Question
The diagram below shows a circle centre O, with radius r. The length of arc ABC is \(3\pi {\text{ cm}}\) and \({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{O}}{\rm{C}} = \frac{{2\pi }}{9}\).
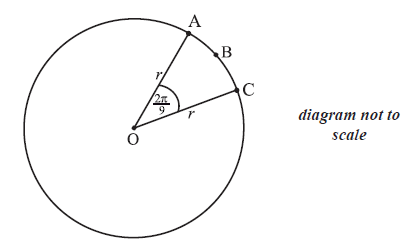
Find the value of r.
Find the perimeter of sector OABC.
Find the area of sector OABC.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
evidence of appropriate approach M1
e.g. \(3\pi = r\frac{{2\pi }}{9}\)
\(r = 13.5\) (cm) A1 N1
[2 marks]
adding two radii plus \(3\pi \) (M1)
\({\text{perimeter}} = 27 + 3\pi \) (cm) (\(= 36.4\)) A1 N2
[2 marks]
evidence of appropriate approach M1
e.g. \(\frac{1}{2} \times {13.5^2} \times \frac{{2\pi }}{9}\)
area \( = 20.25\pi \) (\({\text{cm}}^2\)) (\(= 63.6\)) A1 N1
[2 marks]
Question
The circle shown has centre O and radius 3.9 cm.
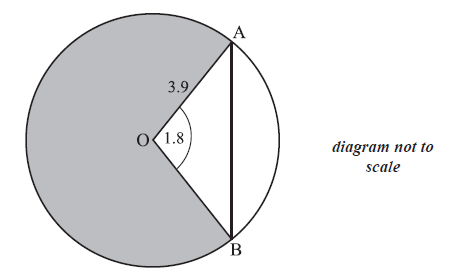
Points A and B lie on the circle and angle AOB is 1.8 radians.
Find AB.
Find the area of the shaded region.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
METHOD 1
choosing cosine rule (M1)
substituting correctly A1
e.g. \({\rm{AB}} = \sqrt {{{3.9}^2} + {{3.9}^2} – 2(3.9)(3.9)\cos 1.8} \)
\({\rm{AB}} = 6.11\) (cm) A1 N2
METHOD 2
evidence of approach involving right-angled triangles (M1)
substituting correctly A1
e.g. \(\sin 0.9 = \frac{x}{{3.9}}\) , \(\frac{1}{2}{\rm{AB}} = 3.9\sin 0.9\)
\({\rm{AB}} = 6.11\) (cm) A1 N2
METHOD 3
choosing the sine rule (M1)
substituting correctly A1
e.g. \(\frac{{\sin 0.670 \ldots }}{{3.9}} = \frac{{\sin 1.8}}{{{\rm{AB}}}}\)
\({\rm{AB}} = 6.11\) (cm) A1 N2
[3 marks]
METHOD 1
reflex \({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{O}}{\rm{B}} = 2\pi – 1.8\) \(( = 4.4832)\) (A2)
correct substitution \(A = \frac{1}{2}{(3.9)^2}(4.4832 \ldots )\) A1
area =34.1 (cm2) A1 N2
METHOD 2
finding area of circle \(A = \pi {(3.9)^2}\) \(( = 47.78 \ldots )\) (A1)
finding area of (minor) sector \(A = \frac{1}{2}{(3.9)^2}(1.8)\) \(( = 13.68 \ldots )\) (A1)
subtracting M1
e.g. \(\pi {(3.9)^2} – 0.5{(3.9)^2}(1.8)\) , \(47.8 – 13.7\)
area = 34.1 (cm2) A1 N2
METHOD 3
finding reflex \({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{O}}{\rm{B}} = 2\pi – 1.8\) \(( = 4.4832)\) (A2)
finding proportion of total area of circle A1
e.g. \(\frac{{2\pi – 1.8}}{{2\pi }} \times \pi {(3.9)^2}\) , \(\frac{\theta }{{2\pi }} \times \pi {r^2}\)
area = 34.1 (cm2) A1 N2
[4 marks]
Question
The following diagram shows a circle with centre O and radius 4 cm.
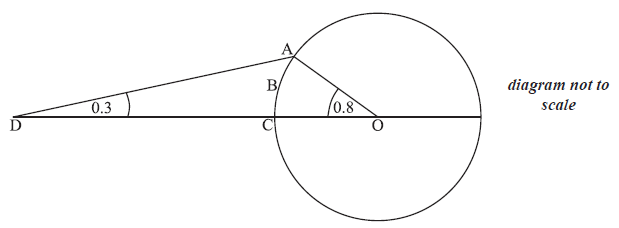
The points A, B and C lie on the circle. The point D is outside the circle, on (OC).
Angle ADC = 0.3 radians and angle AOC = 0.8 radians.
Find AD.
Find OD.
Find the area of sector OABC.
Find the area of region ABCD.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
choosing sine rule (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(\frac{{{\rm{AD}}}}{{\sin 0.8}} = \frac{4}{{\sin 0.3}}\)
\({\text{AD}} = 9.71{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
METHOD 1
finding angle \({\rm{OAD}} = \pi – 1.1 = (2.04)\) (seen anywhere) (A1)
choosing cosine rule (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \({\rm{O}}{{\rm{D}}^2} = {9.71^2} + {4^2} – 2 \times 9.71 \times 4 \times \cos (\pi – 1.1)\)
\({\text{OD}} = 12.1{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N3
METHOD 2
finding angle \({\rm{OAD}} = \pi – 1.1 = (2.04)\) (seen anywhere) (A1)
choosing sine rule (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(\frac{{{\rm{OD}}}}{{\sin (\pi – 1.1)}} = \frac{{9.71}}{{\sin 0.8}} = \frac{4}{{\sin 0.3}}\)
\({\text{OD}} = 12.1{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N3
[4 marks]
correct substitution into area of a sector formula (A1)
e.g. \({\rm{area}} = 0.5 \times {4^2} \times 0.8\)
\({\text{area}} = 6.4{\text{ (c}}{{\text{m}}^2}{\text{)}}\) A1 N2
[2 marks]
substitution into area of triangle formula OAD (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(A{\rm{ = }}\frac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 12.1 \times \sin 0.8\) , \(A{\rm{ = }}\frac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 9.71 \times \sin 2.04\) , \(A{\rm{ = }}\frac{1}{2} \times 12.1 \times 9.71 \times \sin 0.3\)
subtracting area of sector OABC from area of triangle OAD (M1)
e.g. \({\text{area ABCD}} = 17.3067 – 6.4\)
\({\text{area ABCD}} = 10.9{\text{ (c}}{{\text{m}}^2}{\text{)}}\) A1 N2
[4 marks]
Question
The diagram below shows a circle with centre O and radius 8 cm.
