mutualism. The sheep and cattle show competition for common resources like food, i.e. grass.
Orchid are epiphytes which grow on trees and derive nutrients from it. In this process, trees are neither harmed nor helped. Thus, it is type commensalism relationship.
Question
The impact of immigration on population density is [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) negative
(b) Both positive and negative
(c) neutralised by natality
(d) positive
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Population density is the member of individuals present per unit area or volume at a given time. It is calculated by the formula $D=N / S$, where $D=$ Density, $\mathrm{N}=$ Total number of individuals and $S=$ Number of units of space. Since immigration increases the number of individuals in an area, population density increase. Thus, immigration has positive impact on population density.
Question
According to Alexander von Humboldt [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
(a) species richness decreases with increasing area of exploration
(b) species richness increases with increasing area, but only up to limit
(c) there is no relationship between species richness and area explored
(d) species richness goes on increasing with increasing area of exploration
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Alexander von Humboldt was a German naturalist and geographer. He proposed that within a region, species richness increases with increasing explored area, but only up to a limit.
Accordingly, the relation between species richness and area for a wide variety of taxa turn out to be rectangular hyperbola. The relationship appears as a straight line on logarithmic scale and described by the equation : $\log S=\log C=Z \log A$
Where, S-Species richness, A-Area Z-Regression coefficient,
$C-Y$-Intercept.
Question
Which of the following is not an attribute of a population?[NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) Natality
(b) Mortality
(c) Species interaction
(d) Sex ratio
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Species interaction is not an attribute of a population. Rest Natality (Birth rate) Mortality(Death rate) and Sex radio are population attributes.
Question
Secondary metabolites such as nicotine, strychnine and caffeine are produced by plants for their [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) growth response
(b) defence action
(c) effect on reproduction
(d) nutritive value
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
A wide variety of chemical substances (i.e. secondary metabolites) that we extract from plants on a commercial scale (nicotine, caffeine, quinine, strychnine, opium, etc) are produced by them (plants) as defence against grazers and browsers.
Question
Between which among the following, the relationship is not an example of commensalism? [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) Orchid and the tree on which it grows
(b) Cattle egret and grazing cattle
(c) Sea anemone and clown fish
(d) Female wasp and fig species
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Among the given examples, relationship between wasp and fig species does not show commensalism. In this relationship, one species derives the benefit and other neither harmed nor benefitted.
Wasp and fig tree show mutualism.
Here fig flower is pollinated by wasp and wasp lays its egg into fruit and leaves them there for development.
Other options show examples of commensalism.
Question
Carnivorous animals-lions and leopards, occupy the same niche but lions predate mostly larger animals and leopards take smaller ones. This mechanism of competition is referred to as [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) character displacement
(b) altruism
(c) resource partitioning
(d) competitive exclusion
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Carnivorous animals, lions and leopard, occupy the same niche but lion predates mostly larger animals and leopard takes smaller ones. This is called resource partitioning. It is a mechanism in which there is the division of limited resources by species to help avoid competition in an ecological niche. In any environment, organisms compete for limited resources, so organisms and different species have to find ways to coexist with one another. That is why lions predate mostly larger animals and leopards take smaller ones.
Question
Which of the following statements is correct? [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) Lichens do not grow in polluted areas
(b) Algal component of lichens is called mycobiont
(c) Fungal component of lichens is called phycobiont
(d) Lichens are not good pollution indicators
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
(a) Statement (a) is correct. Lichens do not grow in polluted area. Rest statements are incorrect.
The correct forms of the statements are as follows
(b) Algal component of lichens is called phycobiont.
(c) Fungal component of lichens is called mycobiont.
(d) Lichens are good pollution indicators.
Question
Pinus seed cannot germinate and establish without fungal association. This is because [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) it has obligate association with mycorrhizae
(b) it has very hard seed coat
(c) its seeds contain inhibitors that prevent germination
(d) its embryo is immature
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Pinus has an obligate association with mycorrhizae due to which the Pinus seeds are unable to germinate and establish in the absence of fungal partner. Fungus or mycorrhizae help the Pinus roots to absorb water and minerals by increasing their surface area. In turn, the fungus derives food from the plant.
Question
Match Column I with Column II.
