Question
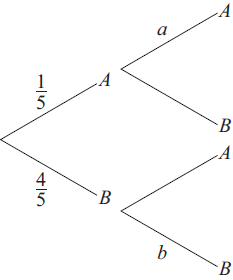
Phoebe chooses a biscuit from a blue tin on a shelf. The tin contains one chocolate biscuit and four plain biscuits. She eats the biscuit and chooses another one from the tin. The tree diagram below represents the situation with the four possible outcomes where A stands for chocolate biscuit and B for plain biscuit.
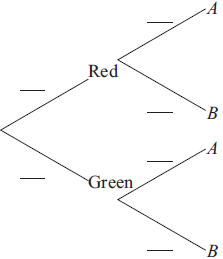
On another shelf there are two tins, one red and one green. The red tin contains three chocolate biscuits and seven plain biscuits and the green tin contains one chocolate biscuit and four plain biscuits. Andrew randomly chooses either the red or the green tin and randomly selects a biscuit.
Write down the value of a.[1]
Write down the value of b.[2]
Find the probability that both biscuits are plain.[3]
Copy and complete the tree diagram below.
 [3]
[3]
Find the probability that he chooses a chocolate biscuit.[3]
Find the probability that he chooses a biscuit from the red tin given that it is a chocolate biscuit.[3]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a = 0 \(\left( {\frac{0}{4}} \right)\) (A1)[1 mark]
\(b = \frac{3}{4}(0.75,{\text{ }}75\% )\) (A2)(G2)[2 marks]
\(\frac{4}{5} \times \frac{3}{4}\) (M1)(A1)
\(\frac{{12}}{{20}}\left( {\frac{3}{5},{\text{ }}0.6,{\text{ 60% }}} \right)\) (A1)(ft)(G2)
Note: Award (M1) for multiplying two probabilities, (A1) for using their probabilities, (A1) for answer.[3 marks]
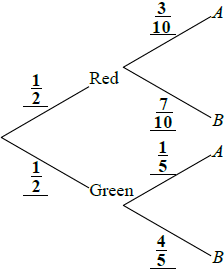 (A1)(A1)(A1)
(A1)(A1)(A1)
Note: Award (A1) for each pair.[3 marks]
\(\frac{1}{2} \times \frac{3}{{10}} + \frac{1}{2} \times \frac{1}{5}\) (M1)(M1)
\( = \frac{5}{{20}}\left( {\frac{1}{4},{\text{ }}0.25,{\text{ 25% }}} \right)\) (A1)(ft)(G2)
Note: Award (M1) for two products seen with numbers from the problem, (M1) for adding two products. Follow through from their tree diagram.[3 marks]
\(\frac{{\frac{1}{2} \times \frac{3}{{10}}}}{{\frac{1}{4}}}\) (M1)(A1)
\( = \frac{3}{5}{\text{ }}\left( {0.6,{\text{ 60 }}\% } \right)\) (A1)(ft)(G2)
Note: Award (M1) for substituted conditional probability formula, (A1) for correct substitution.
Follow through from their part (b) and part (c) (i).[3 marks]
Question
A group of 66 people went on holiday to Hawaii. During their stay, three trips were arranged: a boat trip (\(B\)), a coach trip (\(C\)) and a helicopter trip (\(H\)).
From this group of people:
| 3 | went on all three trips; |
| 16 | went on the coach trip only; |
| 13 | went on the boat trip only; |
| 5 | went on the helicopter trip only; |
| x | went on the coach trip and the helicopter trip but not the boat trip; |
| 2x | went on the boat trip and the helicopter trip but not the coach trip; |
| 4x | went on the boat trip and the coach trip but not the helicopter trip; |
| 8 | did not go on any of the trips. |
One person in the group is selected at random.
Draw a Venn diagram to represent the given information, using sets labelled \(B\), \(C\) and \(H\).[5]
Show that \(x = 3\).[2]
Write down the value of \(n(B \cap C)\).[1]
Find the probability that this person
(i) went on at most one trip;
(ii) went on the coach trip, given that this person also went on both the helicopter trip and the boat trip.[4]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
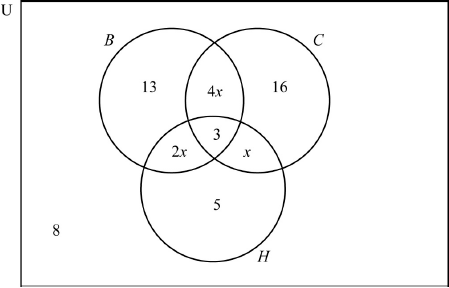 (A5)
(A5)
Notes: Award (A1) for rectangle and three labelled intersecting circles (U need not be seen),
(A1) for 3 in the correct region,
(A1) for 8 in the correct region,
(A1) for 5, 13 and 16 in the correct regions,
(A1) for \(x\), \(2x\) and \(4x\) in the correct regions.[5 marks]
\(8 + 13 + 16 + 3 + 5 + x + 2x + 4x = 66\) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for either a completely correct equation or adding all the terms from their diagram in part (a) and equating to 66.