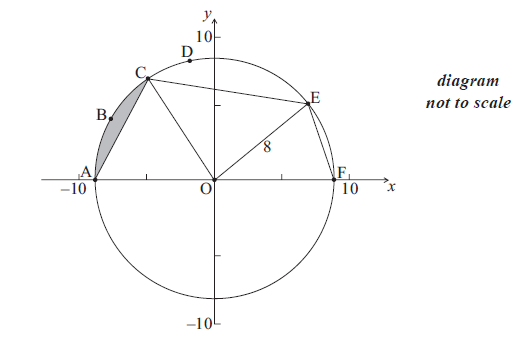
The points A, B, C, D, E and F are on the circle, and [AF] is a diameter. The length of arc ABC is 6 cm.
Find the size of angle AOC .
Hence find the area of the shaded region.
The area of sector OCDE is \(45{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\).
Find the size of angle COE .
Find EF .
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
appropriate approach (M1)
e.g. \(6 = 8\theta \)
\({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{O}}{\rm{C}} = 0.75\) A1 N2
[2 marks]
evidence of substitution into formula for area of triangle (M1)
e.g. \({\rm{area}} = \frac{1}{2} \times 8 \times 8 \times \sin (0.75)\)
area \(= 21.8 \ldots \) (A1)
evidence of substitution into formula for area of sector (M1)
e.g. \({\rm{area}} = \frac{1}{2} \times 64 \times 0.75\)
area of sector \(= 24\) (A1)
evidence of substituting areas (M1)
e.g. \(\frac{1}{2}{r^2}\theta – \frac{1}{2}ab\sin C\) , \({\text{area of sector}} – {\text{area of triangle}}\)
area of shaded region \( = 2.19{\text{ c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\) A1 N4
[6 marks]
attempt to set up an equation for area of sector (M1)
e.g. \(45 = \frac{1}{2} \times {8^2} \times \theta \)
\({\rm{C}}\widehat {\rm{O}}{\rm{E}} = 1.40625\) (1.41 to 3 sf) A1 N2
[2 marks]
METHOD 1
attempting to find angle EOF (M1)
e.g. \(\pi – 0.75 – 1.41\)
\({\rm{E}}\widehat {\rm{O}}{\rm{F}} = 0.985\) (seen anywhere) A1
evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \({\rm{EF}} = \sqrt {{8^2} + {8^2} – 2 \times 8 \times 8 \times \cos 0.985} \)
EF \(= 7.57{\text{ cm}}\) A1 N3
METHOD 2
attempting to find angles that are needed (M1)
e.g. angle EOF and angle OEF
\({\rm{E}}\widehat {\rm{O}}{\rm{F}} = 0.9853 \ldots \) and \({\text{O}}\widehat {\rm{E}}{\text{F (or O}}\widehat {\text{F}}{\text{E)}} = 1.078 \ldots \) A1
evidence of choosing sine rule (M1)
correct substitution (A1)
e.g. \(\frac{{{\rm{EF}}}}{{\sin 0.985}} = \frac{8}{{\sin 1.08}}\)
EF \(= 7.57{\text{ cm}}\) A1 N3
METHOD 3
attempting to find angle EOF (M1)
e.g. \(\pi – 0.75 – 1.41\)
\({\rm{E}}\widehat {\rm{O}}{\rm{F}} = 0.985\) (seen anywhere) A1
evidence of using half of triangle EOF (M1)
e.g. \(x = 8\sin \frac{{0.985}}{2}\)
correct calculation A1
e.g. \(x = 3.78\)
EF \(= 7.57{\text{ cm}}\) A1 N3
[5 marks]
Question
Consider the following circle with centre O and radius 6.8 cm.
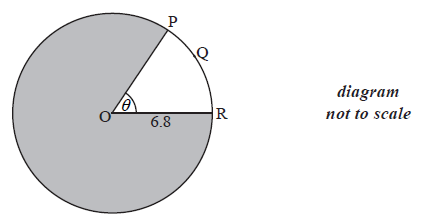
The length of the arc PQR is 8.5 cm.
Find the value of \(\theta \) .
Find the area of the shaded region.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
correct substitution (A1)
e.g. \(8.5 = \theta (6.8)\) , \(\theta = \frac{{8.5}}{{6.8}}\)
\(\theta = 1.25\) (accept \({71.6^ \circ }\) ) A1 N2
[2 marks]
METHOD 1
correct substitution into area formula (seen anywhere) (A1)
e.g. \(A = \pi {(6.8)^2}\) , \(145.267 \ldots \)
correct substitution into area formula (seen anywhere) (A1)
e.g. \(A = \frac{1}{2}(1.25)({6.8^2})\) , 28.9
valid approach M1
e.g. \(\pi {(6.8)^2} – \frac{1}{2}(1.25)({6.8^2})\) ; \(145.267 \ldots – 28.9\) ; \(\pi {r^2} – \frac{1}{2}{r^2}\sin \theta \)
\(A = 116\) (\({\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\)) A1 N2
METHOD 2
attempt to find reflex angle (M1)
e.g. \(2\pi – \theta \) , \(360 – 1.25\)
correct reflex angle (A1)
\({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{O}}{\rm{B}} = 2\pi – 1.25\) (\( = 5.03318 \ldots \))
correct substitution into area formula A1
e.g. \(A = \frac{1}{2}(5.03318 \ldots )({6.8^2})\)
\(A = 116\) (\({\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2}\)) A1 N2
[4 marks]
Question
The following diagram shows a triangle ABC.