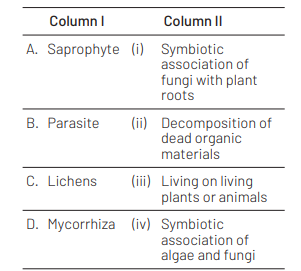
Choose the correct answer from the option given below: [NEET (National) 2019]
A B C D
(a) (iii) (ii) (i) (iv)
(b) (ii) (i) (iii) (iv)
(c) (ii) (iii) (iv) (i)
(d) (i) (ii) (iii) (iv)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
A)-(ii), (B)-(iii), (C)-(iv)(D)-(i)
Saprophytes are decomposers which help in the decomposition of dead organic material, e.g. Agaricus. Parasites are the entitites which live on other living plants or animals and derive nutrition from them, e.g. tapeworm in humans. Lichens represent symbiotic association between algae and fungi. Mycorrhiza is symbiotic association of fungi and plant roots.
Question
Which one of the following plants shows a very close relationship with a species of moth, where none of the two can complete its life cycle without the other? [NEET 2018]
(a) Banana
(b) Yucca
(c) Hydrilla
(d) Viola
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Yucca gloriosa has developed an obligate symbiotic relationship with Pronuba yuccasella moth. The moth cannot complete its life cycle with the association of Yucca flowers and in turn Yucca has no other pollinator.
Hydrilla is a hydrophilous plant while Viola is an entomophilous plant. Bananas are usually parthenocarpic fruits. Therefore, they do not require pollination.
Concept Enhancer The female moth visits the Yucca flowers at night and collects pollen in the form of balls. The moth, then inserts its ovipositor into ovary of the flower to lay eggs. The temperature of the ovary is suitable for hatching of Pronubas eggs and works as an incubator. After that, it climbs to the top of the style and pushes the pollen ball into stylar canal. Thus, pollination occurs. Some seeds are eaten by larvae which escape after piercing the ovary wall.
Question
Natality refers to [NEET 2018]
(a) number of individuals leaving the habitat
(b) birth rate
(c) death rate
(d) number of individuals entering a habitat
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Natality is birth rate. It refers to the number of births during a given period in the population that are added to the initial density.
Death rate is termed as mortality. It refers to the number of deaths in the population during a given period. Immigration is the number of individuals of the same species that have come int the habitat, on the other hand emigration is the number of individuals of the population who left the habitat.
Question
Which one of the following population interactions is widely used in medical science for the production of antibiotics? [NEET 2018]
(a) Parasitism
(b) Mutualism
(c) Commensalism
(d) Amensalism
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Amensalism is widely used in medical science for the production of antibiotics.
It involves, the secretion of chemicals called allochemics by one microbial group to harm other microbes, e.g.. Penicillium secretes chemicals to inhibit the growth of Staphylococcus bacteria. These chemicals can be used in medical science for the production of antibiotics. On the other hand, no such chemicals are secreted in parasitism, mutualism and commensalism.
Question
In a growing population of a country, [NEET 2018]
(a) reproductive and pre-reproductive individuals are equal in number
(b) reproductive individuals are less than the post-reproductive individuals
(c) pre-reproductive individuals are more than the reproductive individuals
(d) pre-reproductive individuals are less than the reproductive individuals
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
In a growing population, younger population (or pre-reproductive individuals) size is larger than that of reproductive individuals. Such population is represented by a triangular-shaped age pyramid. Whereas, the equal number of reproductive and pre-reproductive individuals represents a stable population and the age pyramid is bell-shaped. Less number of pre-reproductive individuals than reproductive individuals represents declining population and age pyramid appears urn-shaped. The similar case is seen when reproductive individuals are less than the post-reproductive individuals.
Question
Asymptote in a logistic growth curve is obtained, when [NEET 2017]
(a) The value of ‘ $r$ ‘ approaches zero
(b) $K=N$
(c) $K>N$
(d) $K<N$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
When $K=N$ in a logististics growth curve, it is asymptote. It means a population growing in a habitat with limited resources show initially a lag phase, followed by phase of acceleration and deceleration and finally an asymptote, i.e. when the population density $(\mathrm{N})$ reaches the carrying capacity $(K)$
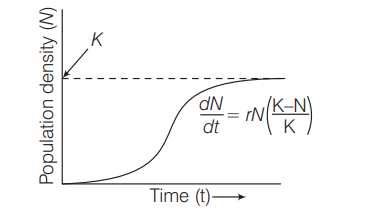
Population growth curve is logistic, when responses are limiting the growth,
here $K$ is carrying capacity and $N$ is population density.
