Question
Match the following columns and select the correct option from the codes given below. [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
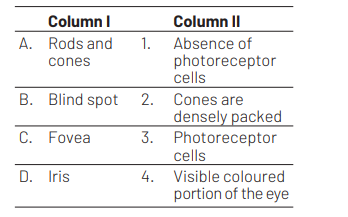
Codes
A B C D
(a) 3 1 2 4
(b) 2 3 1 4
(c) 3 4 2 1
(d) 2 4 3 1
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The option (a) is correct match which is as follows. Rods and cones are photoreceptor cells of eye.Blind spot is the area where there is absence of any photoreceptor cells in the eye.
Fovea is the area in the eye where cones are densely packed. Iris is the visible coloured portion of the eye.
Question
Match the following columns and select the correct option. [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
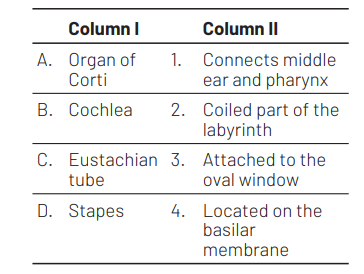
A B C D
(a) 3 1 4 2
(b) 4 2 1 3
(c) 1 2 4 3
(d) 2 3 1 4
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Option (b) is correct because organ of Corti is located on the basilar membrane. The coiled portion of the labyrinth is called cochlea. The Eustachian tube connects the middle ear cavity with the pharynx. The middle ear contains ossicle called stapes that is attached to the oval window of the cochlea.
Question
Which of the following receptors are specifically responsible for maintenance of the balance of body and posture? [NEET (Odisha) 2019]
(a) Basilar membrane and otoliths
(b) Hair cells and organ of Corti
(c) Tectorial membrane and macula
(d) Crista ampullaris and macula
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The inner ear contains crista ampullaris and macula as the specific receptors of the vestibular apparatus responsible for maintenance of balance of the body and posture.
Question
Which of the following statements is correct? [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) Cornea consists of dense connective tissue of elastin and can repair itself
(b) Cornea is convex, transparent layer which is highly vascularised
(c) Cornea consists of dense matrix of collagen and is the most sensitive portion of the eye
(d) Cornea is an external, transparent and protective proteinaceous covering of the eyeball
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The statement that cornea consists of dense matrix of collagen and is the most sensitive portion of the eye is correct. Rest statements are incorrect. The correct information about the statements is as follows The outer layer of the wall of eyeball, sclera, consists of a dense connective tissue containing mainly collagen and some elastic fibre. Cornea is convex, transparent layer which is non-vascularised. The cornea is the clear part of eye’s protective covering.
Question
The transparent lens in the human eye is held in its place by [NEET 2018]
(a) smooth muscles attached to the iris
(b) ligaments attached to the iris
(c) ligaments attached to the ciliary body
(d) smooth muscles attached to the ciliary body
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The lens in the human eye is held in place by the suspensory ligaments attached to the ciliary body. The function of other components are as follows The smooth muscles attached to the ciliary body helps to control the shape of lens. Smooth muscles of iris help in regulating the diameter of pupil. Pactinate ligament attached to iris is involved in the drainage of aqueous humor because it contains spaces between the fibres.
Question
Photosensitive compound in human eye is made up of [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) opsin and retinal
(b) opsin and retinol
(c) transducin and retinene
(d) guanosine and retinol
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Photosensitive pigment rhodopsin in human eye is made up of opsin protein and retinal [aldehyde form of vitamin-A (retinol)]. These pigments are present in the rod cells of retina layer of eye.
Question
Choose the correct statement. [NEET 2016, Phase II]
(a) Nociceptors respond to changes in pressure
(b) Meissner’s corpuscles are thermoreceptors
(c) Photoreceptors in the human eye are depolarised during darkness and become hyperpolarised in response to the light stimulus
(d) Receptors do not produce graded potentials
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The photosensitive compounds (Rhodopsin) in the human eye is composed of opsin (a protein) and retinal (an aldehyde of vitamin-A, i.e. retinol).
