IB Biology SL (Standard level)- 2024 – Practice Questions- All Topics
Topic 1.4 Introduction to cells
Topic 1 Weightage : 17 %
All Questions for Topic 1.4 –Types of Transport, Simple Diffusion, Osmosis, Osmolarity, Facilitated Diffusion, Active Transport, Vesicular Transport, Bulk Transport, Cotransport, Kidney Dialysis
Question
The diagram shows a section through a membrane. What are the modes of transport in the diagram?
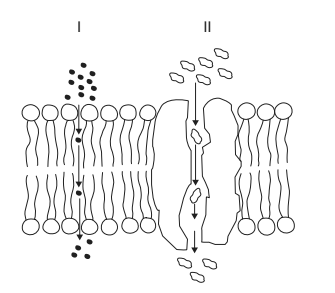
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
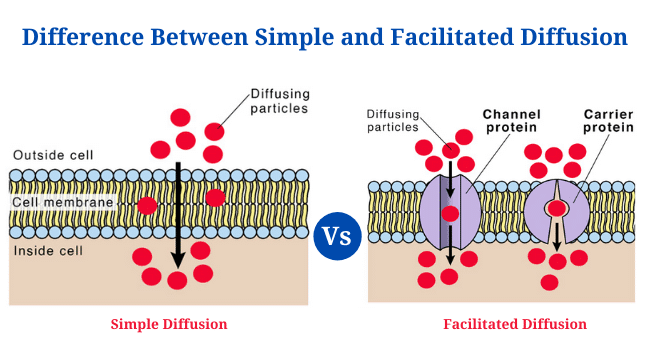
The difference between simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion is in their mechanism of transporting molecules across the cell membrane. Simple diffusion allows the direct transport of molecules across the cell membrane, while facilitated diffusion occurs via transmembrane proteins** like carrier proteins, channel proteins, and aquaporins. Some other differences are:
- Simple diffusion is not solute specific, while facilitated diffusion is directed by the specificity between solute and carrier molecules.
- Simple diffusion is mostly involved in the passage of small non-polar molecules, while facilitated diffusion is commonly involved in the movement of large and polar molecules across a biological membrane.
- Simple diffusion is not inhibited by an inhibitor molecule, while facilitated diffusion can be inhibited by specific inhibitor molecules.
- Simple diffusion has a relatively low speed, while facilitated diffusion has a relatively higher speed.
Both simple and facilitated diffusion are types of passive transport that do not require any energy and are driven by the concentration gradient across the membrane
Question
A human organ is being prepared for transplant. In what type of solution must it be bathed?
A hypertonic solution
A hypotonic solution
Pure water containing no solutes
A solution with the same osmolarity as the organ tissue.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
When a human organ is being prepared for transplant, it must be bathed in a solution with the same osmolarity as the organ tissue. Osmolarity measures the amount of solute concentration. If an organ is placed in a hypertonic solution (i.e., a solution that has a higher solute concentration), the organ bathed in a hypertonic solution will continue to absorb more water, which can eventually burst the organ when it is too much. If an organ is placed in a hypotonic solution (i.e., a solution that has a lower solute concentration), the organ bathed will have to lose more solution because itself has more solute than the solution and can lead to shrinkage. But when the osmolarity is the same, the organ will have the same solute concentration as the solution and will help keep the organ in its original form; it will not absorb or lose any solution.
Dialysis membrane was set up to model digestion and absorption in the small intestine.
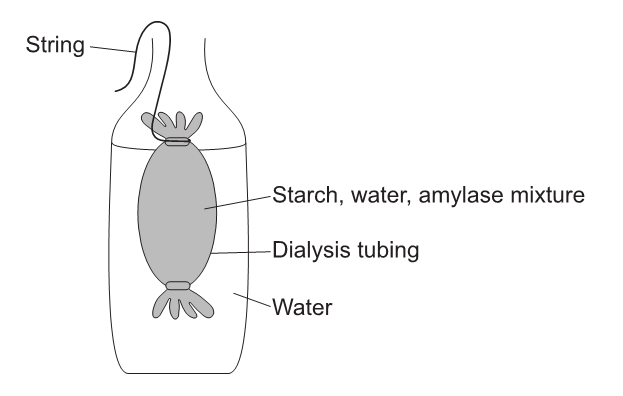
What is a limitation of this model?
A. There can be no active transport.
B. Maltose will pass through the membrane.
C. Lipase should be present with protein.
D. The membrane is not permeable to starch.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
A
A dialysis membrane can be used to model digestion and absorption in the small intestine. It is an accurate model because both are partially permeable so smaller particles can pass through the membrane whilst larger particles cannot; the membrane therefore allows the passive movement of solutes in diffusion, and water molecules in osmosis.
