IIT JEE Main Maths -Unit 8- Evaluation of Simple and Definite Integrals- Study Notes-New Syllabus
IIT JEE Main Maths -Unit 8- Evaluation of Simple and Definite Integrals – Study Notes – New syllabus
IIT JEE Main Maths -Unit 8- Evaluation of Simple and Definite Integrals – Study Notes -IIT JEE Main Maths – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- Evaluation of Simple and Definite Integrals
- Evaluation of Simple Integrals of the Type
- Reduction Formulae and Special Trigonometric Integrals
Evaluation of Simple and Definite Integrals
Integration is the reverse process of differentiation. The value of an integral can be of two types:
- Indefinite Integral: Represents a family of functions and includes a constant of integration \( C \).
- Definite Integral: Represents a numerical value corresponding to the area under a curve between two limits \( a \) and \( b \).
Indefinite Integral (Recap)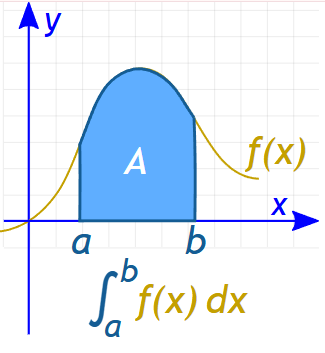
$ \int f(x)\,dx = F(x) + C $
Here, \( F'(x) = f(x) \). This represents the general anti-derivative of \( f(x) \).
Definite Integral — Definition
If \( F(x) \) is an anti-derivative of \( f(x) \) on the interval \([a, b]\), then
$ \int_a^b f(x)\,dx = F(b) – F(a) $
This is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus.
Properties of Definite Integrals
| Property | Formula |
|---|---|
| Additivity | \( \displaystyle \int_a^b f(x)\,dx + \int_b^c f(x)\,dx = \int_a^c f(x)\,dx \) |
| Reversal of limits | \( \displaystyle \int_a^b f(x)\,dx = -\int_b^a f(x)\,dx \) |
| Zero width | \( \displaystyle \int_a^a f(x)\,dx = 0 \) |
| Constant multiple | \( \displaystyle \int_a^b k f(x)\,dx = k \int_a^b f(x)\,dx \) |
| Linearity | \( \displaystyle \int_a^b [f(x) \pm g(x)]\,dx = \int_a^b f(x)\,dx \pm \int_a^b g(x)\,dx \) |
Geometrical Meaning
The definite integral \( \displaystyle \int_a^b f(x)\,dx \) represents the net area between the curve \( y = f(x) \) and the x-axis from \( x = a \) to \( x = b \):
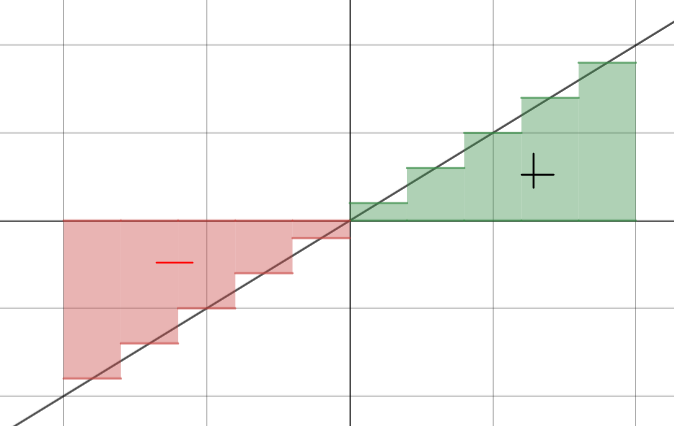
- Area above x-axis → positive
- Area below x-axis → negative
Evaluation Technique
- Find the indefinite integral \( F(x) \) of \( f(x) \).
- Apply the limits: \( F(b) – F(a) \).
- Simplify to obtain the numerical result.