Question
Mycorrhizae are the example of [NEET 2017]
(a) fungistasis
(b) amensalism
(c)antibiosis
(d) mutualism
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Mutualism is an association of two species in, which both species are benefitted. Mycorrhiza is a mutualistic relationship between fungal hyphae and roots of higher plants. The fungus helps in mineral nutrition absorption for the plants with, which they are associated and obtained in turn, nutrients from plants. Concept Enhancer
Amensalism is an interaction between different species, in which one species is harmed and other is neither benefitted nor harmed, e.g. Penicillium.
Antibiosis It is an antagonistic association between two or more organism, in which one is adversely affected, e.g. antibiosis includes the relationship between antibiotic and bacteria.
Fungistasis inhibits the growth of fungi.
Question
Gause’s principle of competitive exclusion states that [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) Competition for the same resources excludes species having different food preferences
(b) No two species can occupy the same niche indefinitely for the same limiting resources
(c) Larger organisms exclude smaller ones through competition
(d) More abundant species will exclude the less abundant species through competition
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Gause’s principle of competitive exclusion states that no two species can occupy the same niche indefinitely for the same limiting resources
Question
When does the growth rate of a population following the logistic model equal zero? The logistic model is given as $d N / d t=r N(1-N / K)$ [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) when $N$ nears the carrying capacity of the habitat
(b) when N/K equals zero
(c) when death rate is greater than birth rate
(d) when $N / K$ is exactly one
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
In logistic growth model population growth equation is described as
$
\frac{d N}{d t}=r N\left(\frac{K-N}{K}\right)
$
where, $N=$ Population density at time $t$
$r=$ Intrinsic rate of natural increase
$\mathrm{K}=$ Carrying capacity
when, $\frac{N}{K}=1$ then $\frac{K-N}{K}=0$
Therefore, $\frac{d N}{d t}=0$
Question
The principle of competitive exclusion was stated by [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) CDarwin
(b) GF Gause
(c) MacArthur
(d) Verhulst and Pearl
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The principle of competitive exclusion is stated by GF Gause. He studied the effects of interspecific competition between two closely related species. He stated that two species competing for the same food resource cannot coexist at the same place as highest degree of competitiveness exists between them.
Question
If ‘ $+$ ‘ sign is assigned to beneficial interaction, ‘ -‘ sign to detrimental and ‘ 0 ‘ sign to neutral interaction, then the population interaction represented by ‘+’ -‘ refers to [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) mutualism
(b) amensalism
(c) commensalism
(d) parasitism
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Parasitism is a relationship between two living organisms of different species in which one organism, i.e. parasite obtains its food directly from the host. In this relationship the parasite is benefitted $(+)$ and the host is harmed (-). So, this type of population interaction is represented by’ ‘” $^{\prime \prime}-$.
Question
Which of the following is correct for r-selected species? [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) Large number of progeny with small size
(b) Large number of progeny with large size
(c) Small number of progeny with small size
(d) Small number of progeny with large size
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
$r$-selected are the species having the ability to produce large number of progenies (offsprings) with small size. The population growth of these species is a function of biotic potential.
Hence, option (a) is correct.
Question
In which of the following interactions both partners are adversely affected? [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) Competition
(b) Predation
(c) Parasitism
(d) Mutualism
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Competition is a negative interaction that occurs among organisms whenever two or more organisms require the same limited resource.
Question
A biologist studied the population of rats in a barn. He found that the average natality was 250, average mortality 240, immigration 20 and emigration 30. The net increase in population is [NEET 2013]
(a) 10
(b) 15
(c) 05
(d) zero
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
A population has birth rates and death rates. The rates are expressed as change in numbers (increase or decrease) with respect to members of the population.
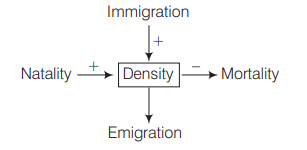
In this case, the net increases in population will be zero. Because Birth rate (B) + Immigration (I) − Death rate (D) + Emmigration (I) = Density of population.
