IB Mathematics SL 5.7 The second derivative AA SL Paper 1- Exam Style Questions- New Syllabus
Question
(i) Determine the value of \(k\).
(ii) Calculate the total length \(T\) for this value of \(x\).
(iii) Determine the corresponding value of \(y\).
(ii) Justify whether the value of \(T\) at \(x = k\) represents a local minimum or a local maximum.
Most-appropriate topic codes (Mathematics: analysis and approaches guide):
• SL 5.7: The second derivative; Graphical behaviour of functions — Part e
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
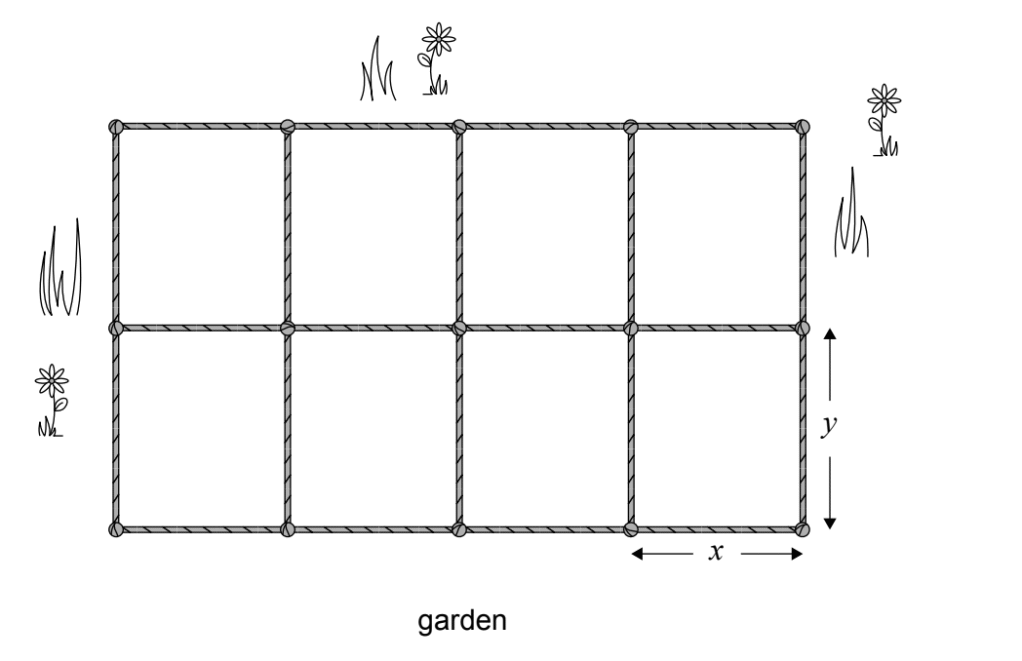
The total area consists of 8 congruent rectangles: \(8 \times (x \times y) = 60\).
Isolating \(y\):
\(y = \frac{60}{8x} = \frac{7.5}{x}\).
(b)
In a \(4 \times 2\) grid:
– Horizontal cord lines: There are 3 lines spanning the full width (\(4x\)). Total = \(3 \times 4x = 12x\).
– Vertical cord lines: There are 5 lines spanning the full height (\(2y\)). Total = \(5 \times 2y = 10y\).
Total length \(T = 12x + 10y\).
Substituting \(y = \frac{7.5}{x}\):
\(T = 12x + 10\left(\frac{7.5}{x}\right) = 12x + \frac{75}{x}\). (Shown)
(c)
Rewrite as \(T = 12x + 75x^{-1}\).
\(\frac{dT}{dx} = 12 – 75x^{-2} = 12 – \frac{75}{x^2}\).
(d)
(i) Set \(\frac{dT}{dx} = 0\):
\(12 = \frac{75}{k^2} \implies k^2 = \frac{75}{12} = 6.25\).
\(k = \sqrt{6.25} = 2.5\) (since \(x > 0\)).
(ii) \(T = 12(2.5) + \frac{75}{2.5} = 30 + 30 = 60 \text{ m}\).
(iii) \(y = \frac{7.5}{2.5} = 3 \text{ m}\).
(e)
(i) \(\frac{d^2T}{dx^2} = \frac{d}{dx}(12 – 75x^{-2}) = 150x^{-3} = \frac{150}{x^3}\).
(ii) At \(x = 2.5\), \(\frac{d^2T}{dx^2} = \frac{150}{(2.5)^3} > 0\).
Since the second derivative is positive, the function has a local minimum at \(x = 2.5\).
