IBDP Physics- B.5 Current and circuits - IB Style Questions For SL Paper 1A -FA 2025
Question
Three combinations of resistors are shown. The resistors are identical.
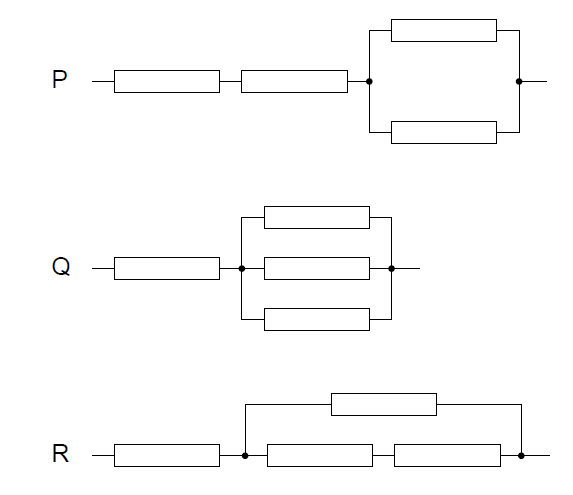
What is the total resistance of each combination of resistors in order of increasing resistance?
A. P Q R
B. Q P R
C. P R Q
D. Q R P
B. Q P R
C. P R Q
D. Q R P
▶️ Answer/Explanation
Concise working (let each resistor be \(R\)):
Combination Q: \(R_{\!Q}=R+\left(R\parallel R\parallel R\right)=R+\frac{R}{3}=\frac{4R}{3}\)
Combination R: \(R_{\!R}=R+\left(R\parallel 2R\right)=R+\frac{R(2R)}{R+2R}=R+\frac{2R}{3}=\frac{5R}{3}\)
Combination P: \(R_{\!P}=2R+\left(R\parallel R\right)=2R+\frac{R}{2}=\frac{5R}{2}\)
Since \( \frac{4R}{3} < \frac{5R}{3} < \frac{5R}{2}\), the increasing order is Q, R, P.
✅ Answer: (D)
Question
Four identical lamps are connected in a circuit. The current through lamp \(L\) is \(I\).

The lamps are rearranged using the same cell.

What is the current through \(L\)?
A. \(\frac{I}{4}\)
B. \(I\)
C. \(I\)
D. \(2I\)
B. \(I\)
C. \(I\)
D. \(2I\)
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Detailed solution

In both arrangements, lamp \(L\) ends up with the same potential difference across it (the overall series/parallel structure seen by the cell is equivalent).
Since all lamps are identical (same resistance), the current through lamp \(L\) is unchanged.
✅ Answer: C
Question
\(P\) and \(Q\) are two conductors of the same material connected in series. Conductor \(Q\) has a diameter twice that of \(P\).
What is \(\dfrac{\text{drift speed of electrons in } P}{\text{drift speed of electrons in } Q}\)?
What is \(\dfrac{\text{drift speed of electrons in } P}{\text{drift speed of electrons in } Q}\)?

A. \(4\)
B. \(2\)
C. \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
D. \(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
B. \(2\)
C. \(\dfrac{1}{2}\)
D. \(\dfrac{1}{4}\)
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Since conductors \(P\) and \(Q\) are connected in series, the same current flows through both.
Drift speed \(v_d\) is given by \(v_d = \dfrac{I}{nqA}\), so for the same material and same current, the drift speed is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area \(A\).
The diameter of \(Q\) is twice that of \(P\), so \(A_Q = (2)^2 A_P = 4A_P\).
Therefore,
\(\dfrac{v_P}{v_Q} = \dfrac{A_Q}{A_P} = 4\).
✅ Answer: A
Drift speed \(v_d\) is given by \(v_d = \dfrac{I}{nqA}\), so for the same material and same current, the drift speed is inversely proportional to the cross-sectional area \(A\).
The diameter of \(Q\) is twice that of \(P\), so \(A_Q = (2)^2 A_P = 4A_P\).
Therefore,
\(\dfrac{v_P}{v_Q} = \dfrac{A_Q}{A_P} = 4\).
✅ Answer: A
