Question
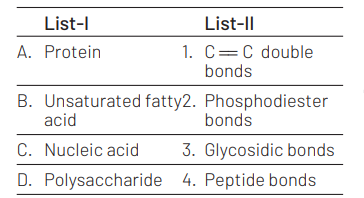
Match the List-I with List-II. [NEET 2021]
Choose the correct answer from the options given below.
A B C D
(a) $4 \quad 123$
(b) $1 \quad 4 \quad 3 \quad 2$
(c) $2 \quad 1 \quad 4 \quad 3$
(d) $431 \quad 2$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
(A)-(4), (B)-(1), (C)-(2), (D) (3)
Proteins are polypetides, they are linear chain of amino acids linked by peptide bond. Unsaturated fatty acids are carbon chains containing one or more double bonds with terminal carboxylic acid. The two sugar molecules of nucleic acids are linked together vio phosphodiester bond. Polysaccharides are long chain of sugar molecules joined with a covalent bond, i.e. glycosidic linkage.
Question
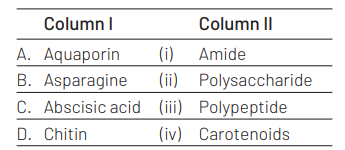
Match the items in Column I with those in Column II. [NEET (Oct.) 2020]
Select the correct option.
A B C D
(a) (iii) (i) (iv) (ii)
(b) (ii) (iii) (iv) (i)
(c) (ii) (i) (iv) (iii)
(d) (iii) (i) (ii) (iv)
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Option (a) is correct match which is as follows
Chemically, aquaporins are major intrinsic proteins that form pores in the membranes of cell. Asparagine is beta-amide derivative of aspartic acid. Abscisic acid is an apo-carotenoid.
Chitin is a heteropolysaccharide consisting of two types of monosaccharide monomers.
Question
DNA precipitation out of a mixture of biomolecules can be achieved by treatment with [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) chilled ethanol
(b) methanol at room temperature
(c) chilled chloroform
(d) isopropanol
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Chilled ethanol is used to precipitate DNA out of a mixture of biomolecules. Low temperature protects the DNA by slowing down the activity of enzymes that could break it apart and ethanol helps in the quick precipitation of DNA.
Question
Which one of the following statements is wrong? [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) Cellulose is a polysaccharide
(b) Uracil is a pyrimidine
(c) Glycine is a sulphur containing amino acid
(d) Sucrose is a disaccharide
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Glycine is the simplest amino acid in which functional group ‘ $R$ is replaced by hydrogen atom $(\mathrm{H})$.
Question
Which of the following biomolecules does have a phosphodiester bond? [CBSE AIPMT 2015]
(a) Fatty acids in a diglyceride
(b) Monosaccharides in a polysaccharide
(c) Amino acids in a polypeptide
(d) Nucleic acids in a nucleotide
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Phosphodiester bond is in responsible for linking nucleotides in nucleic acid (DNA and RNA).
Question
Given below is the diagrammatic representation of one of the categories of small molecular weight organic compounds in the living tissues. Identify the category shown and the one blank component $X$ in it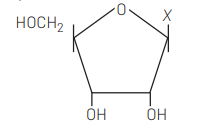
[CBSE AIPMT 2012] Category Component
(a) Cholesterol – Guanine
(b) Amino acid $-\mathrm{NH}_2$
(c) Nucleotide – Adenine
(d) Nucleoside – Uracil
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
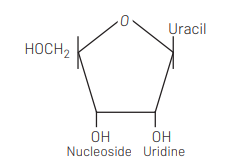
Nucleoside is made up of ribose sugar and nitrogenous base only. Uracil forms nucleoside with only ribose sugar. So, the option with category nucleoside component uracil is correct.
Question
Which one of the following structural formula of two organic compounds is correctly identified along with its related function? [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
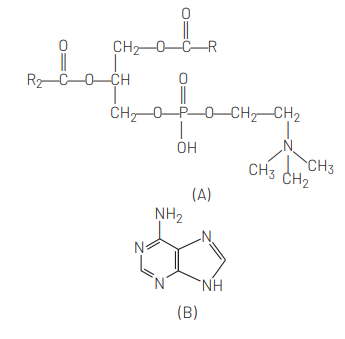
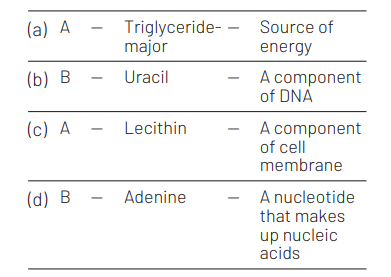
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Lecithin is a phospholipid composed of choline and inositol. It is found in all living cells as a major component of cell membrane.
