IB Mathematics SL 5.4 Tangents and Normals AA SL Paper 2- Exam Style Questions- New Syllabus
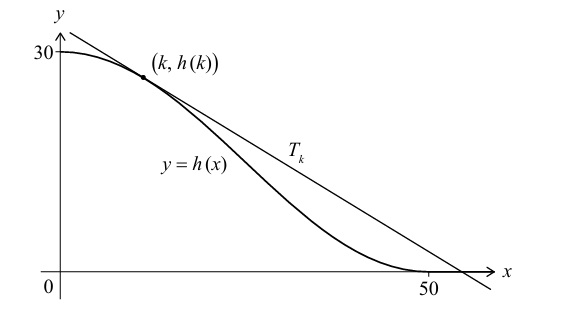
Question
Most-appropriate topic codes (Mathematics: analysis and approaches guide):
• SL 5.1: Derivative interpreted as the gradient function — Part a
• SL 5.4: Tangents at a given point and their equations — Part b
• SL 3.5: The equation of a straight line through the origin is \( y = x \tan \theta \) — Part b
▶️ Answer/Explanation
(a)
To find the gradient, we differentiate \( h(x) \) using the chain rule:
\( h'(x) = 15 \cdot \left[ -\sin\left( \frac{\pi x}{50} \right) \right] \cdot \frac{\pi}{50} \)
Simplify the coefficient:
\( h'(x) = -\frac{15\pi}{50} \sin\left( \frac{\pi x}{50} \right) = -\frac{3\pi}{10} \sin\left( \frac{\pi x}{50} \right) \)
At \( x = k \), the gradient is:
\( h'(k) = -\frac{3\pi}{10} \sin\left( \frac{\pi k}{50} \right) \)
\( \displaystyle \boxed{-\frac{3\pi}{10} \sin\left( \frac{\pi k}{50} \right)} \)
(b)
The gradient \( m \) of a line making an angle \( \theta \) with the positive \( x \)-axis is given by \( m = \tan \theta \).
Given \( \theta = \frac{\pi}{8} \), the gradient is \( \tan\left( \frac{\pi}{8} \right) \approx 0.414 \).
Depending on the direction of the slope, the gradient can be positive or negative. We set:
\( -\frac{3\pi}{10} \sin\left( \frac{\pi k}{50} \right) = \pm \tan\left( \frac{\pi}{8} \right) \)
Case 1: \( \sin\left( \frac{\pi k}{50} \right) = \frac{10}{3\pi} \tan\left( \frac{\pi}{8} \right) \approx 0.439… \)
Solutions in the domain \( 0 \leq k \leq 50 \) (where \( 0 \leq \frac{\pi k}{50} \leq \pi \)):
\( \frac{\pi k}{50} = \arcsin(0.439…) \approx 0.455 \implies k \approx 7.24 \)
\( \frac{\pi k}{50} = \pi – 0.455 \approx 2.687 \implies k \approx 42.8 \)
Case 2: \( \sin\left( \frac{\pi k}{50} \right) = -\frac{10}{3\pi} \tan\left( \frac{\pi}{8} \right) \approx -0.439… \)
For this case, \( \sin \theta \) is negative, which occurs for \( \pi < \theta < 2\pi \). This corresponds to \( k > 50 \), which is outside the given domain.
Valid solutions: \( \boxed{k \approx 7.24, \ k \approx 42.8} \)