It is present in the rod cells (Photoreceptors). Light induces dissociation of retinol, from opsin thus changing the structure of opsin. This creates potential differences in the photoreceptors and they become hyperpolarised. However, during darkness rhodopsin is resynthesised from opsin and retinine to restore the dark vision and photoreceptors are depolarised.
The correct form of other statements are
(a) Nociceptors are sensory nerve cells that respond to potentially damaging chemical or mechanical stimuli and send them to brain and spinal cord.
(b) Meissner’s receptors are tactile receptors receiving the stimuli of pressure.
(d) Receptors always produce graded potentials.
Question
In mammalian eye, the ‘fovea’ is the center of the visual field, where [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) high density of cones occur, but has no rods
(b) the optic nerve leaves the eye
(c) only rods are present
(d) more rods than cones are found
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
At the posterior pole of the eye lateral to the blind spot, there is a yellowish pigmented spot called macula lutea with a central pit called the fovea. It is a thinned-out portion of the retina where only the cones are densely packed. It is the point where the visual acuity (resolution) is the highest.
Question
Which one of the following statements is not correct? [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) Retinal is the light absorbing portion of visual photopigments
(b) In retina the rods have the photopigment rhodopsin, while cones have three different photopigments
(c) Retinal is a derivative of vitamin-C
(d) Rhodopsin is the purplish red protein present in rods only
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Retinal pigment of epithelium shields the retina from excess incoming light. It supplies omega-3 fatty acid and glucose to the retina. The former is used for building photoreceptive by membranes the latter used for energy retinal is supplied by the visual vitamin-A cycle.
Question
Parts $A, B, C$ and $D$ of the human eyes are shown in the diagram. Select the option, which gives correct identification along with its functions/characteristics [NEET 2013]
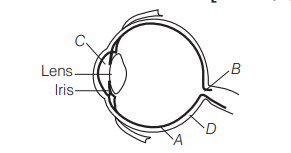
(a) A-Retina-contains photoreceptors-rods and cones
(b) B-Blind spot-has only a few rods and cones
(c) C-Aqueous chamber-reflects the light, which does not pass through the lens
(d) D-Choroidits anterior part forms ciliary body
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
A-Retina-Contains photoreceptors rods and cones. The daylight vision is function of cones and twilight vision is related to rods.
B-Blind spot-Photoreceptor cells are not present in this part.
C-Aqueous chamber contains a thin watery fluid called aqueous humour. D-Sclera is the external layer of eye having dense connective tissue.
Question
Which part of the human ear plays no role in hearing as such but is otherwise very much required? [CBSE AIPMT 2012]
(a) Eustachian tube
(b) Organ of Corti
(c) Vestibular apparatus
(d) Ear ossicles
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The inner ear contains a complex system called vestibular apparatus which is located above the cochlea. It has no role in hearing but is influenced by gravity and movements. Its specific receptors called crista and macula are responsible for maintenance of balance of the body and posture.
Question
The purplish red pigment rhodopsin contained in the rods type of photoreceptor cells of the human eyes is a derivative of [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) vitamin-C
(b) vitamin- $D$
(c) vitamin-A
(d) vitamin-B
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
There are two types of photoreceptor cells of retina, namely rods and cones. The rods contain a purplish red protein called the rhodopsin (visual purple), which is a derivative of vitamin-A.
Question
Cornea transplant in human is almost never rejected. This is because [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) its cells are least penetrable by bacteria
(b) it has no blood supply
(c) it is composed of enucleated cells
(d) it is a non-living layer
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Comea is a transparent portion that forms the anterior one-sixth of the eyeball. The cornea admits and helps to focus light waves as they enter the eye. It is avascular, i.e., has no blood supply therefore, cornea transplant in human is almost never rejected.