Therefore, Density
=[250+20]-[240+30]=0
Question
A sedentary sea anemone gets attached to the shell lining of hermit crab. The association is [NEET 2013]
(a) ectoparasitism
(b) symbiosis
(c) commensalism
(d)amensalism
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
This type of mutualism to called symbiosis. In this type, the sea anemone grows on the back of the hermit crab. It protects the crab with the help of its nematocysts. In ectoparasitism an ectoparasite live on the outside of host, e.g. human body louse. In this interaction, the parasite gets the benefit at the expense of the host. Commensalism is an association between organisms in which one or both the species are benefitted and neither species is harmed. In amensalism one species is harmed, whereas the other is unaffected.
Question
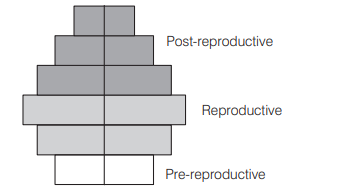
What type of human population is represented by the following age pyramid? [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) Vanishing population
(b) Stable population
(c) Declining population
(d) Expanding population
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
An age pyramid is a graphic representation of proportion of various age groups of a population with pre-reproductive at the base, reproductive in the middle and post reproductive at the top. For human population, the age pyramids show age distribution of males and females in a combined diagram. The shape of the age pyramids reflects the growth status of the population. In a declining population the shape of pyramid is urn-shaped.
Question
Consider the following four conditions (I-IV) and select a correct pair of them as adaptation to environment in desert lizards. Conditions [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
I. Burrowing in soil to escape high temperature.
II. Losing heat rapidly from the body during high temperature.
III. Bask in sun when temperature is low.
IV. Insulating body due to thick fatty dermis.
(a) III, IV
(b) I, III
(c) II, IV
(d) I, II
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Desert lizards bask in the sun and absorb heat when their body temperature drops below the comfort zone, but move into shade when the ambient temperature starts increasing. Some species are capable of burrowing into the soil to hide and escape from the above-ground heat.
Question
Which one of the following is categorised as a parasite in true sense? [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) The female Anopheles bites and sucks blood from humans
(b) Human foetus developing inside the uterus draws nourishment from the mother
(c) Head louse living on the human scalp as well as laying eggs on human hair
(d) The cuckoo (koel) lays its eggs in crow’s nest
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Human head louse (Pediculus) lives among hair and surface of human body feeding on blood. It spreads diseases like typhus. It is a true parasite.
Question
Which one of the following is one of the characteristics of a biological community? [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) Stratification
(b) Natality
(c) Mortality
(d) Sex-ratio
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Organisms are not uniformly distributed throughout a community. They usually occur in definite zones. This spatial arrangement of populations is called stratification which is characteristic of biological community. Natality, mortality, age structure and sex-ratio are the basic characteristics of a population.
Question
A country with a high rate of population growth took measures to reduce it. The figure below shows age sex pyramids of populations. A and B twenty years apart. Select the correct interpretation about them [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
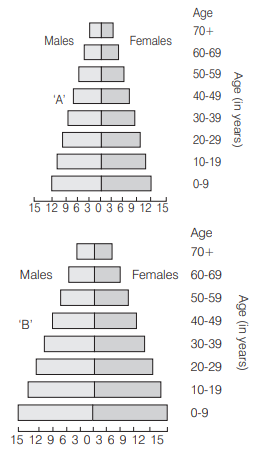
(a) ‘A’ is more recent and shows slight reduction in the growth rate
(b) ‘B’ is earlier pyramid and shows stabilised growth rate
(c) ‘B’ is more recent showing that population is very young
(d) ‘A’ is the earlier pyramid and no change has occurred in the growth rate
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Interpretation ‘ $a$ ‘ is correct for the given figures. As ‘A’ is more recent and shows slight reduction in the growth rate.
Question
A high density of elephant population in an area can result in [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) mutualism
(b) intraspecific competition
(c) interspecific competition
(d) predation on one another
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Intraspecific competition is an important density dependent factor regulating populations. Intraspecific competition occurs between the members of same population.