\({\rm{BC}} = 6\) , \({\rm{C}}\widehat {\rm{A}}{\rm{B}} = 0.7\) radians , \({\rm{AB}} = 4p\) , \({\rm{AC}} = 5p\) , where \(p > 0\) .
Consider the circle with centre B that passes through the point C. The circle cuts the line CA at D, and \({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{D}}{\rm{B}}\) is obtuse. Part of the circle is shown in the following diagram.

(i) Show that \({p^2}(41 – 40\cos 0.7) = 36\) .
(ii) Find p .
Write down the length of BD.
Find \({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{D}}{\rm{B}}\) .
(i) Show that \({\rm{C}}\widehat {\rm{B}}{\rm{D}} = 1.29\) radians, correct to 2 decimal places.
(ii) Hence, find the area of the shaded region.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i) evidence of valid approach (M1)
e.g. choosing cosine rule
correct substitution (A1)
e.g. \({6^2} = {(5p)^2} + {(4p)^2} – 2 \times (4p) \times (5p)\cos 0.7\)
simplification A1
e.g. \(36 = 25{p^2} + 16{p^2} – 40{p^2}\cos 0.7\)
\({p^2}(41 – 40\cos 0.7) = 36\) AG N0
(ii) \(1.85995 \ldots \)
\(p = 1.86\) A1 N1
Note: Award A0 for \(p = \pm 1.86\) , i.e. not rejecting the negative value.
[4 marks]
\({\text{BD}} = 6\) A1 N1
[1 mark]
evidence of valid approach (M1)
e.g. choosing sine rule
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(\frac{{\sin {\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{D}}{\rm{B}}}}{{4p}} = \frac{{\sin 0.7}}{6}\)
\({\text{acute }}{\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{D}}{\rm{B = 0}}{\rm{.9253166}} \ldots \) (A1)
\(\pi – 0.9253166 \ldots = 2.216275 \ldots \)
\({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{D}}{\rm{B}} = 2.22\) A1 N3
[4 marks]
(i) evidence of valid approach (M1)
e.g. recognize isosceles triangle, base angles equal
\(\pi – 2(0.9253 \ldots )\) A1
\({\rm{C}}\widehat {\rm{B}}{\rm{D}} = 1.29\) AG N0
(ii) area of sector BCD (A1)
e.g. \(0.5 \times (1.29) \times {(6)^2}\)
area of triangle BCD (A1)
e.g. \(0.5 \times {(6)^2}\sin 1.29\)
evidence of subtraction M1
\(5.92496 \ldots \)
\(5.937459 \ldots \)
\({\text{area}} = 5.94\) A1 N3
[6 marks]
Question
Consider the following circle with centre O and radius r .
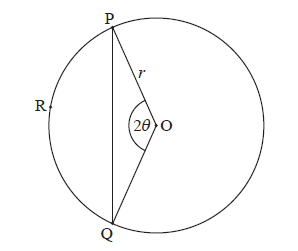
The points P, R and Q are on the circumference, \({\rm{P}}\widehat {\rm{O}}{\rm{Q}} = 2\theta \) , for \(0 < \theta < \frac{\pi }{2}\) .
Use the cosine rule to show that \({\rm{PQ}} = 2r\sin \theta \) .
Let l be the length of the arc PRQ .
Given that \(1.3{\rm{PQ}} – l = 0\) , find the value of \(\theta \) .
Consider the function \(f(\theta ) = 2.6\sin \theta – 2\theta \) , for \(0 < \theta < \frac{\pi }{2}\) .
(i) Sketch the graph of f .
(ii) Write down the root of \(f(\theta ) = 0\) .
Use the graph of f to find the values of \(\theta \) for which \(l < 1.3{\rm{PQ}}\) .
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
correct substitution into cosine rule A1
e.g. \({\rm{P}}{{\rm{Q}}^{\rm{2}}} = {r^2} + {r^2} – 2(r)(r)\cos (2\theta )\) , \({\rm{P}}{{\rm{Q}}^{\rm{2}}} = 2{r^2} – 2{r^2}(\cos (2\theta ))\)
substituting \(1 – 2{\sin ^2}\theta \) for \(\cos 2\theta \) (seen anywhere) A1
e.g. \({\rm{P}}{{\rm{Q}}^{\rm{2}}} = 2{r^2} – 2{r^2}(1 – 2{\sin ^2}\theta )\)
working towards answer (A1)
e.g. \({\rm{P}}{{\rm{Q}}^{\rm{2}}} = 2{r^2} – 2{r^2} + 4{r^2}{\sin ^2}\theta \)
recognizing \(2{r^2} – 2{r^2} = 0\) (including crossing out) (seen anywhere)
e.g. \({\rm{P}}{{\rm{Q}}^{\rm{2}}} = 4{r^2}{\sin ^2}\theta \) , \({\rm{PQ}} = \sqrt {4{r^2}{{\sin }^2}\theta } \)
\({\rm{PQ = 2}}r{\rm{sin}}\theta \) AG N0
[4 marks]
\({\rm{PRQ}} = r \times 2\theta \) (seen anywhere) (A1)
correct set up A1
e.g. \(1.3 \times 2r\sin \theta – r \times (2\theta ) = 0\)
attempt to eliminate r (M1)
correct equation in terms of the one variable \(\theta \) (A1)
e.g. \(1.3 \times 2\sin \theta – 2\theta = 0\)
1.221496215
\(\theta = 1.22\) (accept \(70.0^\circ \) (69.9)) A1 N3
[5 marks]
(i)
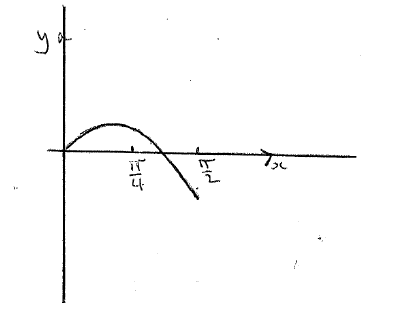 A1A1A1 N3
A1A1A1 N3
Note: Award A1 for approximately correct shape, A1 for x-intercept in approximately correct position, A1 for domain. Do not penalise if sketch starts at origin.
