Question
Grass leaves curl inwards during very dry weather.Select the most appropriate reason from the following [NEET (National) 2019]
(a) Flaccidity of bulliform cells
(b) Shrinkage of air spaces in spongy mesophyll
(c) Tyloses in vessels
(d) Closure of stomata
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Flaccidity of bulliform cells is the most appropriate reason for the curling of grass leaves during dry weather.
Bulliform cells are present between the epidermal cells of the leaf and they help to minimise the water loss due to transpiration during water stress period.
Question
Stomatal movement is not affected by [NEET 2018]
(a) $\mathrm{O}_2$ concentration
(b) Light
(c) Temperature
(d) $\mathrm{CO}_2$ concentration
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Stomatal movement is not affected by $\mathrm{CO}_2$ concentration. Stomata are tiny pore complexes found in the epidermis of leaves and other soft aerial parts.
They are meant for the gaseous exchange but are also the main source of transpiration. Stomatal movements are affected by many factors like light, temperature and $\mathrm{CO}_2$ concentration. In the majority of plants, the stomata are open in light and close in darkness. Normally high temperature above $30^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ reduces stomatal opening in many species. Low $\mathrm{CO}_2$ concentration usually induces opening of stomata while high $\mathrm{CO}_2$ concentration closes the same.
Question
Stomatal movement is not affected by [NEET 2018]
(a) $\mathrm{O}_2$ concentration
(b) Light
(c) Temperature
(d) $\mathrm{CO}_2$ concentration
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Stomatal movement is not affected by $\mathrm{O}_2$ concentration. Stomata are tiny pore complexes found in the epidermis of leaves and other soft aerial parts. They are meant for the gaseous exchange but are also the main source of transpiration. Stomatal movements are affected by many factors like light, temperature and $\mathrm{CO}_2$ concentration. In the majority of plants, the stomata are open in light and close in darkness. Normally high temperature above $30^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ reduces stomatal opening in many species. Low $\mathrm{CO}_2$ concentration usually induces opening of stomata while high $\mathrm{CO}_2$ concentration closes the same.
Question
Stomata in grass leaf are [NEET 2018]
(a) rectangular
(b) kidney-shaped
(c) dumb-bell-shaped
(d) barrel-shaped
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Epidermis of all green aerial parts of plants contain minute opening called stomata. It is surrounded by guard cells and neighbouring subsidiary cells collectivity termed as stomatal apparatus. Kidney-shaped or bean-shaped guard cells are present in dicots only, while in monocots like grasses, these cells are dumb-bell shaped. Guard cells differ from rest of the cells in shape, size and thickenings.
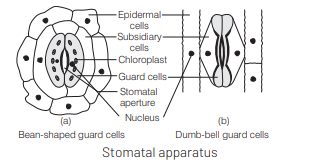
Question
Which of the following facilitates opening of stomatal aperture? [NEET 2017]
(a) Contraction of outer wall of guard cells
(b) Decrease in turgidity of guard cells
(c) Radial orientation of cellulose microfibrils in the cell wall of guard cells
(d) Longitudinal orientation of cellulose microfibrils in the cell wall of guard cells
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Stomata are tiny pore complexes. Each stomata is surrounded by two specialised green epidermal cells called guard cells. The opening of the stoma is facilitated by the orientation of the microfibril in the cell walls of the guard cells. Cellulose microfibrils are oriented radially rather than longitudinally making it easier for the stoma to open.
Question
Water vapour comes out from the plant leaf through the stomatal opening. Through the same stomatal opening carbon dioxide diffuses into the plant during photosynthesis. Reason out the above statements using the following options. [NEET 2016, Phase I]
(a) Both processes can happen together because the diffusion coefficient of water and $\mathrm{CO}_2$ is different
(b) The above processes happen only during night time
(c) One process occurs during day time and the other at night
(d) Both processes cannot happen simultaneously
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (a)
Diffusion of water vapour and $\mathrm{CO}_2$ are independent process. Their diffusion depends on the difference in their partial pressure in the atmosphere as well as inside the leaves.
Question
In land plants, the guard cells differ from other epidermal cells in having [CBSE AIPMT 2011]
(a) mitochondria
(b) endoplasmic reticulum
(c) chloroplasts
(d) cytoskeleton
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The guard cells of stomata in land plants are specialised epidermal cells which contain chloroplasts. In rest of epidermal cells, chloroplasts are absent. The chloroplasts of guard cells are capable of poor photosynthesis as there is absence of NADP reductase enzyme.
Question
Guard cells help in [CBSE AIPMT 2009]
(a) protection against grazing
(b) transpiration
(c) guttation
(d) fighting against infection
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Guard cells help in transpiration. Stomata are surrounded by two specialised epidermal cells, called guard cells. Because of their small size guard cells are rapidly influenced by turgor changes and thus regulate the opening and closing of stomata. Stomata are involved in releasing water vapour into the atmosphere. This process is known as transpiration.