Award (M0)(A0) if their equation has no \(x\).
\(7x = 66 – 45\) OR \(7x + 45 = 66\) (A1)
Note: Award (A1) for adding their like terms correctly, but only when the solution to their equation is equal to 3 and is consistent with their original equation.
\(x = 3\) (AG)
Note: The conclusion \(x = 3\) must be seen for the (A1) to be awarded.[2 marks]
15 (A1)(ft)
Note: Follow through from part (a). The answer must be an integer.[1 mark]
(i) \(\frac{{42}}{{66}}{\text{ }}\left( {\frac{7}{{11}},{\text{ }}0.636,{\text{ }}63.6\% } \right)\) (A1)(ft)(A1)(G2)
Note: Award (A1)(ft) for numerator, (A1) for denominator. Follow through from their Venn diagram.
(ii) \(\frac{3}{9}{\text{ }}\left( {\frac{1}{3},{\text{ }}0.333,{\text{ }}33.3\% } \right)\) (A1)(A1)(ft)(G2)
Note: Award (A1) for numerator, (A1)(ft) for denominator. Follow through from their Venn diagram.[4 marks]
Question
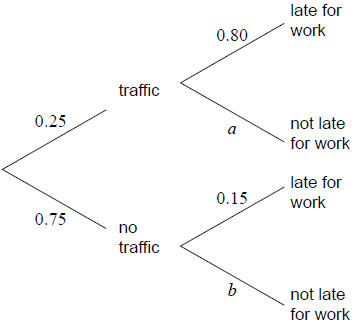
In a company it is found that 25 % of the employees encountered traffic on their way to work. From those who encountered traffic the probability of being late for work is 80 %.
From those who did not encounter traffic, the probability of being late for work is 15 %.
The tree diagram illustrates the information.
The company investigates the different means of transport used by their employees in the past year to travel to work. It was found that the three most common means of transport used to travel to work were public transportation (P ), car (C ) and bicycle (B ).
The company finds that 20 employees travelled by car, 28 travelled by bicycle and 19 travelled by public transportation in the last year.
Some of the information is shown in the Venn diagram.
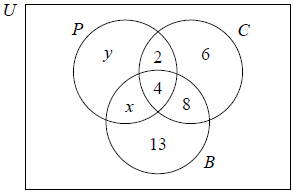
There are 54 employees in the company.
Write down the value of a.[1]
Write down the value of b.[1]
Use the tree diagram to find the probability that an employee encountered traffic and was late for work.[2]
Use the tree diagram to find the probability that an employee was late for work.[3]
Use the tree diagram to find the probability that an employee encountered traffic given that they were late for work.[3]
Find the value of x.[1]
Find the value of y.[1]
Find the number of employees who, in the last year, did not travel to work by car, bicycle or public transportation.[2]
Find \(n\left( {\left( {C \cup B} \right) \cap P’} \right)\).[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a = 0.2 (A1)[1 mark]
b = 0.85 (A1)[1 mark]
0.25 × 0.8 (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for a correct product.
\( = 0.2\,\,\,\left( {\,\frac{1}{5},\,\,\,20\% } \right)\) (A1)(G2)[2 marks]
0.25 × 0.8 + 0.75 × 0.15 (A1)(ft)(M1)
Note: Award (A1)(ft) for their (0.25 × 0.8) and (0.75 × 0.15), (M1) for adding two products.
\( = 0.313\,\,\,\left( {0.3125,\,\,\,\frac{5}{{16}},\,\,\,31.3\% } \right)\) (A1)(ft)(G3)
Note: Award the final (A1)(ft) only if answer does not exceed 1. Follow through from part (b)(i).[3 marks]
\(\frac{{0.25 \times 0.8}}{{0.25 \times 0.8 + 0.75 \times 0.15}}\) (A1)(ft)(A1)(ft)
Note: Award (A1)(ft) for a correct numerator (their part (b)(i)), (A1)(ft) for a correct denominator (their part (b)(ii)). Follow through from parts (b)(i) and (b)(ii).
\( = 0.64\,\,\,\left( {\frac{{16}}{{25}},\,\,64{\text{% }}} \right)\) (A1)(ft)(G3)
Note: Award final (A1)(ft) only if answer does not exceed 1.[3 marks]
(x =) 3 (A1)[1 Mark]
(y =) 10 (A1)(ft)
Note: Following through from part (c)(i) but only if their x is less than or equal to 13.[1 Mark]
54 − (10 + 3 + 4 + 2 + 6 + 8 + 13) (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for subtracting their correct sum from 54. Follow through from their part (c).
= 8 (A1)(ft)(G2)
Note: Award (A1)(ft) only if their sum does not exceed 54. Follow through from their part (c).[2 marks]
6 + 8 + 13 (M1)
Note: Award (M1) for summing 6, 8 and 13.
27 (A1)(G2)[2 marks]
