IBDP Online Test Series By iitianacademy
Comprehensive Test Preparatory package targeted towards IBDP
Question
Discuss the endosymbiotic theory for the origin of eukaryotes.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes;
mitochondria/chloroplasts evolved from (independent) prokaryotic cells;
taken in by larger (heterotrophic) cell by endocytosis;
theory supported by characteristics of chloroplasts/mitochondria;
[2 max] for mitochondria/chloroplast characteristics:
mitochondria/chloroplasts have naked DNA;
mitochondria/chloroplasts divide/carry out fission;
mitochondria/chloroplasts have 70S ribosomes / synthezise own proteins;
mitochondria/chloroplasts have double membranes;
cristae similar to mesosomes / thylakoid have similar structures in prokaryotes;
but theory cannot be falsified as it predicts something occurring in the past;
theory does not explain the origins of cilia/flagella/linear chromosomes/meiosis;
weaker evidence that cilia/flagella evolved from attached bacteria/spirochetes;
Examiners report
Many candidates were able to score four or more marks on this question on the endosymbiotic theory by describing it and looking at the supporting evidence shown by the structure of chloroplasts or mitochondria. However, even those candidates scoring well seldom „discussed‟ the fact that evidence was weak for evolution of other organelles such as cilia or flagella and that the theory cannot be falsified.
Question
Define analogous characteristics using one example to illustrate your answer.
Outline two pieces of evidence that support the endosymbiotic theory for the origin of eukaryotes.
List two anatomical features that define humans as primates.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
analogous structure similar in appearance/function but with different evolutionary history e.g. wing of bat and wing of bird;
smaller/70S ribosomes in mitochondria/chloroplasts (as in prokaryotes);
circular DNA in mitochondria/chloroplasts (as in prokaryotes);
mitochondria/chloroplasts have double membrane;
similar size/shape of mitochondria/chloroplasts to prokaryotes;
opposable thumb;
large range of shoulder movement;
good vision / stereoscopic vision / overlapping field view;
large brain relative to body size;
tailless primate;
Y-5 cusps of molars;
Examiners report
Those that knew the correct definition did well.
The main pieces of evidence supporting the endosymbiotic theory for the origin of eukaryotes seen were double membranes and the presence of circular DNA.
The most popular answers here were those of humans having an opposable thumb and stereoscopic vision. Many though only gained one mark point here with the answer of opposable thumb.
Question
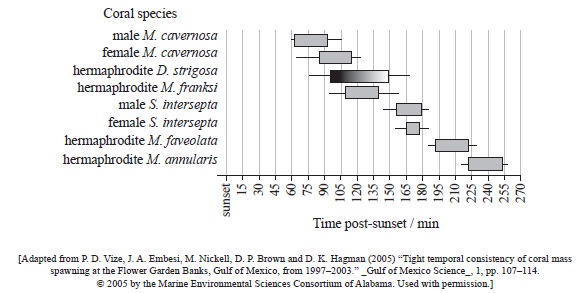
Corals can be male, female or hermaphrodite (both male and female) and the release of their gametes is called spawning. Data was collected to study the spawning behaviour in the Gulf of Mexico of three genera of coral: Montastraea, Stephanocoenia and Diploria. The spawning behaviour is expressed in minutes post-sunset. Peak spawning windows are shown as grey bars and the range as black bars.
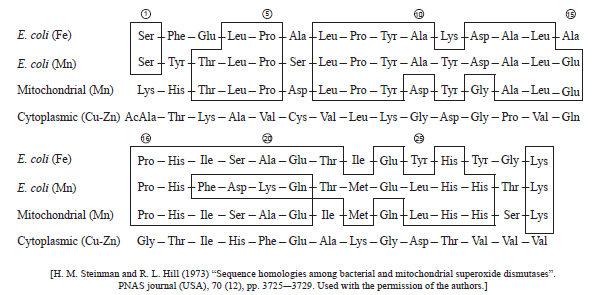
Superoxide dismutase is an enzyme used by cells to protect themselves against oxidative damage. These enzymes can have different metals as part of their structure.
A study to compare two dismutases from Escherichia coli bacteria and two dismutases from eukaryotic cells was undertaken. The following enzymes were used:
- E. coli dismutase with iron (Fe)
- E. coli dismutase with manganese (Mn)
- eukaryotic mitochondrial dismutase with manganese (Mn)
- eukaryotic cytoplasmic dismutase with copper-zinc (Cu-Zn).
The following shows part of the amino acid sequences of these enzymes. Boxes enclose identical amino acids in the sequence of the two E. coli and mitochondrial dismutases.
State the range of the time of spawning for the male M. cavernosa.
State how many amino acids are in the same position in the E. coli (Fe), E. coli (Mn) and the mitochondrial dismutase sequences shown.
State the amino acids which are present in the same position in at least one bacterial dismutase and in both eukaryotic dismutases.
Compare the E. coli (Mn) and the mitochondrial dismutases.
The sequences of the two bacterial dismutases and the mitochondrial dismutase show a high degree of homology. Discuss how this supports the endosymbiotic theory for the origin of mitochondria.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
from 60 to 105 minutes (post-sunset) / 45 minutes
11
Ile and Glu (both needed to award the mark)
a. share 17 (out of 29) amino acids in common / more amino acids similar than different;
b. both have Mn in the enzyme (as cofactor);
c. greatest difference between them is from amino acid 18 to 22;
d. mitochondrial has Gly (position 12) while E. coli (Mn) never has Gly;
e. Leu is most common amino acid in both appearing four times / other valid comparison;
a. endosymbiotic theory states bacteria were engulfed by organisms to become mitochondria;
b. sequence comparison between mitochondrial and bacterial dismutase supports this hypothesis;
c. more similarity in the amino acid sequence between mitochondrial and bacterial dismutase than between mitochondrial and cytoplasmic dismutase;
Examiners report
Most candidates performed well in the data analysis with (e) being the best discriminator of the better candidates.
Many candidates responded correctly to (a).
Many candidates responded correctly to (a) and (b), although some candidates only stated one of Ile and Glu.
[N/A]
Many candidates were familiar with the endosymbiotic theory and gained marks in (e).
