Question
Match the following columns and select the correct option. [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
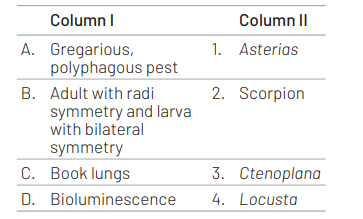
A B C D
(a) 4 1 2 3
(b) 3 2 1 4
(c) 2 1 3 4
(d) 1 3 2 4
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
The correct option is (a). It can be explained as follows Locusta is a gregareous pest. In echinoderms, adults are radially symmetrical but larvae are bilaterally symmetrical. Scorpions respire through book lungs. Bioluminescence is well-marked in ctenophores.
Question
Bilaterally symmetrical and acoelomate animals are exemplified by [NEET (Sep.) 2020]
(a) Platyhelminthes
(b) Aschelminthes
(c) Annelida
(d) Ctenophora
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Platyhelminthes are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and acoelomate animals with organ level of organisation. Aschelminthes are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and pseudocoelomate with organ system grade of body organisation. Annelida are bilaterally symmetrical, triploblastic and truly schizocoelomate. Ctenophora are biradially symmetrical,triploblastic and acoelomates.
Question
Planaria possess high capacity of [CBSE AIPMT 2014]
(a) metamorphosis
(b) regeneration
(c) alternation of generation
(d) bioluminescence
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Planaria is a flatworm belonging to phylum-Platyhelminthes. They are the simplest form of multicellular animal.
They have high capacity of regeneration of new tissue at the wound site via cell proliferation (blastema formation) and the remodelling of pre-existing tissue to restore symmetry and proportion. This is due the neoblast cells.
These cells are usually scattered through out the body and are able to participate in any type of development. The regenerative capacity of different body sections is an indicator of the presence of different numbers of neoblast cells.
Question
One example of animal having a single opening to the outside that serves both as mouth as well as anus is [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) Octopus
(b) Asterias
(c) Ascidia
(d) Fasciola
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Fasciola hepatica(sheep liver fluke) belongs to phylum-Platyhelminthes.
These worms have incomplete alimentary canal, there is a single opening for both ingestion and egestion. This is also called as blind sac body plan.
Question
Which one of the following kinds of animals are triploblastic? [CBSE AIPMT 2010]
(a) Flatworms
(b) Sponges
(c) Ctenophores
(d) Corals
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Flatworms (phylum-Platyhelminthes) are triploblastic animals. The cells of the body wall are arranged in three layers. i.e. ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm.
Sponges, ctenophores and corals are diploblastic animals.
Question
During its life cycle, Fasciola hepatica (liver fluke) infects its intermediate host and primary host at the following larval stages respectively [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) metacercaria and cercaria
(b) miracidium and metacercaria
(c) redia and miracidium
(d) cercaria and redia
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Liver fluke (Fasciola hepatica) is a ‘digenetic’ endoparasite, i.e. its life cycle completes within two hosts. The primary host is sheep and the secondary or intermediate host is fresh water gastropod, snail. Fasciola hepatica infects its intermediate host at miracidium stage and its primary host at metacercaria stage.
Question
Which one belongs to Platyhelminthes? [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) Schistosoma
(b) Trypansoma
(c) Plasmodium
(d) Wuchereria
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Schistosoma is the common human blood fluke and belongs to Platyhelminthes. It is a genus of trematodes.
It is a parasitic flatworm responsible for a highly significant group of infections in humans termed as Schistosomiasis.
Question
What is true about Taenia saginata? [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) Life history has pig as intermediate host
(b) There are two large suckers on scolex
(c) Rostellar hooks are absent
(d) Rostellum has double circle of hooks
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Taenia saginata do not possess rostellum and rostellar hooks.
Question
What is correct about Taenio? [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) Male organs occur in posterior proglottids
(b) Male organs occur in anterior proglottids
(c) Female organs occur in anterior proglottids
(d) Mature proglottids contain both male and female organs
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Body of Taenia is divided into scolex, neck and strobilla. Strobilla is the main body and made of proglottids. A proglottid is a unit of body enclosing a complete set of genitalia.
Mature proglottids are in the middle having both male and female reproductive organs.
Question
The excretory structures of flat worms/Taenia are [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) flame cells
(b) protonephridia
(c) Malpighian tubules
(d) green glands
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Excretory structures of flatworms/Taenia are flame cells. Longitudinal and cross-connecting excretory canals drain fluid from flame cells in each proglottid. Main excretory products are ammonia and fatty acids.
Question
Bladderworm/cysticercus is the larval stage of [CBSE AIPMT 1991]
(a) tapeworm
(b) roundworm
(c) pinworm
(d) liver fluke
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Bladderworm/Cysticercus is the larval stage of tapeworm. It is found in the muscles of pig and this is the stage through which man gets infected by eating raw or poorly cooked ‘measly pork’.
Question
Transfer of Taenia to secondary host occurs as [CBSE AIPMT 1989, 90]
(a) oncosphere
(b) cysticercus
(c) morula
(d) egg
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Oncospheres pass through faecal matter of man. Secondary host pig acquires infection by ingesting the oncospheres.