Question
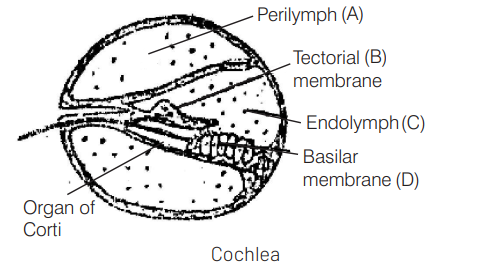
Given below is a diagrammatic cross section of a single loop of human cochlea. [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
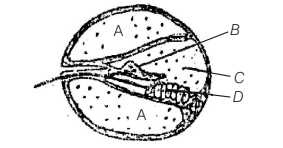
Which one of the following options correctly represents the names of three different parts?
(a) B-Tectorial membrane, C-Perilymph, D-Secretory cells
(b) $C$-Endolymph, $D-$ Sensary hair cells, A- Serum
(c) D-Sensory hair cells, A-Endolymph, B-Tectorial membrane
(d) A-Perilymph, B-Tectorial membrane, C-Endolymph
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Cochlea is the main hearing organ, which is connected with saccule by short ductus reunions leading from the saccule. It consists of three fluid filled chambers or canals the upper scala vestibuli, lower scala tympani and middle scala media. Both scala vestibuli and scala tympani are filled with perilymph (A) while scala media is filled with endolymph.(C) The tectorial membrane (B) overhangs the sensory hair in scala media.
Question
Which one of the following is the correct difference between rod cells and cone cells of our retina? [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
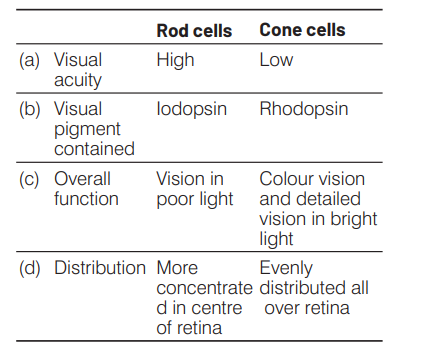
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The rods contain the rhodopsin (visual purple) pigment and enable the animals to see in darkness. Therefore, present in large number in nocturnal animals. The cones contain the iodopsin (visual violet) pigment and chiefly concerned with distinction in colour and light vision during day time.
Question
Bowman’s glands are located in the [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) proximal end of uriniferous tubules
(b) anterior pituitary
(c) female reproductive system of cockroach
(d) olfactory epithelium of our nose
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Many olfactory glands (Bowman’s glands) occur below the olfactory epithelium that secrete mucus over the epithelium to keep it moist.
Question
What is the intensity of sound in normal conversation? [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) 10-20 dB
(b) $35-60 \mathrm{~dB}$
(c) $70-90 \mathrm{~dB}$
(d) 120-150 dB
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The intensity of sound in normal conversation is around $35-60 \mathrm{~dB}$. The word noise is orginated from the Latin word nausea and is defined as unwanted or unpleasant sound that causes discomfort. Intensity of some noise sources is as follows
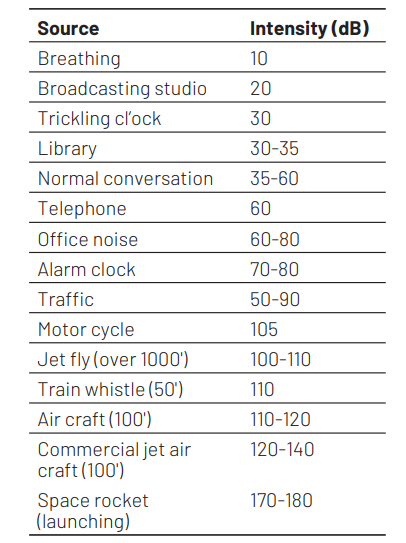
Question
Characteristic feature of human cornea is that [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) it is secreted by conjunctiva and glandular tissue
(b) it is lacrimal gland which secretes tears
(c) blood circulation is absent in cornea
(d) in old age it become hard and white layer deposits on it which causes the cataract
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Human eye is about 1 inch in diameter and is covered and protected by the sclera, which is made up of tough connective tissue. The front of eye is transparent thus allows the light to enter the eye. This portion of the eye’s outer layer is called cornea. It lacks a blood supply. It derives nutrients vio aqueous humour from cell body. Cornea not only allows light to enter the eye but also bend it as well. This makes it a characteristic feature of human eye, i.e. camea.