Question
Which one of the following is the correct matching of three items and their grouping category? [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
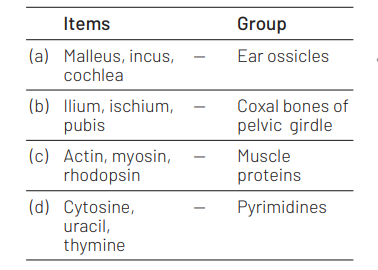
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
There are total five nitrogenous bases found in nucleic acids. Out of these adenine, guanine (purines) and cytosine, thymine (pyrimidines) are present in DNA, while RNA contains uracil in place of thymine (both pyrimidines) along with rest 3 similar to DNA.
Question
Which one of the following pairs of nitrogenous bases of nucleic acids, is wrongly matched with the category mentioned against it? [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) Thymine, Uracil – Pyrimidines
(b) Uracil, Cytosine – Pyrimidines
(c) Guanine, Adenine-Purines
(d) Adenine, Thymine – Purines
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
DNA and RNA the principal genetic materials of living organisms are chemically called nucleic acids. These are polymers of nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of phosphoric acid, pentose sugar and nitrogenous base. The nitrogenous bases are of two types, i.e. purine and pyrimidines.
Purines are heterocyclic and two rings, e.g. adenine, guanine.
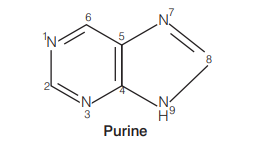
Pyrimidines are single ring compound, e.g. thymine, cytosine, uracil.
Question
In the DNA molecule [CBSE AIPMT 2008]
(a) the total amount of purine nucleotides and pyrimidine nucleotides is not always equal
(b) there are two strands which run parallel in the $5^{\prime} \rightarrow 3^{\prime}$ direction
(c) the proportion of adenine in relation to thymine varies with the organism
(d) there are two strands which run antiparallel one in $5^{\prime} \rightarrow 3^{\prime}$ direction and other in $3^{\prime} \rightarrow 5^{\prime}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
In DNA molecule the adjacent deoxyribonucleotides are joined in a chain by phosphodiester bridges or bonds, which link the $5^{\prime}$ carbon of deoxyribose of one mononucleotide unit with $3^{\prime}$ carbon of deoxyribose of next mononucleotide unit.
According to Watson and Crick DNA molecule consists of two such polynucleotide chains wrapped helically around each other, with the sugar phosphate chain on the outside and purine and pyrimidine on the inside of helix.
The two strands run antiparallel, i.e. one strand has phosphodiester linkage in $3^{\prime}$ $\rightarrow 5^{\prime}$ direction while other strand has phosphodiester linkage in $5^{\prime} \rightarrow 3^{\prime}$ direction. Chargaff $(1950)$ suggested that despite wide compositional variations exhibited by different types of DNA the total amount of purines equaled the total amount of pyrimidines $(A+G=T+C)$.
Question
The two polynucleotide chains in DNA are [CBSE AIPMT 2007]
(a) parallel
(b) discontinuous
(c)antiparallel
(d) semiconservative
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
In 1953 James Watson and Francis Crick suggested that in a DNA molecule there are two polynucleotide chains arranged antiparallel or in opposite directions.
Question
One turn of the helix in a B-form DNA is approximately [CBSE AIPMT 2006]
(a) $0.34 \mathrm{~nm}$
(b) $3.4 \mathrm{~nm}$
(c) $2 \mathrm{~nm}$
(d) $20 \mathrm{~nm}$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
B-DNA is helical structure with $20 \AA$ diameter and the distance between the two base pairs is $3.4 \AA$ and there are 10 base pairs in each turn or pitch (one round). Hence, one turn of the helix is approximately $34 \AA$ or $3.4 \mathrm{~nm}(10 \AA=1.0 \mathrm{~nm})$. Z-DNA (in comparision to B-DNA) is left handed double helical structure in which double helix winds to left in zig-zag pattern (instead of right, like B-DNA).