(ii) \(1.221496215\)
\(\theta = 1.22\) A1 N1
[4 marks]
evidence of appropriate approach (may be seen earlier) M2
e.g. \(2\theta < 2.6\sin \theta \) , \(0 < f(\theta )\) , showing positive part of sketch
\(0 < \theta < 1.221496215\)
\(0 < \theta = 1.22\) (accept \(\theta < 1.22\) ) A1 N1
[3 marks]
Question
The following diagram shows a circular play area for children.
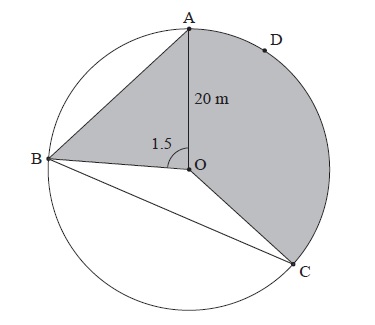
The circle has centre O and a radius of 20 m, and the points A, B, C and D lie on the circle. Angle AOB is 1.5 radians.
Find the length of the chord [AB].
Find the area of triangle AOB.
Angle BOC is 2.4 radians.
Find the length of arc ADC.
Angle BOC is 2.4 radians.
Find the area of the shaded region.
Angle BOC is 2.4 radians.
The shaded region is to be painted red. Red paint is sold in cans which cost \(\$ 32\) each. One can covers \(140{\text{ }}{{\text{m}}^2}\). How much does it cost to buy the paint?
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Note: In this question, do not penalise for missing or incorrect units. They are not included in the markscheme, to avoid complex answer lines.
METHOD 1
choosing cosine rule (must have cos in it) (M1)
e.g. \({c^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} – 2ab\cos C\)
correct substitution (into rhs) A1
e.g. \({20^2} + {20^2} – 2(20)(20)\cos 1.5\) , \({\rm{AB}} = \sqrt {800 – 800\cos 1.5} \)
\({\rm{AB = 27}}{\rm{.26555}} \ldots \)
\({\rm{AB}} = 27.3\) \([27.2{\text{, }}27.3]\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
METHOD 2
choosing sine rule (M1)
e.g. \(\frac{{\sin A}}{a} = \frac{{\sin B}}{b}\) , \(\frac{{{\rm{AB}}}}{{\sin O}} = \frac{{{\rm{AO}}}}{{\sin B}}\)
correct substitution A1
e.g. \(\frac{{{\rm{AB}}}}{{\sin 1.5}} = \frac{{20}}{{\sin (0.5(\pi – 1.5))}}\)
\({\rm{AB}} = 27.26555 \ldots \)
\({\rm{AB}} = 27.3\) \([27.2{\text{, }}27.3]\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
correct substitution into area formula A1
e.g. \(\frac{1}{2}(20)(20)\sin 1.5\) , \(\frac{1}{2}(20)(27.2655504 \ldots )\sin(0.5(\pi – 1.5))\)
\({\rm{area}} = 199.498997 \ldots \) (accept \(199.75106 = 200\) , from using 27.3)
\({\rm{area}} = 199\) \([199{\text{, }}200]\) A1 N1
[2 marks]
appropriate method to find angle AOC (M1)
e.g. \(2\pi – 1.5 – 2.4\)
correct substitution into arc length formula (A1)
e.g. \((2\pi – 3.9) \times 20\) , \(2.3831853 \ldots \times 20\)
\({\text{arc length}} = 47.6637 \ldots \)
\({\text{arc length}} = 47.7\) \((47.6{\text{, }}47.7]\) (i.e. do not accept \(47.6\)) A1 N2
Notes: Candidates may misread the question and use \({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{O}}{\rm{C}} = 2.4\) . If working shown, award M0 then A0MRA1 for the answer 48. Do not then penalize \({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{O}}{\rm{C}}\) in part (d) which, if used, leads to the answer \(679.498 \ldots \)
However, if they use the prematurely rounded value of 2.4 for \({\rm{A}}\widehat {\rm{O}}{\rm{C}}\) , penalise 1 mark for premature rounding for the answer 48 in (c). Do not then penalize for this in (d).
[3 marks]
calculating sector area using their angle AOC (A1)
e.g. \(\frac{1}{2}(2.38 \ldots )({20^2})\) , \(200(2.38 \ldots )\) , \(476.6370614 \ldots \)
shaded area = their area of triangle AOB + their area of sector (M1)
e.g. \(199.4989973 \ldots + 476.6370614 \ldots \) , \(199 + 476.637\)
\({\text{shaded area}} = 676.136 \ldots \) (accept \(675.637 \ldots = 676\) from using 199)
\({\text{shaded area}} = 676\) \([676{\text{, }}677]\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
dividing to find number of cans (M1)
e.g. \(\frac{{676}}{{140}}\) , \(4.82857 \ldots \)
5 cans must be purchased (A1)
multiplying to find cost of cans (M1)
e.g. \(5(32)\) , \(\frac{{676}}{{140}} \times 32\)
cost is 160 (dollars) A1 N3
[4 marks]
Question
The following diagram shows a circle with centre O and radius \(r\) cm.
