Question
The reaction that produces urea in liver cells is shown.
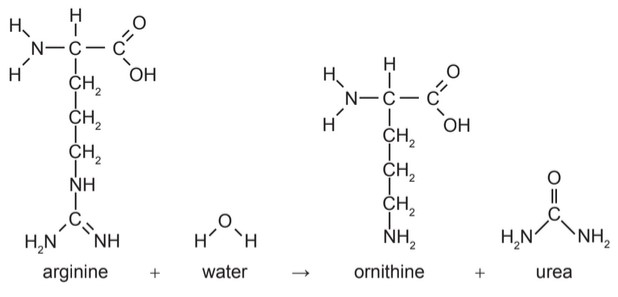
(a) Arginine and ornithine are in the same group of biochemicals. Identify this group.
(b) This reaction forms part of a metabolic cycle. Outline one feature of a metabolic cycle that distinguishes it from a chain.
(c) Predict what effect arginase has on the activation energy of this reaction.
(d) The concentration of urea in blood plasma is typically about 30mg per 100ml. In urine it can be as high as 1800mg per 100ml. Explain how this increase in concentration is achieved.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) amino acids;
(b)
a. initial molecule/substrate/intermediates are regenerated;
b. products become substrates/reactants;
(c) reduced/lowered (activation energy);
(d)
a. urea is toxic/ a (excretory) waste product removed from the body/ blood
(plasma) by the kidneys/in the urine (to be excreted in the urine);
b. urea filtered out from blood in glomerulus/Bowman’s capsule;
c. water reabsorbed from filtrate (by osmosis);
d. in proximal convoluted tubule/descending loop of Henle/collecting duct;
e. loop of Henle maintains hypertonic conditions in the medulla;
f. little/no urea reabsorbed from filtrate;
Question
(a) Outline four types of membrane transport, including their use of energy. [4]
(b) Draw the structure of a dipeptide. [3]
(c) ADH (antidiuretic hormone) is a peptide hormone that is produced in the hypothalamus. Explain its action in the human body. [8]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a
a. simple diffusion is passive movement of molecules/ions along a concentration gradient
b. facilitated diffusion is passive movement of molecules/ions along a concentration gradient through a protein channel «without use of energy»
c. osmosis is the passage of water through a membrane from lower solute concentration to higher
d. active transport is movement of molecules/ions against the concentration gradient «through membrane pumps» with the use of ATP/energy
e. endocytosis is the infolding of membrane/formation of vesicles to bring molecules into cell with use of energy OR exocytosis is the infolding of membrane/formation of vesicles to release molecules from cell with use of energy mpa, mpb and mpc require reference to concentration. OWTTE Active transport requires mention of the use of energy.
f. chemiosmosis occurs when protons diffuse through ATP synthase «in membrane» to produce ATP
b
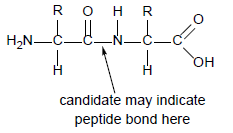
a. two amino acids, one with NH2/NH3 + end and one with COOH/COO– end
b. peptide bond between C=0 and N—H correctly drawn
c. «chiral» C with H and R group on each amino acid
d. peptide bond labelled/clearly indicated between C terminal of one amino acid and N terminal of the second amino acid
c
a. ADH plays a role in osmoregulation/regulating blood solute concentration
b. acts on the collecting ducts of the kidney
c. acts in «late» distal convoluted tubule
d. hypothalamus detects plasma/blood osmolarity/solute concentration
e. if plasma/blood is too concentrated/hypertonic, «posterior» pituitary
releases ADH OWTTE for all mp.
f. ADH stimulates insertion of aquaporins/water channels / increases permeability of collecting duct
g. water moves «through aquaporins» by osmosis into the medulla/blood
h. urine becomes more concentrated/smaller volume
i. negative feedback occurs
j. if blood is hypotonic no ADH is released OWTTE for negative feedback acceptable.
k. water is not reabsorbed from the collecting ducts/permeability of the collecting duct decreases
l. urine becomes more dilute/less concentrated / higher volume
Question
Nitrogen is part of many important substances in living organisms.
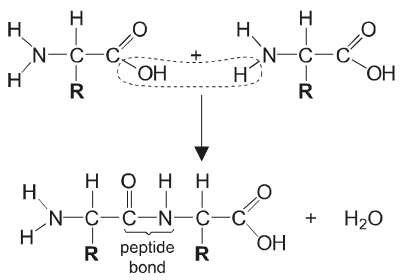
Draw labelled diagrams to show a condensation reaction between two amino acids.
Nitrogen is part of many important substances in living organisms.
Distinguish between transcription and translation.
Nitrogen is part of many important substances in living organisms.