Question
Stomata of a plant open due to [CBSE AIPMT 2003]
(a) influx of hydrogen ions
(b) influx of calcium ions
(c) influx of potassium ions
(d) efflux of potassium ions
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
Accumulation of $\mathrm{K}^*$ ions in the guard cells during the day time is responsible for migration of water molecules from subsidiary cells to guard cells. This increases turgidity of guard cells and thus stomata open.
Question
Opening and closing of stomata is due to [CBSE AIPMT 2002]
(a) hormonal change in guard cells
(b) change in turgor pressure of guard cells
(c) gaseous exchange
(d) respiration
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
When the guard cells become turgid, the stomata open. On the other hand, if the guard cells loose water, these become flaccid, the inner walls sag and the pore closes.
Thus, stomatal movement occurs due to changes in turgor pressure of guard cells.
Question
Glycolate induces opening of stomata in [CBSE AIPMT 2001]
(a) presence of oxygen
(b) low $\mathrm{CO}_2$ concentration
(c) high $\mathrm{CO}_2$ concentration
(d) absence of $\mathrm{CO}_2$
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Light causes photosynthesis which leads to reduction in $\mathrm{CO}_2$ concentration $\rightarrow$ synthesis of glycolate $\rightarrow$ oxidation of glycolate $\rightarrow$ ATP synthesis $\rightarrow$ activation of $\mathrm{K}^{+}$pump $\rightarrow$ movement of $\mathrm{K}^{+}$in guard cell $\rightarrow$ movement of water into guard cells $\rightarrow$ swelling of guard cell $\rightarrow$ opening of stomata.
Question
Which of the following is used to determine the rate of transpiration in plants? [CBSE AIPMT 1994]
(a) Porometer
(b) Potometer
(c) Auxanometer
(d) Tensiometer
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Potometer is an apparatus for measuring the rate of transpiration. It is also known as Transpirometer.
Question
Which of the following is an effective adaptation for better gas exchange in plants? [CBSE AIPMT 1993]
(a) Presence of multiple epidermis
(b) Presence of hair on the lower epidermis
(c) Presence of waxy cuticle covering the epidermis of the leaves
(d) The location of the stomata primarily on the lower surface of the leaf, the side turned away from the direct sun rays
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (d)
Stomata are meant for the gaseous exchange but are also the main source of transpiration. The presence of stomata on the lower surface of leaf, the side turned away from the direct sun rays is an effective adaptation for better gaseous exchange in plants.
Question
Conversion of starch to organic acid is essential for [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) stomatal closure
(b) stomatal opening
(c) stomatal initiation
(d) stomatal growth
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The starch hydrolyse into glucose 1-phosphate so that, osmotic potential becomes lower in guard cells. As a result of this water enters into the guard cell by osmotic diffusion from surrounding epidermal and mesophyll cells. Guard cells become turgid and stomata will open. The starch-sugar interconversion theory about the mechanism of stomatal movement was given by Seyere (1923) and modified by Steward (1964).
Question
In guard cells when sugar is converted into starch the stomatal pore [CBSE AIPMT 1992]
(a) opens fully
(b) opens partially
(c) closes completely
(d) remains unchanged
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
According to starch-sugar interconversion theory, during night the glucose 1-phosphate(sugar) converts into starch in guard cells and thus increasing the osmotic potential. The guard cells release water, become flaccid and stomata closes.
Question
In a terrestrial habitat which of the following is affected by temperature and rainfall condition? [CBSE AIPMT 1989]
(a) Translocation
(b) Transpiration
(c) Transformation
(d) Thermodenaturation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Transpiration increases with increase in temperature and decreases with rainfall conditions. Transpiration will also depends on number of stomata as more stomata may provide more pores for transpiration.
Question
Basis of stomatal opening is [CBSE AIPMT 1988]
(a) exosmosis
(b) endosmosis
(c) decrease in cell sap concentration
(d) plasmolysis of guard cells
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
The entry of water into a cell when placed in less concentrated solution is called endosmosis. Due to increase in osmotic pressure and diffusion pressure deficit of guard cells endosmosis of water from the surrounding epidermal and mesophyll cells takes place into the guard cells. The guard cells swell and the stomata open.
Question
Stomata in angiosperms open and close due to [CBSE AIPMT 1988]
(a) their genetic constitution
(b) effect of hormones
(c) change of turgor pressure in guard cells
(d) pressure of gases inside the leaves
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (c)
The turgor pressure of guard cell increases due to the osmotic diffusion of water from the surrounding epidermal and mesophyll cells. Thus, the guard cells swell and stomata open.
Question
The spraying of phenyl mercuric acetate in leaves [CBSE AIPMT 1988]
(a) increases transpiration
(b) reduces transpiration
(c) increases rate of photosynthesis
(d) causes guttation
Answer/Explanation
Ans. (b)
Phenyl mercuric acetate is an antitranspirant. It covers the stomata as a film and resist the diffusion of water therefore, reduces the rate of transpiration. Other antitranspirants include Abscisic Acid (ABA) and aspirin.