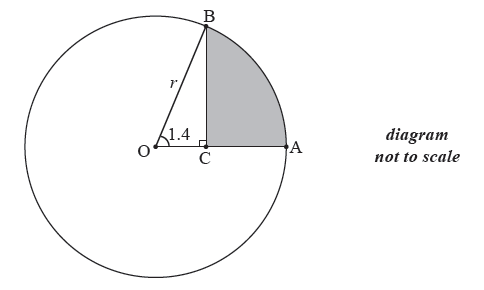
Points A and B are on the circumference of the circle and \({\rm{A}}\hat {\rm{O}}{\rm{B}} = 1.4\) radians .
The point C is on [OA] such that \({\rm{B}}\hat {\rm{C}}{\rm{O}} = \frac{\pi }{2}\) radians .
Show that \({\rm{OC}} = r\cos 1.4\) .
The area of the shaded region is \(25\) cm2 . Find the value of \(r\) .
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
use right triangle trigonometry A1
eg \(\cos 1.4 = \frac{{{\rm{OC}}}}{r}\)
\({\rm{OC}} = r\cos 1.4\) AG N0
[1 mark]
correct value for BC
eg \({\rm{BC}} = r\sin 1.4\) , \(\sqrt {{r^2} – {{(r\cos 1.4)}^2}} \) (A1)
area of \(\Delta {\rm{OBC}} = \frac{1}{2}r\sin 1.4 \times r\cos 1.4\) \(\left( { = \frac{1}{2}{r^2}\sin 1.4 \times \cos 1.4} \right)\) A1
area of sector \({{\rm{OAB}} = \frac{1}{2}{r^2} \times 1.4}\) A1
attempt to subtract in any order (M1)
eg sector – triangle, \({\frac{1}{2}{r^2}\sin 1.4 \times \cos 1.4 – 0.7{r^2}}\)
correct equation A1
eg \({0.7{r^2} – \frac{1}{2}r\sin 1.4 \times r\cos 1.4 = 25}\)
attempt to solve their equation (M1)
eg sketch, writing as quadratic, \(\frac{{25}}{{0.616 \ldots }}\)
\(r = 6.37\) A1 N4
[7 marks]
Note: Exception to FT rule. Award A1FT for a correct FT answer from a quadratic equation involving two trigonometric functions.
Question
Consider a circle with centre \(\rm{O}\) and radius \(7\) cm. Triangle \(\rm{ABC}\) is drawn such that its vertices are on the circumference of the circle.
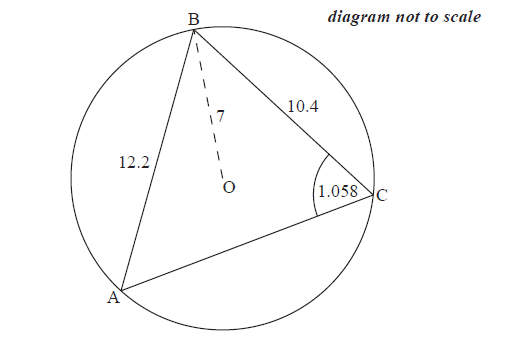
\(\rm{AB}=12.2\) cm, \(\rm{BC}=10.4\) cm and \(\rm{A}\hat{\rm{C}}\rm{B}=1.058\) radians.
Find \({\rm{B\hat AC}}\).
Find \({\text{AC}}\).
Hence or otherwise, find the length of arc \({\text{ABC}}\).
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Notes: In this question, there may be slight differences in answers, depending on which values candidates carry through in subsequent parts. Accept answers that are consistent with their working.
Candidates may have their GDCs in degree mode, leading to incorrect answers. If working shown, award marks in line with the markscheme, with FT as appropriate.
Ignore missing or incorrect units.
evidence of choosing sine rule (M1)
eg \(\frac{{\sin \hat A}}{a} = \frac{{\sin \hat B}}{b}\)
correct substitution (A1)
eg \(\frac{{\sin \hat A}}{{10.4}} = \frac{{\sin 1.058}}{{12.2}}\)
\({\rm{B\hat AC}} = 0.837\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
Notes: In this question, there may be slight differences in answers, depending on which values candidates carry through in subsequent parts. Accept answers that are consistent with their working.
Candidates may have their GDCs in degree mode, leading to incorrect answers. If working shown, award marks in line with the markscheme, with FT as appropriate.
Ignore missing or incorrect units.
METHOD 1
evidence of subtracting angles from \(\pi \) (M1)
eg \({\rm{A\hat BC}} = \pi – A – C\)
correct angle (seen anywhere) A1
\({\rm{A\hat BC}} = \pi – 1.058 – 0.837,{\text{ }}1.246,{\text{ }}71.4^\circ \)
attempt to substitute into cosine or sine rule (M1)
correct substitution (A1)
eg \({12.2^2} + {10.4^2} – 2 \times 12.2 \times 10.4\cos 71.4,{\text{ }}\frac{{{\text{AC}}}}{{\sin 1.246}} = \frac{{12.2}}{{\sin 1.058}}\)
\({\text{AC}} = 13.3{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N3
METHOD 2
evidence of choosing cosine rule M1
eg \({a^2} = {b^2} + {c^2} – 2bc\cos A\)
correct substitution (A2)
eg \({12.2^2} = {10.4^2} + {b^2} – 2 \times 10.4b\cos 1.058\)
\({\text{AC}} = 13.3{\text{ (cm)}}\) A2 N3
[5 marks]
Notes: In this question, there may be slight differences in answers, depending on which values candidates carry through in subsequent parts. Accept answers that are consistent with their working.
