Living Things—What Do We Need To Know?
- Classification means to group living things based on similar characteristics.
- How to classify something as living or non-living —MRS GREN (Movement, Respiration, Sensitivity, Growth, Reproduction, Excretion and Nutrition)
- Understand that scientists have organised living things into 5 broad groups called kingdoms: plants, animals, fungi, protest and prokaryote. Children only need to know the characteristics of living things within the groups animals, plants and fungi. This will help them to classify animals into their similar and different characteristics
- To be able to group things (living and non-living) using a classification key.
- Learn about the work of Carl Linnaeus. Understand how his work impacts how we classify living things today.
- Understand what micro-organisms are and learn about the 3 distinct categories within this group (bacteria, virus and fungi). Know that some bacteria can be helpful/beneficial for our health and some can be harmful to our health. Learn how to stop harmful bacteria from spreading.
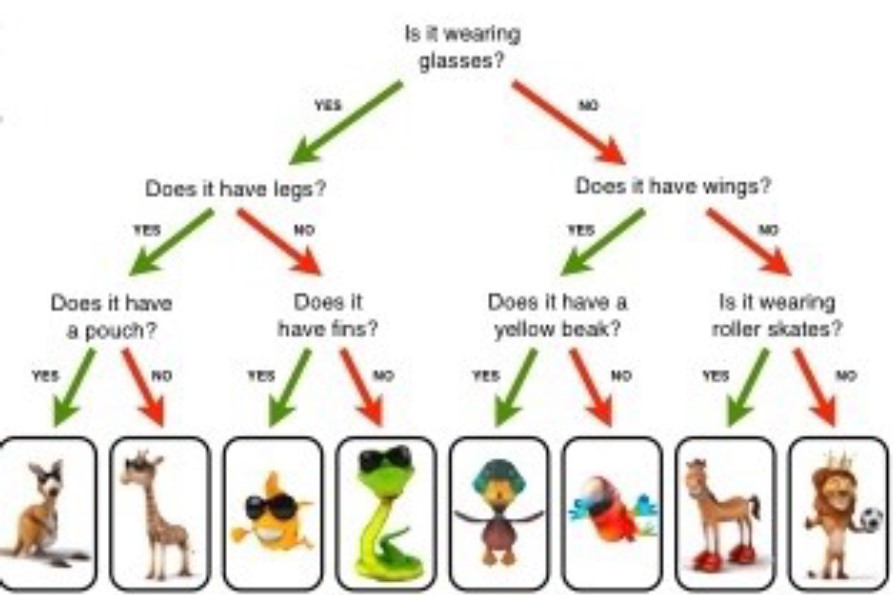
What is a classification key?
A classification key is a tool that uses yes/no questions to group living
The 7 Levels of Classification
Today we use 7 different levels of classification. These are as follows:
KINGDOM (KEEPING)
PHYLUM (PRECIOUS)
CLASS (CREATURES)
ORDER (ORGANISED)
FAMILY (FOR)
GENUS (GRUMPY)
SPECIES (SCIENTISTS)
Here is an example of how humans are classified. You will see that our species is homo sapiens.
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Primates
Family: Hominidae
Genus: Homo
Species: Homo sapiens

Focus Scientist
Carl Linnaeus (1707-1778) was a botanist, zoologist and physician. He’s most famous for simplifying the naming system scientists use to describe the millions of species on Earth.

Key Vocabulary
classification: a way of grouping things based on similar characteristics.
classification key: a series of questions about the organism’s physical characteristics.
living: alive now or once was alive. Has all of the 7 characteristics from MRS GREN.
non-Living: not alive now and never was alive. Does not possess all of the 7 MRS GREN characteristics e.g. fire.
vertebrate: living things with a backbone e.g. dogs, fish and humans.
invertebrate: living things without a backbone e.g. fly, spider, jellyfish.
amphibian: cold-blooded vertebrate animals (e.g. frogs and toads) that have gills and live in water as young but breathe air as adults.
bird: warm-blooded, egg-laying animals that have vertebrae, or a backbone. They are different from mammals because they lay hard -shelled eggs and have feathers. A bird has four limbs—two that are wings—along with a beak and no teeth.
fish: an animal that lives in water and has fins for swimming and gills for breathing. Fish are cold-blooded animals with skeletons inside their bodies. Most fish have scales on their skin.
mammal: an animal that breathes air, has a backbone, and grows hair at some point during its life. In addition, all female mammals have glands that can produce milk. Mammals include a wide variety of animals, from cats to humans to whales.
reptile: a cold-blooded animal (as a snake, lizard, turtle, or alligator) that breathes air and usually has the skin covered with scales or bony plates.
environment: all of the conditions that affect a living thing.
organism: a living thing made up of one or more cells and able to carry on the activities of life (e.g. using energy, growing, or reproducing).
characteristic: any feature that helps identify something.