Question
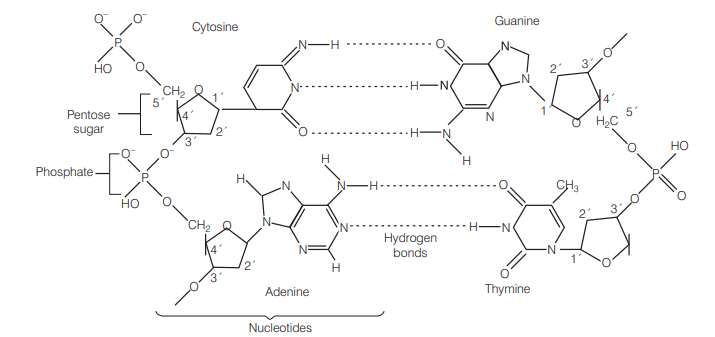
Nucleotides are building blocks of nucleic acids. Each nucleotide is a composite molecule formed by [CBSE AIPMT 2005, 1991]
(a) base-sugar-phosphate
(b) base-sugar- $\mathrm{OH}$
(c)(base-sugar-phosphate
(d) sugar-phosphate
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Nucleotides are the building blocks of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). A single nucleotide is composed of a phosphate molecule, a five carbon sugar (either ribose or deoxyribose) and a purine (adenine or guanine) or a pyrimidine (thymine or cytosine or uracil) nitrogenous base.
Question
ATP is a [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) nucleotide
(b) nucleosome
(c) nucleoside
(d) purine
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
A nucleotide contains (a) a 5-C sugar (b) a phosphate molecule (c) a nitrogenous base. ATP is also a nucleotide. It also has a 5-C sugar (ribose), 3 phosphate molecules and a nitrogenous base (adenine).
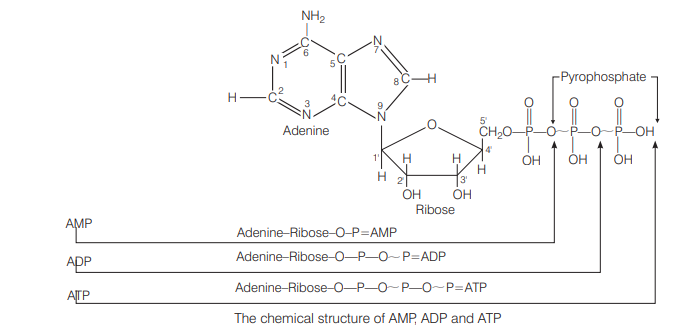
Adenine + sugar (ribose) $\rightarrow$ Adenosine
Adenosine $+1$ phosphate $\rightarrow$ Adenosine Monophosphate (AMP)
AMP $+1$ phosphate $\rightarrow$ Adenosine Diphosphate (ADP)
Question
Which one of the following amino acids is an essential part of human diet ? [CBSE AIPMT 2000]
(a) Glycine
(b) Phenylalanine
(c) Serine
(d) Aspartic acid
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
For human beings, eight amino acids are essential. These are leucine, isoleucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan and valine.
Question
Radioactive thymidine when added to the medium surrounding living mammalian cells gets incorporated into the newly synthesised DNA. Which of the following types of chromatin is expected to become radioactive if cells are exposed radioactive thymidine as soon as they enter the S-phase? [CBSE AIPMT 1998]
(a) Heterochromatin
(b) Euchromatin
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Neither (a) nor (b) but only the nucleolus
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
In the beginning of S-phase, DNA replication occurs. DNA replication can occur in diffuse/less tightly coiledeuchromatin. So active DNA stains light in colour when stained with acetocarmin and feulgen reagent in comparison to heterochromatin.
Question
DNA synthesis can be specifically measured by estimating the incorporation of radio labelled [CBSE AIPMT 1997]
(a) uracil
(b)adenine
(c) thymidine
(d) deoxyribose sugar
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
DNA consists of deoxyribose sugar, phosphate molecules and nitrogenous bases-adenine, guanine, cytosine and thymine, whereas RNA consists of ribose sugar, phosphate molecules and nitrogenous bases-adenine, guanine, cytosine and uracil.
Thus, estimating the incorporation of radiolabelled thymine can measure DNA synthesis and radiolabelled uracil can measure RNA synthesis, as all other nitrogenous bases are similar in both DNA and RNA.