Explain how insects excrete nitrogenous wastes.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. at least one of the amino acid structures completely correct
b. peptide bond shown with N–C and C=O and N–H correct
c. release of water clearly shown
a. DNA is transcribed AND mRNA is translated
Disallow the first mark, if a candidate gets transcription and translation the wrong way round, but allow marks
after that up to [3 max]
b. transcription produces RNA AND translation produces polypeptide/protein
c. RNA polymerase used in only in transcription and ribosomes only in translation
d. transcription in the nucleus «of eukaryotes» and translation in the cytoplasm
e. tRNA needed for translation but not transcription
f. nucleotides linked in transcription and amino acids in translation
OR
sugar-phosphate/phosphodiester bonds in transcription and peptide bonds in translation
[Max 4 Marks]
a. excreted as uric acid
b. excretion by Malpighian tubules
c. nitrogenous waste/ammonia «accumulates» in hemolymph
d. nitrogenous waste/ammonia absorbed by Malpighian tubules
e. ammonia converted to uric acid
f. conversion to uric acid requires energy/ATP
g. high solute concentration in Malpighian tubules
OR
active transport of ions/Na+/K+ into Malpighian tubules
h. water absorbed by osmosis flushes uric acid/nitrogenous waste to «hind» gut
i. water/ions reabsorbed from the feces and returned to hemolymph
j. uric acid precipitates/becomes solid/forms a paste so can pass out with little water
k. uric acid excreted/egested with the feces
l. water conservation/osmoregulation
OR
reduces mass of water «in body»
m. uric acid is non-toxic
[Max 8 Marks]
Question
Draw molecular diagrams to show the condensation reaction between two amino acids to form a dipeptide.
Outline the roles of the different binding sites for tRNA on ribosomes during translation.
Explain the production of antibodies.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. each amino acid with a COO–/COOH group at one end AND a NH2/NH3+ at the other
Both needed.
mp a requires the double bond to be shown between the C and O.
b. CH in middle with H or R group attached
c. peptide bond correctly drawn between N and C=0
d. COO–/COOH group at one end of dipeptide AND NH2/NH3+ at other end
Both needed.
e. loss of water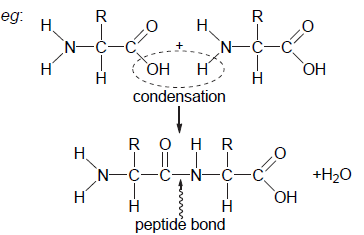
a. A, P and E binding sites are on the large subunit of the ribosome
b. initiation of translation starts with binding of met-tRNA to the start codon
c. large sub-unit binds with «start» tRNA in the P site
d. A binding site holds the tRNA with the next amino acid to be added
e. peptide bond is formed between the amino acids of the A site and the polypeptide at the P site
f. polypeptide is transferred to the tRNA in the A site
g. the tRNA «with polypeptide» in A site then moves to P site
OR
P binding site holds the tRNA attached to the growing polypeptide
h. E binding site «exit» is where the tRNA «from P site without amino acid» leaves the ribosome
Accept annotated diagrams of the sites.
a. each antibody corresponds to a specific antigen
b. antibodies are necessary for immunity/resistance to «infectious» disease
c. macrophage/phagocyte ingests/engulfs pathogen
d. macrophage/phagocyte digests pathogen
e. macrophage/phagocyte displays antigen from pathogen
f. antigens of a pathogen correspond to a specific T lymphocytes/cells
OR
T lymphocytes/cells are activated by antigen binding
g. T lymphocytes/cells activate B lymphocytes/cells
h. «B cells» divide by mitosis to form many/clones of plasma cells
i. plasma cells secrete specific antibody
j. some «activated» B lymphocytes/cells act as memory cells
Accept annotated diagrams of the process
Question
Oxygen is needed to complete aerobic cell respiration.
Explain how chemical energy for use in the cell is generated by electron transport and chemiosmosis.
Outline four different functions of membrane proteins.
Distinguish between anabolism, catabolism and metabolism.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. NAD/FAD carries/is reduced by gaining «two» H «atoms»/«two» electrons
b. reduced NAD produced in glycolysis/link reaction/Krebs cycle
c. reduced NAD/FAD delivers electrons/hydrogen «atoms» to ETC
d. ETC is in mitochondrial inner membrane/cristae
e. electrons release energy as they flow along the chain/from carrier to carrier
f. electrons from ETC accepted by oxygen/oxygen is the final electron acceptor
g. proteins in the inner mitochondrial membrane/electron carriers act as proton pumps
h. protons pumped into intermembrane space/proton gradient across inner mitochondrial membrane/proton concentration higher in intermembrane space than in matrix
i. energy «from electrons» used to pump protons into intermembrane space/generate a proton gradient / high H+ concentration is a store of «potential» energy
j. ATP synthase in inner mitochondrial membrane/cristae
k. energy released as protons pass down the gradient/through ATP synthase
l. ATP synthase converts ADP to ATP/phosphorylates ADP
m. oxidative phosphorylation «is ATP production using energy from oxidizing foods»
Accept H+ but not H/hydrogen in place of protons in any part of the answer.
Accept NADH or FADH in place of reduced NAD or FAD.
a. receptor/binding site for hormone/neurotransmitter
b. cell-to-cell communication / cell recognition
c. channels «for passive transport» / facilitated diffusion
d. pumps / active transport
e. cell adhesion
f. «immobilized» enzymes/enzymes embedded in the membrane
g. electron transport / electron carriers
a. metabolism is all enzyme-catalyzed reactions in a cell/organism/is anabolism plus catabolism
b. anabolism is synthesis of polymers/complex/larger molecules/larger substances «from smaller molecules/monomers»
c. catabolism is breaking down «complex» molecules/substances «into simpler/smaller ones/into monomers»