Question
When we migrate from dark to light, we fail to see for some time but after a time visibility becomes normal. It is an example of [CBsE AIPMT 2001]
(a) accommodation
(b) adaptation
(c) mutation
(d) photoperiodism
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
It takes some time for rhodopsin to split. into scotopsin and retinal (bleaching) and release of transmitter passing nerve impulse va bipolar and ganglion cells to the optic nerves. This is a case of adaptation. It differs from accommadation which is a reflex mechanism by which the focus of the eye change to make the images of distant and near objects sharp on the retina.
Question
In the chemistry of vision in mammals, the photosensitive substance is called [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) sclerotin
(b) retinal
(c) rhodopsin
(d) melanin
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Rods of the retina contain the light-sensitive pigment rhodopsin which is formed by a combination of the protein molecule called scotopsin and a small light absorbing molecule called retinene(retinal).
Question
In frog, ‘fenestra ovalis’ is [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) the opening in the auditory capsule which separates the middle ear trom internal ear
(b) the air-tilled cavity of the middle ear
(c) the communication between the pharynx and the tympanic cavity
(d) the external opening of the tympanic cavity which is covered by the tympanic membrane
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
‘Fenestra ovalis’ is an oval aperture through which tympanic cavity is connected with auditory capsule which houses the internal ear.
Question
Comea transplantation is outstandingly successful because [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) cornea is easy to preserve
(b) comea is not linked up with blood vascular and immune systems
(c) the technique involved is very simple
(d) comea is easily available
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Comea is non-vascular, i.e. no blood supply so, its transplantation is outstandingly successtul.
Question
Retina is most sensitive at [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) optic disc
(b) periphery
(c) macula lutea
(d) fovea centralis
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Retina is most sensitive at fovea centralis. It is with a depression, fovea centralis in its middle-N it is the area of most distinct day vision. Yellow spot ar macula lutea or area centralis is a small area on retina which lies opposite to optical axis of the lens. Only cones are present in this area so, it most sensitive to day light vision.
Question
Function of iris is to [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) move lens forward and backward
(b) refract light rays
(c) bring about movements of eyelids
(d) alter the size of pupil
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Iris controls the amount of light that reaches the photosensars at the back of the eye. It consists of circular sphincters and radial dilatars. The function of iris is to alter the size of pupil.
Question
Light rays entering the eye are controlled by [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) pupil
(b) iris
(c) cornea
(d)lens
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Pupil is the black hole in the centre of the iris. It is the area through which light enters the eyeball, i.e. pupill is the aperture that controls the light entering into the eye.
Question
Iris is part of [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) sclerotic
(b) choroid/uvula
(c) choroid and retina
(d) sclerotic and choroid
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Iris consists at two layers, outer ane lies in continuation with choroid, while inner one is in continuation with retina.
Question
Sensitive pigmented layer of eye is [CBSE AIPMT 1989]
(a) cornea
(b) retina
(c) sclerotic
(d)iris
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Retina consists of a pigmented layer and a nervous tissue layer, first there is the photoreceptor layer containing photosensitive cells, the rods and cones. Rod cells are sensitive towards light and are used for vision in dim light, having no ability to detect colour, whereas cones are used tor bright light vision with the ability to make coloured images of the object.
Next is the intermediate layer containing short sensory bipolar neurons. Bipolar cells inturn synapse with the retinal ganglion cells, whose axons bundle together as the optic nerve.
Question
Acute vision is present in [CBSE AIPMT 1988]
(a) vulture
(b) shark.
(c) bat
(d) frog
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Acute vission is found in birds like vulture.