Candidates may have their GDCs in degree mode, leading to incorrect answers. If working shown, award marks in line with the markscheme, with FT as appropriate.
Ignore missing or incorrect units.
METHOD 1
valid approach (M1)
eg \(\cos {\rm{A\hat OC}} = \frac{{{\text{O}}{{\text{A}}^2} + {\text{O}}{{\text{C}}^2} – {\text{A}}{{\text{C}}^2}}}{{2 \times {\text{OA}} \times {\text{OC}}}}\), \({\rm{A\hat OC}} = 2 \times {\rm{A\hat BC}}\)
correct working (A1)
eg \({\text{13.}}{{\text{3}}^2} = {7^2} + {7^2} – 2 \times 7 \times 7\cos {\rm{A\hat OC}},{\text{ }}O = 2 \times 1.246\)
\({\rm{A\hat OC}} = 2.492{\text{ }}(142.8^\circ )\) (A1)
EITHER
correct substitution for arc length (seen anywhere) A1
eg \(2.492 = \frac{l}{7},{\text{ }}l = 17.4,{\text{ }}14\pi \times \frac{{142.8}}{{360}}\)
subtracting arc from circumference (M1)
eg \(2\pi r – l,{\text{ }}14\pi = 17.4\)
OR
attempt to find \({\rm{A\hat OC}}\) reflex (M1)
eg \(2\pi – 2.492,{\text{ }}3.79,{\text{ }}360 – 142.8\)
correct substitution for arc length (seen anywhere) A1
eg \(l = 7 \times 3.79,{\text{ }}14\pi \times \frac{{217.2}}{{360}}\)
THEN
\({\text{arc ABC}} = 26.5\) A1 N4
METHOD 2
valid approach to find \({\rm{A\hat OB}}\) or \({\rm{B\hat OC}}\) (M1)
eg choosing cos rule, twice angle at circumference
correct working for finding one value, \({\rm{A\hat OB}}\) or \({\rm{B\hat OC}}\) (A1)
eg \(\cos {\rm{A\hat OB}} = \frac{{{7^2} + {7^2} – {{12.2}^2}}}{{2 \times 7 \times 7}}\), \({\rm{A\hat OB}} = 2.116,{\rm{B\hat OC}} = 1.6745\)
two correct calculations for arc lengths
eg \({\text{AB}} = 7 \times 2 \times 1.058{\text{ }}( = 14.8135),{\text{ }}7 \times 1.6745{\text{ }}( = 11.7216)\) (A1)(A1)
adding their arc lengths (seen anywhere)
eg \(r{\rm{A\hat OB}} + r{\rm{B\hat OC}},{\text{ }}14.8135 + 11.7216,{\text{ }}7(2.116 + 1.6745)\) M1
\({\text{arc ABC}} = 26.5{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N4
Note: Candidates may work with other interior triangles using a similar method. Check calculations carefully and award marks in line with markscheme.
[6 marks]
Question
The following diagram shows a circle with centre \(\rm{O}\) and radius \(5 \rm\,{cm}\).
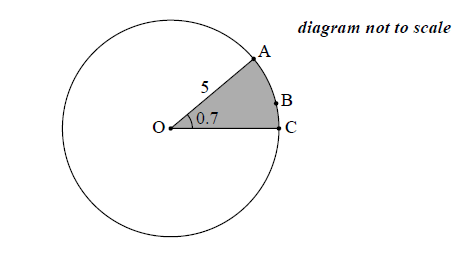
The points \(\rm{A}\), \(rm{B}\) and \(rm{C}\) lie on the circumference of the circle, and \({\rm{A\hat OC}} = 0.7\) radians.
Find the length of the arc \({\text{ABC}}\).
Find the perimeter of the shaded sector.
Find the area of the shaded sector.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
correct substitution into arc length formula (A1)
eg \(0.7 \times 5\)
arc length \(= 3.5\) (cm) A1 N2
[2 marks]
valid approach (M1)
eg \(3.5 + 5 + 5,{\text{ arc}} + 2r\)
perimeter \(= 13.5\) (cm) A1 N2
[2 marks]
correct substitution into area formula (A1)
eg \(\frac{1}{2}(0.7){(5)^2}\)
\({\text{area}} = 8.75{\text{ (c}}{{\text{m}}^2}{\text{)}}\) A1 N2
[2 marks]
Question
The following diagram shows a circle with centre \(O\) and radius \(8\) cm.
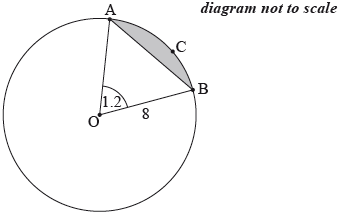
The points \(A\), \(B\) and \(C\) are on the circumference of the circle, and \({\rm{A\hat OB}}\) radians.
Find the length of arc \(ACB\).
Find \(AB\).
Hence, find the perimeter of the shaded segment \(ABC\).
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
correct substitution into formula (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;\)\(l = 1.2 \times 8\)
\(9.6{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N2
[2 marks]
METHOD 1
evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
eg\(\;\;\;\)\(2{r^2} – 2 \times {r^2} \times \cos ({\rm{A\hat OB)}}\)
correct substitution into right hand side (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;\)\({8^2} + {8^2} – 2 \times 8 \times 8 \times \cos (1.2)\)
\(9.0342795\)
\({\text{AB}} = 9.03{\text{ }}[9.03,{\text{ }}9.04]{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N2
METHOD 2
evidence of choosing sine rule (M1)
eg\(\;\;\;\)\(\frac{{{\text{AB}}}}{{\sin ({\rm{A\hat OB)}}}} = \frac{{{\text{OB}}}}{{\sin ({\rm{O\hat AB)}}}}\)
finding angle \(OAB\) or \(OBA\) (may be seen in substitution) (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;\)\(\frac{{\pi – 1.2}}{2},{\text{ }}0.970796\)
\({\text{AB}} = 9.03{\text{ }}[9.03,{\text{ }}9.04]{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
correct working (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;\)\(P = 9.6 + 9.03\)
\(18.6342\)
\(18.6{\text{ }}[18.6,{\text{ }}18.7]{\text{ (cm)}}\) A1 N2
[2 marks]
Total [7 marks]
Question
The following diagram shows a square \(ABCD\), and a sector \(OAB\) of a circle centre \(O\), radius \(r\). Part of the square is shaded and labelled \(R\).
