IB PHYSICS SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 4.1 – Oscillations
Topic 4 Weightage : 5 %
All Questions for Topic 4.1 – Simple harmonic oscillations , Time period, frequency, amplitude, displacement and phase difference , Conditions for simple harmonic motion
Question
An object performs simple harmonic motion (shm). The graph shows how the velocity v of the object varies with time t.
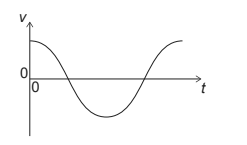
The displacement of the object is x and its acceleration is a. What is the variation of x with t and the variation of a with t ?
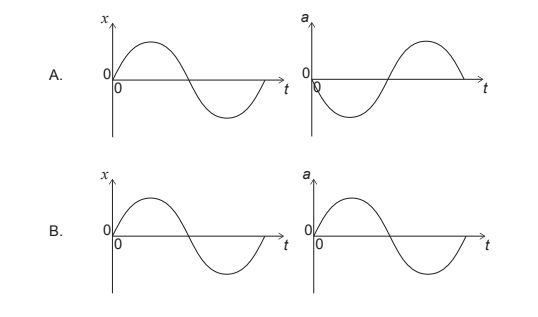
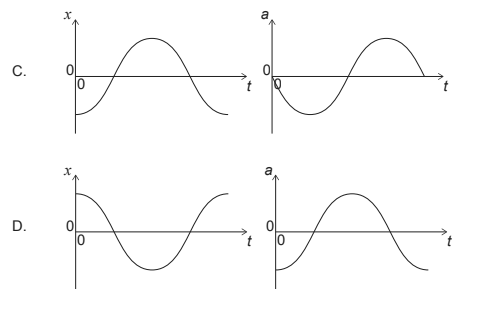
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
The displacement, velocity and acceleration of S.H.M. vary simple harmonically with the same time period and frequency.
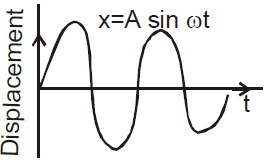

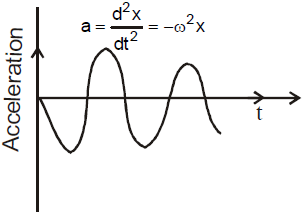
Phase difference between displacement – velocity is π/2 , Velocity – acceleration is π/2. and between displacement and acceleration is π.
Question
A small point mass m is placed at the same distance from two identical fixed spherical masses far from any other masses.
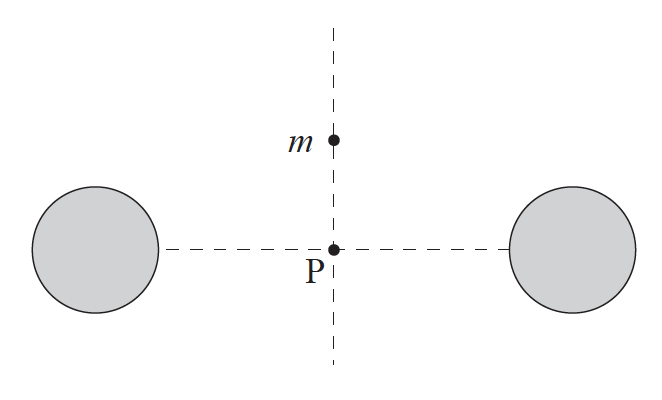
The point mass is released from rest. The point mass will
A. move upwards.
B. stay where it is.
C. move towards P and stop there.
D. oscillate about point P.
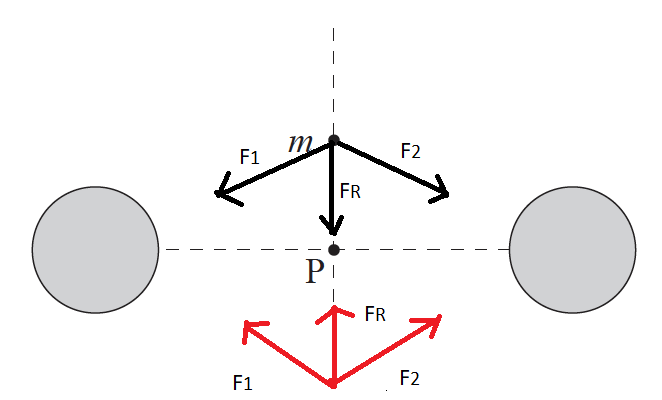
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
Question
The graph shows how the displacement varies with time for an object undergoing simple harmonic motion.
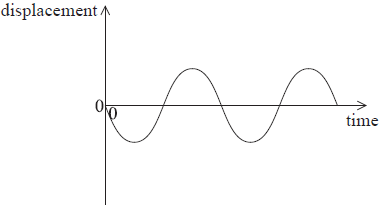
Which graph shows how the object’s acceleration a varies with time t?
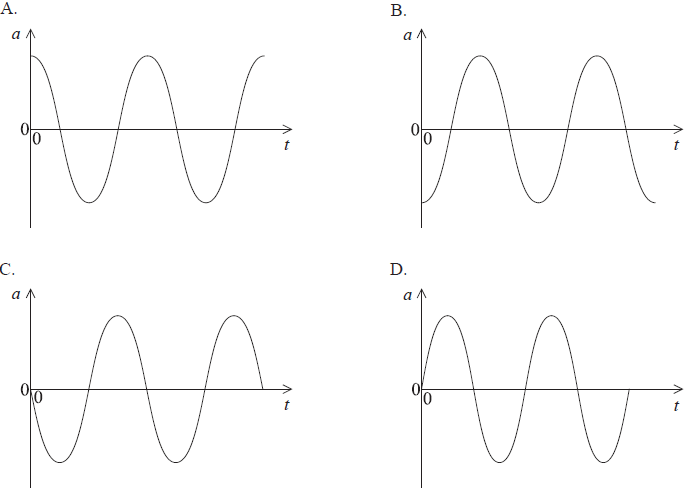
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
The displacement, velocity and acceleration of S.H.M. vary simple harmonically with the same time period and frequency.
