All living things go through these 7 life processes

- Chickens, like all birds, lay eggs. Inside an egg that has been fertilised, a chick will grow and eventually hatch.
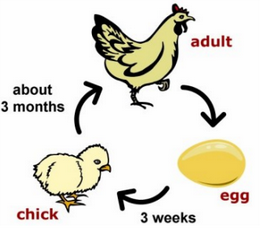
- A similarity of female birds, mammals most reptiles and some species of fish is that their eggs are fertilised inside the female.
- Mammal life cycle
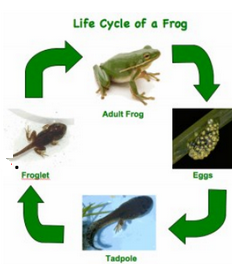
Frogs start off life as a mass of eggs called frogspawn. The eggs then hatch into tadpoles. They then gradually grow a set of back legs, and front legs. They lose their gills, and their tail shrinks.
A butterfly starts its life as an egg, which hatches into a caterpillar. Eventually, the caterpillar forms a chrysalis . Inside the chrysalis, it undergoes metamorphosis, before emerging as an adult butterfly.
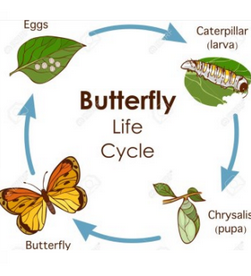
Both animals go though meta- morphosis.
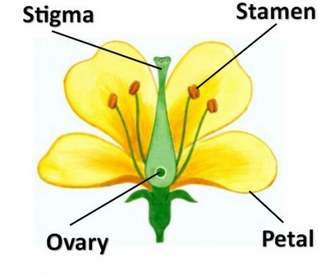
Sexual reproduction of a plant
- The stamen is the male part of the flower which holds pollen
- The carpel is the female part of the flower which contains eggs.
- Pollen travels from the anthers of one flower to the stigma of another plant. This is called pollination. Plants rely on bees or other insects to carry their pollen while some pollen floats in the wind.
- After pollination, the pollen grain and the egg join together, fertilisation.
- The fertilised egg will develop into a seed.
Asexual reproduction of a plant
Plant cuttings: Some plants stems can grow roots if they are planted in the correct conditions, such as geraniums. This allows for people to make lots of copies of the same plant.
Runners: Some plants, like strawberry plants, grow runners which have new plants on the end. These plants are an exact copy of the parent plant from which they have grown.
Bulbs: Other plants (onions, daffodils, garlic and tulips) produce bulbs which will grow if they are planted. The bulbs form under the soil. This helps the plant to survive during the winter months.
Focus Scientist
Jane Goodall, a behaviourist, is best known for her 60 year research on social interactions of wild chimpanzees.

Sir David Attenborough, a naturalist, who has dedicated his life to the study of natural history

Key Vocabulary
behaviourist: someone who studies animal behaviour: how they learn from their environment, rather than emotions or feelings.
naturalist: an expert in, or a student of, natural history.
seed dispersal: it is the way seeds get from the parent plant to a new place.
stigma: the stigma is the area where pollen is received.
stamen: the stamen is the part of the flower that produces pollen. There are two main parts of the stamen: the filament and anther.
life processes: there are seven life processes that every living thing has in common.
asexual reproduction: offspring obtain all of their information from just one individual (one parent).
pollination: the transference of pollen to a flower, or plant to allow fertilisation. Happens in sexual reproduction
life cycles: the series of changes that an animal or plant goes through from the beginning to the end of its life.
root: the part of a plant which attaches it to the ground. It transfers water and nutrients to the rest of the plant.
germination: the development of a plant from a seed or spore after a period of dormancy.
Life Cycles
Animals
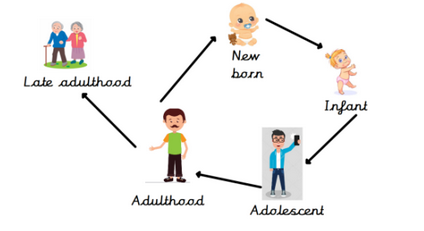
Animals have a life cycle thats starts with sexual reporduction.
An egg is fertilised by a sperm. This grows into an embryo which then develops into a baby. The baby grows up into an adult when it is able to reproduce itself before growing old and dying.
There are different types of animal and the process varies slightly in each type