Question
The nitrogenous organic base purine occurring in RNA is [CBSE AIPMT 1996]
(a) cytosine
(b) thymine
(c) guanine
(d) uracil
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Purines are 9-membered double ring nitrogen bases which possess nitrogen at 1, 3, 7 and 9 positions, e.g. adenine (A), guanine (G). These purines are present in both DNA and RNA.
Question
Two free ribonucleotide units are interlinked with [CBSE AIPMT 1995]
(a) peptide bond
(b) covalent bond
(c) hydrogen bond
(d) phosphodiester bond
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
The bonds that exist between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and hydroxyl group of sugar (ribose or deoxyribose) of the adjacent nucleotide is known as phosphodiester bond.
Question
Which is wrong about nucleic acids? [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) DNA is single stranded in some viruses
(b) RNA is double stranded occasionally
(c) Length of ane helix is $45 \AA$ in B-DNA
(d) One turn of Z-DNA has 12 bases
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Length of one helix or the pitch per turn and $46 \AA$ in Z-model of DNA. In Z-DNA sugar moieties are seen in opposite direction. So the 3-5 diester bond forms zig-zag structure in Z-DNA.
Question
Adenine is [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) purine
(b) pyrimidine
(c) nucleoside
(d) nucleotide
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Nitrogen bases are of two types-purines and pyrimidines. Purines are 9 membered double ring nitrogen bases which possess nitrogen at 1, 3,7 and 9 positions, e.g. adenine (A) guanine (G). Pyrimidines are 6-membered nitrogen bases that contain nitrogen at 1 and 3 positions, e.g. cytosine (C), thymine (T), uracil (U).
Question
Which is distributed more widely in a cell? [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) DNA
(b) RNA
(c) Chloroplasts
(d) Spherosomes
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Ribonucleic Acid(RNA) is a single chain polyribonucleotide which functions as carrier of coded genetic information from DNA to cytoplasm, and takes part in protein and enzyme synthesis. RNA is more common and abundant than DNA. There are six types of RNAs-ribosomal (most abundant), transfer RNA(15\% to total RNA), messenger RNA $(2-5 \%)$ small sized nuclear RNA, small cytoplasmic RNA, and genetic RNA (in viruses called riboviruses).
Question
The basic unit of nucleic acid is [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) pentose sugar
(b) nucleoid
(c) nucleoside
(d) nucleotide
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) are linear mixed polymers of nucleotides, so also called polynucleotides. Nucleic acids were first discovered by Miescher (1868-69) as nuclein and named nucleic acid by Altmann (1889). They are formed of $\mathrm{C}, \mathrm{H}, \mathrm{O}, \mathrm{N}$ and $\mathrm{P}$ comprising nitrogenous heterocyclic bases viz purines or pyrimidines, pentose sugar and phosphoric acid.
Question
DNA is composed of repeating units of [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) ribonucleosides
(b) deoxyribonucleosides
(c) ribonucleotides
(d) deoxyribonucleotides
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Nucleic acids are repeating units of nucleotides, DNA is formed of the repeating units of deoxyribonucleotides and RNA is a mixed polymer chain of ribonucleotides.
Question
In RNA, thymine is replaced by [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) adenine
(b) guanine
(c)cytosine
(d) uracil
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Uracil forms nucleoside with only ribose sugar while thymine forms the same with only deoxyribose sugar. Other nitrogen bases (i.e. adenine, guanine, cytosine) produce nucleosides with both sugars.
Question
RNA does not possess [CBSE AIPMT 1988]
(a) uracil
(b) thymine
(c)adenine
(d) cytosine
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) contains pyrimidine bases-cytosine and uracil and purine bases-adenine and guanine. Thymine is the pyrimidine base present only in DNA and uracil is present only in RNA, though other nitrogenous bases remain the same in both DNA and RNA.
Question
In double helix of DNA, the two DNA strands are [CBSE AIPMT 1988]
(a) coiled around a common axis
(b) coiled around each other
(c) coiled differently
(d) coiled over protein sheath
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Deoxyribo Nucleic Acid (DNA) is helically coiled macromolecule, made up of two antiparallel polydeoxyribonucleotide chains held together by hydrogen bonds. The chains are interlocked and are coiled around a common axis. DNA has a diameter of $20 \AA$. One turn of spiral has a distance of $34 \AA$ containing 10 nucleotides in each turn.