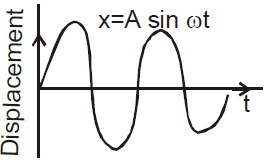


Phase difference between displacement – velocity is π/2 , Velocity – acceleration is π/2. and between displacement and acceleration is π.
Question
Two sound waves from a point source on the ground travel through the ground to a detector. The speed of one wave is 7.5 km s–1, the speed of the other wave is 5.0 km s–1. The waves arrive at the detector 15 s apart. What is the distance from the point source to the detector?
A. 38 km
B. 45 km
C. 113 km
D. 225 km
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
Given in the question,
speed of one wave is 7.5 km/s
speed of other wave is 5 km/s
difference between their arrival time = 15 sec
Formula to use \(time=\frac{distance}{speed}\)
Time difference is given as 15. Let the distance from Source to Detector be x
\(t_1-t_2=15\)
or
\(\frac{x}{5}-\frac{x}{7.5}=15\)
\(2.5x =562.5\)
\(x= 225 km\)
Question
A particle is displaced from rest and released at time t = 0. It performs simple harmonic motion (SHM). Which graph shows the variation with time of the kinetic energy Ek of the particle?
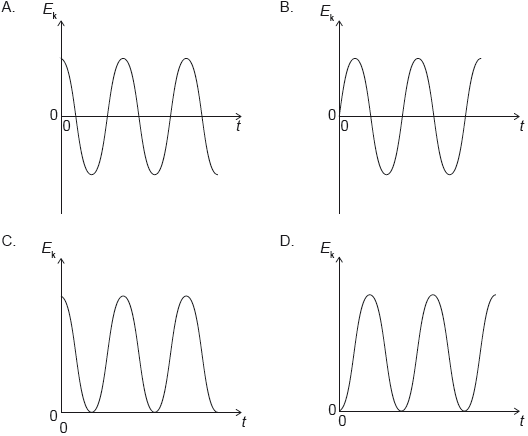
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
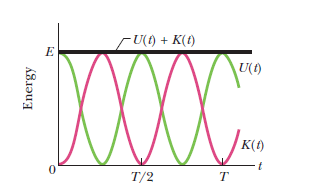
As time changes, the energy shifts between the two types, but the total is constant.
Question
A system that is subject to a restoring force oscillates about an equilibrium position.
For the motion to be simple harmonic, the restoring force must be proportional to
A. the amplitude of the oscillation.
B. the displacement from the equilibrium position.
C. the potential energy of the system.
D. the period of the oscillation.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
B
Ref: https://www.iitianacademy.com/ib-physics-unit-4-oscillations-notes/
EQUATIONS OF S.H.M.
Question
Two travelling waves are moving through a medium. The diagram shows, for a point in the medium, the variation with time t of the displacement d of each of the waves.
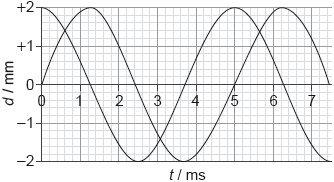
For the instant when t = 2.0 ms, what is the phase difference between the waves and what is the resultant displacement of the waves?
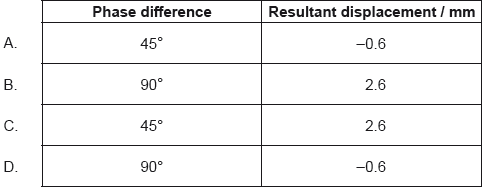
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
D
Ref: https://www.iitianacademy.com/ib-dp-physics-topic-4-waves-4-5-standing-waves-study-notes/
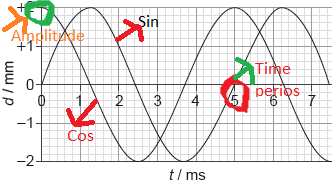
One wave is sine and other is cosine . Hence Phase difference = \(\frac{\pi}{2}\)
\(y_1=Asin\omega t\)
\(y_2 =A cos\omega t\)
\(y=y_1+y_2\)
\(= Asin\omega t +A cos\omega t\)
\(=A\sqrt{2}(sin\omega t \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} +cos\omega t \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}} )\)
\(=A\sqrt{2} (sin\omega t\times cos\frac{\pi}{4} +cos\omega t\times sin\frac{\pi}{4})\)
\(=A\sqrt{2} sin (\omega t +\frac{\pi}{4})\)
\(\omega = \frac{2\pi}{T} =\frac{2\pi}{5}\)
\(\therefore y= 2\times \sqrt{2}sin(\frac{2\pi}{5}\times 2 + \frac{\pi}{4})\)
\(=2\times \sqrt{2}sin(\frac{21\pi}{20})\)
\(=-2\times \sqrt{2}sin(\frac{\pi}{20}) \; \because sin(\pi+\theta) =-sin\theta\)
\(or\)
\(y=0.6\)