Question
The population of an insect species shows an explosive increase in numbers during rainy season followed by its disappearance at the end of the season. What does this show? [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) S-shaped or sigmoid growth of this insect
(b) The food plants mature and die at the end of the rainy season
(c) Its population growth curve is of J-type
(d) The population of its predators increases enormously
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Its population growth curve is $\mathrm{J}$-shaped in which density increases rapidly in exponential fashion and then stops abruptly as environmental resistance or another limiting factor becomes effective more or less suddenly.
Question
Geometric representation of age structure is a characteristic of [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) biotic community
(b) population
(c) landscape
(d) ecosystem
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Geometric representation of age structure is a characteristic of population. In most populations, individuals are of different ages. The proportion of individuals in each age group is called age structure of that population.
Question
If the mean and the median pertaining to a certain character of a population are of the same value, the following is most likely to occur [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) normal distribution
(b) bi-modal distribution
(c) T-shaped curve
(d) skewed curve
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
For a normal distribution the mean, median and mode are actually equivalent.
Question
The formula for exponential population growth is [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) $d t / d N=r N$
(b) $d N / r N=d t$
(c) $r N / d N=d t$
(d) $d \mathrm{~N} / d \mathrm{t}=\mathrm{rN}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
J-shaped form of population growth is mathematically described by an equation of exponential or geometric increase, which is as follows :
$
\frac{d N}{d t}=r N
$
where, $d=$ rate of change
$
t=\text { time }
$
$N=$ number of females at a particular time
$r=$ biotic potential of each female
( $N$ can also be considered as the total
population and $r$ as the biotic potential of each individual).
Question
Niche overlap indicates [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) active cooperation between two species
(b) two different parasites on the same host
(c) sharing of one or more resources between the two species
(d) mutualism between two species
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Niche overlap is a measure of the association of two or more species.
This indicate their similar habitat requirement and may also indicate competition if trophic niche/spatial niche is same and food/space is limiting, e.g. two different parasites on the same host.
Question
Praying mentis is a good example of [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) Mullerian mimicry
(b) warning colouration
(c) social insects
(d) camouflage
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Praying mantis (Mantis religiosa) is a large social insect. It has small triangular head, a long prothorax and an abdomen consisting of ten segments. The wings are well developed and the pincer-like forelegs are modified for grasping prey. It usually inhabits plantation areas. It destroys certain harmful insects so, it is useful.
Question
Animals have the innate ability to escape from predation. Examples for the same are given below. Select the incorrect example [CBSE AIPMT 2005]
(a) enlargement of body size by swallowing air in puffer fish
(b) melanism in moths
(c) poison fangs in snakes
(d) colour change in Chamaeleon
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Animals resist predation by cryptic colouration, deceptive marking. behavioural defenses and the possession of mechanical or chemical defenses.
Example
Enlargement of body size by swallowing air in puffer fish.
Melanism in moths.
Colour change in Chamaeleon.
Question
Mycorrhiza is an example of [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) endoparasitism
(b) decomposers
(c) symbiotic relationship
(d) ectoparasitism
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Mycorrhiza is a result of symbiosis between the roots of higher plants and fungi. In this association, plants provide space and prepared food material to fungi in exchange of this, fungi help in absorption of minerals and water to plants.
Question
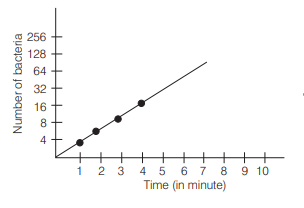
The semilog of per minute growing bacteria is plotted against. time. What will be the shape of graph? [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) Sigmoid
(b) Hyperbola
(c) Ascending straight line
(d) Descending straight line
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Semilog of per minute growing bacterium when plotted against time, would yield ascending straight line.