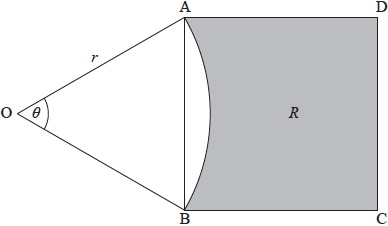
\[{\rm{A\hat OB}} = \theta {\text{, where }}0.5 \ \le \ \theta < \pi .\]
Show that the area of the square \(ABCD\) is \(2{r^2}(1 – \cos \theta )\).
When \(\theta = \alpha \), the area of the square \(ABCD\) is equal to the area of the sector \(OAB\).
(i) Write down the area of the sector when \(\theta = \alpha \).
(ii) Hence find \(\alpha \).
When \(\theta = \beta \), the area of \(R\) is more than twice the area of the sector.
Find all possible values of \(\beta \).
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
area of \({\text{ABCD}} = {\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}\) (seen anywhere) (A1)
choose cosine rule to find a side of the square (M1)
eg\(\;\;\;{a^2} = {b^2} + {c^2} – 2bc\cos \theta \)
correct substitution (for triangle \(AOB\)) A1
eg\(\;\;\;{r^2} + {r^2} – 2 \times r \times r\cos \theta ,{\text{ O}}{{\text{A}}^2} + {\text{O}}{{\text{B}}^2} – 2 \times {\text{OA}} \times {\text{OB}}\cos \theta \)
correct working for \({\text{A}}{{\text{B}}^2}\) A1
eg\(\;\;\;2{r^{\text{2}}} – 2{r^2}\cos \theta \)
\({\text{area}} = 2{r^2}(1 – \cos \theta )\) AG N0
Note: Award no marks if the only working is \(2{r^2} – 2{r^2}\cos \theta \).
[4 marks]
(i) \(\frac{1}{2}\alpha {r^2}\;\;\;\left( {{\text{accept }}2{r^2}(1 – \cos \alpha )} \right)\) A1 N1
(ii) correct equation in one variable (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;2(1 – \cos \alpha ) = \frac{1}{2}\alpha \)
\(\alpha = 0.511024\)
\(\alpha = 0.511\;\;\;({\text{accept }}\theta = 0.511)\) A2 N2
Note: Award A1 for \(\alpha = 0.511\) and additional answers.
[4 marks]
Note: In this part, accept \(\theta \) instead of \(\beta \), and the use of equations instead of inequalities in the working.
attempt to find \(R\) (M1)
eg\(\;\;\;\)subtraction of areas, \({\text{square}} – {\text{segment}}\)
correct expression for segment area (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;\frac{1}{2}\beta {r^2} – \frac{1}{2}{r^2}\sin \beta \)
correct expression for \(R\) (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;2{r^2}(1 – \cos \beta ) – \left( {\frac{1}{2}\beta {r^2} – \frac{1}{2}{r^2}\sin \beta } \right)\)
correct inequality (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;2{r^2}(1 – \cos \beta ) – \left( {\frac{1}{2}\beta {r^2} – \frac{1}{2}{r^2}\sin \beta } \right) > 2\left( {\frac{1}{2}\beta {r^2}} \right)\)
correct inequality in terms of angle only A1
eg\(\;\;\;2(1 – \cos \beta ) – \left( {\frac{1}{2}\beta – \frac{1}{2}\sin \beta } \right) > \beta \)
attempt to solve their inequality, must represent \(R > \) twice sector (M1)
eg\(\;\;\;\)sketch, one correct value
Note: Do not award the second (M1) unless the first (M1) for attempting to find \(R\) has been awarded.
both correct values \(1.30573\) and \(2.67369\) (A1)
correct inequality \(1.31 < \beta < 2.67\) A1 N3
[8 marks]
Total [16 marks]
Question
The following diagram shows a circle with centre \(O\) and radius \(3\) cm.
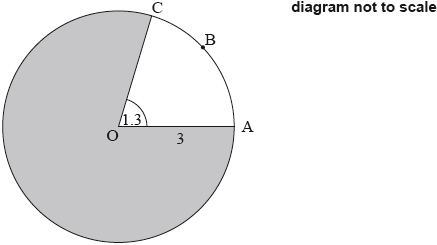
Points A, B, and C lie on the circle, and \({\rm{A\hat OC}} = 1.3{\text{ radians}}\).
Find the length of arc \(ABC\).
