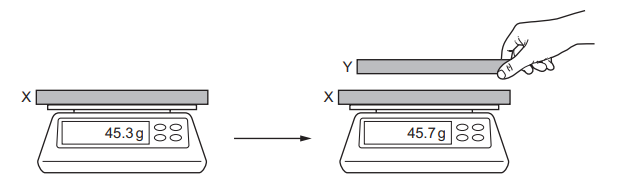
Question
A charged rod X is placed on a balance and another rod Y is brought close to it, as shown.
Which combination of charges would cause the change in the balance reading shown?
| X | Y |
A | negative charge | negative charge |
B | negative charge | positive charge |
C | negative charge | no charge |
D | positive charge | no charge |
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
A student rubs a plastic rod with a cloth. The rod becomes positively charged.
What has happened to the rod?
It has gained electrons.
It has gained protons.
It has lost electrons.
It has lost protons.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C
Question
Diagram 1 shows two thin, uncharged strips of plastic.
Diagram 2 shows the same strips after they have been rubbed with a dry cloth.
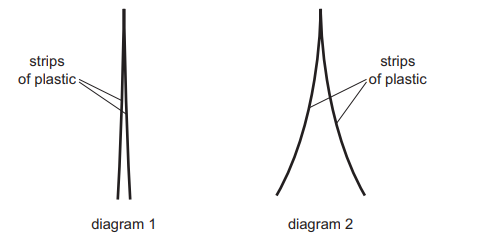
Which row describes the charge on the strips after rubbing, and the force between the strips after rubbing?
| charge on strips | force between strips |
A | opposite | attraction |
B | opposite | repulsion |
C | the same | attraction |
D | the same | repulsion |
Answer/Explanation
Ans: D
Question
A polythene rod becomes negatively charged when it is rubbed with a cloth.
Which statement explains this?
A The rod gains electrons.
B The rod loses electrons.
C The rod gains protons.
D The rod loses protons.
Answer/Explanation
Ans: A
Question
Three statements about electric charge are given.
An ammeter directly measures how much electric charge is in an object.
A moving electric charge can be detected by an ammeter.
A flow of electric charge is an electric current.
Which statements are correct?
A 1 and 2 only B 1 and 3 only C 2 and 3 only D 1, 2 and 3
Answer/Explanation
Ans: C