Question
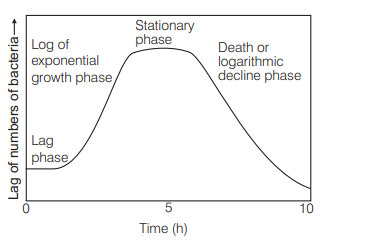
Choose the correct sequence of stages of growth curve for bacteria [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) lag, log, stationary, decline phase
(b) lag, log, stationary phase
(c) stationary, lag, log, decline phase
(d) decline, lag, log phase
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
When microbes are grown in a closed system or batch culture, the resulting growth curve has usually four phases :
(a) lag phase
(b) exponential (log phase)
(c) stationary phase
(d) death phase
Question
Which type of association is found in between entomophilous flower and pollinating agent? [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) Mutualism
(b) Commensalism
(c) Cooperation
(d) Co-evolution
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
A plant and its pollinator have a mutualistic relationship. The plant uses its pollinator to ensure cross pollination while pollinator uses the plant as food.
Question
Which of the following is a correct pair? [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) Cuscuta — Parasite
(b) Dischidia — Insectivorous
(c) Opuntia — Predator
(d) Capsella — Hydrophyte
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Cuscuta, commonly known as dodder or amarbel, is a parasitic plant.
Question
Two different species cannot live for long duration in the same niche or habitat. This law is [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) Allen’s law
(b) Mendel’s law
(c) Gause’s competitive exclusion principle
(d) Weismann’s theory
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The principle of competitive exclusion was postulated by Soviet ecologist GF Gause. It states that if two species are competiting with one another for the same limited resource, then one of the species will be able to use that resource more efficiently than the other and the former will, therefore, eventually eliminate the latter locally.
Question
An orchid resembling the female of an insect, so as to be able to get pollinated is due to the phenomenon of [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) mimicry
(b) pseudocopulation
(c) pseudopollination
(d) pseudoparthenocarpy
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
For its pollination, the orchid Ophyrys speculum has picked on the most selective attraction in the entire animal kingdom. It is pollinated by a hairy wasp, Colpa aurea. The wasp has a fixed habit whereby its males leave the burrows for above ground existence about four weeks before the females emerge for the open-air mating. The orcind opens its flowers about the same time the males appear and they possess an appearance and odour similar to those possessed by the famele wasps. The inexperienced males mistake the Ophrys flowers for their female counterparts and land to perform the act of pseudocopulation. The insect repeats the act with a number of orchid flowers and carries pollinia from one flower to another. This insect-plant relationship is beneficial only to the plant.
Question
The concept that population tends to increase geometrically while food supply increases arithmetically was put forward by [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) Stuart Mill
(b) Adam Smith
(c) Charles Darwin
(d) Thomas Malthus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Malthus in his ‘Essay on the principle of population’ (1798), pointed out that population tends to increase in geometric progression while food supply increases only in arithmetic progression.
Question
Which of the following pair is correctly matched? [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) Uricotelism-Aquatic habitat
(b) Parasitism-Intra-specific relationship
(c) Excessive perspiration-Xeric adaptation
(d) Stream lined body-Aquatic adaptation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The correct pair is stream lined body to aquatic adaptation which helps these animals in swimming.
Question
A mutually beneficial association necessary for survival of both partners are [CBSE AIPMT 91, 88]
(a) mutualism/symbiosis
(b) commensalism
(c) amensalism
(d) Both (a) and (b)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Mutualism is an association between two organisms of different species where both are benefitted but cannot live separately (both favour the growth and survival of each other and their association is obligatory), e.g. pollination by animals, dispersal of fruits and seeds by animals, lichens, etc.
Question
The relation between algae and fungi in a lichen is [CBSE AIPMT 1989]
(a) symbiosis
(b) parasitism
(c) commensalism
(d) protocooperation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The relation between algae and fungi in a lichen is symbiosis. In lichen fungi is for water intake and algae is photosynthetic and prepares food.
Question
Phenomenon when organisms resembling others for escaping from enemies is [CBSE AIPMT 1988]
(a) adaptation
(b) mimicry
(c) homology
(d) analogy
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Mimicry is the phenomenon of resemblance of one species with another. It is a means of adaptation and protection against predation. The species which is copied is called a model, while the animal which copies other is known as mimic, e.g. viceroy butterfly mimics toxic monarch butterfly.
Question
Association between sucker fish (Remora) and shark is [CBSE AIPMT 1988]
(a) commensalism
(b) symbiosis
(c) predation
(d) parasitism
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Remora(Echeneis) has modified its dorsal fin into a sucker. It attaches to the body of sharks, whales, etc. This type of association is known as commensalism, in which one partner gets benefits while other is not harmed.