Find the area of the shaded region.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
correct substitution (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;l = 1.3 \times 3\)
\(l\) = \(3.9\) (cm) A1 N2
[2 marks]
METHOD 1
valid approach (M1)
eg\(\;\;\;\)finding reflex angle, \(2\pi – {\rm{C\hat OA}}\)
correct angle (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;2\pi – 1.3,{\text{ }}4.98318\)
correct substitution (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;\frac{1}{2}(2\pi – 1.3){3^2}\)
\(22.4243\)
\({\text{area}} = 9\pi – 5.85{\text{ (exact), }}22.4{\text{ }} {\text{ }}({\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2})\) A1 N3
METHOD 2
correct area of small sector (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;\frac{1}{2}(1.3){3^2},{\text{ }}5.85\)
valid approach (M1)
eg\(\;\;\;\)circle − small sector, \(\pi {r^2} – \frac{1}{2}\theta {r^2}\)
correct substitution (A1)
eg\(\;\;\;\pi ({3^2}) – \frac{1}{2}(1.3){3^2}\)
\(22.4243\)
\({\text{area}} = 9\pi – 5.85{\text{ }}({\text{exact}}),{\text{ }}22.4{\text{ }}{\text{ }}({\text{c}}{{\text{m}}^2})\) A1 N3
[4 marks]
Total [6 marks]
Question
The following diagram shows a circle, centre O and radius \(r\) mm. The circle is divided into five equal sectors.
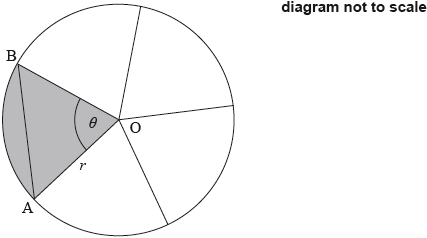
One sector is OAB, and \({\rm{A\hat OB}} = \theta \).
The area of sector AOB is \(20\pi {\text{ m}}{{\text{m}}^2}\).
Write down the exact value of \(\theta \) in radians.
Find the value of \(r\).
Find AB.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(\theta = \frac{{2\pi }}{5}\) A1 N1
[1 mark]
correct expression for area (A1)
eg\(\,\,\,\,\,\)\(A = \frac{1}{2}{r^2}\left( {\frac{{2\pi }}{5}} \right),{\text{ }}\frac{{\pi {r^2}}}{5}\)
evidence of equating their expression to \(20\pi \) (M1)
eg\(\,\,\,\,\,\)\(\frac{1}{2}{r^2}\left( {\frac{{2\pi }}{5}} \right) = 20\pi ,{\text{ }}{r^2} = 100,{\text{ }}r = \pm 10\)
\(r = 10\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
METHOD 1
evidence of choosing cosine rule (M1)
eg\(\,\,\,\,\,\)\({a^2} = {b^2} + {c^2} – 2bc\cos A\)
correct substitution of their \(r\) and \(\theta \) into RHS (A1)
eg\(\,\,\,\,\,\)\({10^2} + {10^2} – 2 \times 10 \times 1{\text{0}}\cos \left( {\frac{{2\pi }}{5}} \right)\)
11.7557
\({\text{AB}} = 11.8{\text{ (mm)}}\) A1 N2
METHOD 2
evidence of choosing sine rule (M1)
eg\(\,\,\,\,\,\)\(\frac{{\sin A}}{a} = \frac{{\sin B}}{b}\)
correct substitution of their \(r\) and \(\theta \) (A1)
eg\(\,\,\,\,\,\)\(\frac{{\sin \frac{{2\pi }}{5}}}{{{\text{AB}}}} = \frac{{\sin \left( {\frac{1}{2}\left( {\pi – \frac{{2\pi }}{5}} \right)} \right)}}{{10}}\)
11.7557
\({\text{AB}} = 11.8{\text{ (mm)}}\) A1 N2
[3 marks]
Question
The diagram shows a circle, centre O, with radius 4 cm. Points A and B lie on the circumference of the circle and AÔB = θ , where 0 ≤ θ ≤ \(\pi \).
Find the area of the shaded region, in terms of θ.
The area of the shaded region is 12 cm2. Find the value of θ.
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
valid approach to find area of segment (M1)
eg area of sector – area of triangle, \(\frac{1}{2}{r^2}\left( {\theta – {\text{sin}}\theta } \right)\)
correct substitution (A1)
eg \(\frac{1}{4}{\left( 4 \right)^2}\theta – \frac{1}{2}{\left( 4 \right)^2}{\text{sin}}\theta ,\,\,\frac{1}{2} \times 16\left[ {\theta – {\text{sin}}\theta } \right]\)
area = 80 – 8 sinθ, 8(θ – sinθ) A1 N2
[3 marks]
setting their area expression equal to 12 (M1)
eg 12 = 8(θ – sinθ)
2.26717
θ = 2.27 (do not accept an answer in degrees) A2 N3
[3 marks]
Question
A circle centre O and radius \(r\) is shown below. The chord [AB] divides the area of the circle into two parts. Angle AOB is \(\theta \) .
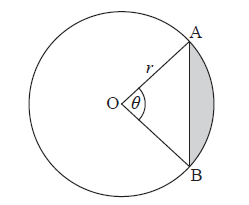
Find an expression for the area of the shaded region.
The chord [AB] divides the area of the circle in the ratio 1:7. Find the value of \(\theta \) .
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
substitution into formula for area of triangle A1
e.g. \(\frac{1}{2}r \times r\sin \theta \)
evidence of subtraction M1
correct expression A1 N2
e.g. \(\frac{1}{2}{r^2}\theta – \frac{1}{2}{r^2}\sin \theta \) , \(\frac{1}{2}{r^2}(\theta – \sin \theta )\)
[3 marks]
evidence of recognizing that shaded area is \(\frac{1}{8}\) of area of circle M1
e.g. \(\frac{1}{8}\) seen anywhere
setting up correct equation A1
e.g. \(\frac{1}{2}{r^2}(\theta – \sin \theta ) = \frac{1}{8}\pi {r^2}\)
eliminating 1 variable M1
e.g. \(\frac{1}{2}(\theta – \sin \theta ) = \frac{1}{8}\pi \) , \(\theta – \sin \theta = \frac{\pi }{4}\)
attempt to solve M1
e.g. a sketch, writing \(\sin x – x + \frac{\pi }{4} = 0\)
\(\theta = 1.77\) (do not accept degrees) A1 N1
[5 marks]

