Question
Respiratory Quotient $(\mathrm{RQ})$ value of tripalmitin is [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) $0.7$
(b) $0.07$
(c) $0.09$
(d) $0.9$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The RQ value of tripalmitin is $0.7$. It can be calculated as follows
Respiratory Quotient (RQ)
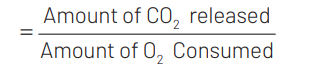
$2\left(\mathrm{C}_{51} \mathrm{H}_{98} \mathrm{O}_6\right)+145 \mathrm{O}_2 \rightarrow 102 \mathrm{CO}_2+98 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$
Tripalmitin
$
\mathrm{RO}=\frac{102 \mathrm{CO}_2}{1450 \mathrm{O}_2}=0.7
$
It is to note that $\mathrm{RQ}$ of common fats is usually less than 1 under aerobic conditions.
Question
How many ATP molecules could maximally be generated from one molecule of glucose, if the complete oxidation of one mole of glucose to $\mathrm{CO}_2$ and $\mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$ yields 686 $\mathrm{kcal}$ and the useful chemical energy available in the high energy phosphate bond of one mole of ATP is $12 \mathrm{kcal}$ [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) 30
(b)$ 57 $
(c) $ 1$
(d) 2
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
One mole of ATP liberates $12 \mathrm{kcal}$ of energy. so $686 \mathrm{kcal}$ will be liberated by $686 / 12=57.1$ ATP molecules.
Question
How many ATP molecules are produced by aerobic oxidation of one molecule of glucose? [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) 2
(b) 4
(c) 38
(d) 34
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
A total of 38 molecules of ATP are produced during aerobic respiration of one molecule of glucose Summary of ATP synthesis
8 ATP from glycolysis.
6 ATP from acetyl Co-A.
24 ATP from Krebs’ cycle.
Total =38ATP from aerobic oxidation of one molecule of glucose.
Question
Net gain of ATP molecules during aerobic respiration is[CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) 36 molecules
(b) 38 molecules
(c) 40 molecules
(d) 48 molecules
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
During aerobic respiration, 38 ATP molecules are gained. If specifically aerobic respiration in eukaryote is asked, then the answer would be 36 ATP because 2 ATP molecules are produced byFADH, which accepts the $\mathrm{H}^{+}$from 2 NADH molecules produced in glycolysis.
Question
Respiratory quotient (RO) for fatty acid is [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) $>1$
(b) $<1$
(c) 1
(d) 0
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Respiratory Quotient (RO)
$
=\frac{\text { Volume of } \mathrm{CO}_2 \text { formed }}{\text { Volume of } \mathrm{O}_2 \text { utilised }}
$
In fats, large amount of $O_2$ is used to combine with $\mathrm{H}_2$, so output of $\mathrm{CO}_2$ is less and $\mathrm{RQ}$ is only $0.70$, i.e., less than unity.
Question
Respiratory substrate yielding maximum number of ATP molecule is[CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) ketogenic amino acids
(b) glucose
(c) amylose
(d) glycogen
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Respiratory substrate yielding maximum number of ATP molecules is glucase. One glucose molecule on aerobic respiration yields 36 ATP molecules.
Question
Maximum amount of energy/ATP is liberated on oxidation of [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) fats
(b) proteins
(c) starch
(d) vitamins
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Fats or lipids are second to carbohydrates as a source of energy. By weight, each gram mol of fat yields about $9.3 \mathrm{kcal}$ of energy, i.e. more than double of that yielded by glucose.
Question
Apparatus to measure rate of respiration and $R Q$ is [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) auxanometer
(b) potometer
(c) respirometer
(d) manometer
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Respirometer is an instrument used to measure the rate of respiration and also Respiratory Quotient (RO). The most common respirometer is Ganong’s respirometer.
Question
When one glucose molecule is completely oxidised, it changes [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) 36 ADP molecules into 36 ATP molecules
(b) 38 ADP molecules into 38 ATP molecules
(c) 30 ADP molecules into 30 ATP molecules
(d) 32 ADP molecules into 32 ATP molecules
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In aerobic respiration or biological oxidation of one glucose molecule, 38 ADP molecules change into 38 ATP molecules, where donor phosphate is inorganic phosphate. ATP molecules are the energy currency of the cell, i.e. the common immediate source of energy in cellular activity.
Question
Which one of the following statements about cytochrome 450 is wrong? [CBSE AIPMT 1999]
(a) It contains iron
(b) It is a coloured cell
(c) It has an important role in metabolism
(d) It is an enzyme involved in oxidation reactions
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Cytochrome is not a coloured cell, instead this is a respiratory pigment-mixture of iron and protein which are electron acceptors. Cytochrome are membrane bound hemeproteins contains heme groups and are primarily responsible for the generation of ATP via electron transport.
Question
$ R O$ is [CBSE AIPMT 1988]
(a) $\mathrm{C} / \mathrm{N}$
(b) $\mathrm{N} / \mathrm{C}$
(c) $\mathrm{CO}_2 / \mathrm{O}_2$
(d) $\mathrm{O}_2 / \mathrm{CO}_2$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Respiratory Quotient $(\mathrm{RO})$ is the ratio of volume of $\mathrm{CO}_2$ evolved to the volume of oxygen consumed per unit time per unit weight. Therefore, $\mathrm{RQ}=\mathrm{CO}_2 \mathrm{~N}_2$. It is useful in knowing the type of respiration, major transformations and respiratory substrate.