Example
Evaluate \( \displaystyle \int_0^2 (3x^2 + 2x + 1)\,dx \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Integrate each term:
\( \displaystyle \int (3x^2 + 2x + 1)\,dx = x^3 + x^2 + x + C. \)
Step 2: Apply limits from 0 to 2:
\( [x^3 + x^2 + x]_0^2 = (8 + 4 + 2) – 0 = 14. \)
Answer: \( 14. \)
Example
Evaluate \( \displaystyle \int_0^{\pi/2} \sin x\,dx \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: \( \displaystyle \int \sin x\,dx = -\cos x + C. \)
Step 2: Apply limits \( 0 \) to \( \pi/2 \):
\( [-\cos x]_0^{\pi/2} = [-(0 – 1)] = 1. \)
Answer: \( 1. \)
Example
Evaluate \( \displaystyle \int_0^1 x e^x\,dx \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Step 1: Use integration by parts:
Let \( u = x \Rightarrow du = dx \), \( dv = e^x dx \Rightarrow v = e^x. \)
Then, \( \displaystyle \int x e^x dx = x e^x – \int e^x dx = e^x(x – 1) + C. \)
Step 2: Apply limits \( 0 \) to \( 1 \):
\( [e^x(x – 1)]_0^1 = [e(1 – 1)] – [1(0 – 1)] = 1 – 1/e. \)
Answer: \( 1 – \dfrac{1}{e}. \)
Properties of Definite Integrals (Symmetry and Substitution)
- Property 1: \( \displaystyle \int_0^a f(x)\,dx = \int_0^a f(a – x)\,dx \)
- Property 2: \( \displaystyle \int_{-a}^{a} f(x)\,dx = 2\int_0^a f(x)\,dx \) if \( f(x) \) is even.
- Property 3: \( \displaystyle \int_{-a}^{a} f(x)\,dx = 0 \) if \( f(x) \) is odd.
Example
Evaluate \( \displaystyle \int_{-2}^2 x^3\,dx \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
\( x^3 \) is an odd function since \( f(-x) = -f(x) \).
Thus, \( \displaystyle \int_{-a}^{a} f(x)\,dx = 0 \) for odd functions.
Answer: \( 0. \)
Evaluation of Simple Integrals of the Type
Below are standard integral forms that are essential for JEE Mains and Advanced. These can be directly used while solving definite or indefinite integrals after applying appropriate substitutions.
Standard Integrals Involving Rational Functions
| Integral | Result |
|---|---|
| \( \displaystyle \int \dfrac{dx}{x^2 + a^2} \) | \( \dfrac{1}{a} \tan^{-1}\!\left(\dfrac{x}{a}\right) + C \) |
| \( \displaystyle \int \dfrac{dx}{x^2 – a^2} \) | \( \dfrac{1}{2a}\ln\!\left|\dfrac{x – a}{x + a}\right| + C \) |
| \( \displaystyle \int \dfrac{dx}{a^2 – x^2} \) | \( \dfrac{1}{2a}\ln\!\left|\dfrac{a + x}{a – x}\right| + C \) |
Standard Integrals Involving Square Roots
| Integral | Result |
|---|---|
| \( \displaystyle \int \dfrac{dx}{\sqrt{x^2 + a^2}} \) | \( \ln\!\left|x + \sqrt{x^2 + a^2}\right| + C \) |
| \( \displaystyle \int \dfrac{dx}{\sqrt{a^2 – x^2}} \) | \( \sin^{-1}\!\left(\dfrac{x}{a}\right) + C \) |
| \( \displaystyle \int \sqrt{x^2 + a^2}\,dx \) | \( \dfrac{x}{2}\sqrt{x^2 + a^2} + \dfrac{a^2}{2}\ln\!\left|x + \sqrt{x^2 + a^2}\right| + C \) |
| \( \displaystyle \int \sqrt{a^2 – x^2}\,dx \) | \( \dfrac{x}{2}\sqrt{a^2 – x^2} + \dfrac{a^2}{2}\sin^{-1}\!\left(\dfrac{x}{a}\right) + C \) |
Integrals Involving Quadratic Expressions
For \( ax^2 + bx + c \), use completing the square before applying standard results:
$ ax^2 + bx + c = a\left[\left(x + \dfrac{b}{2a}\right)^2 + \dfrac{4ac – b^2}{4a^2}\right] $
| Integral | Result |
|---|---|
| \( \displaystyle \int \dfrac{dx}{ax^2 + bx + c} \) | Depends on the discriminant \( D = b^2 – 4ac \): |
| |
Integrals of the Type \( \displaystyle \int \dfrac{px + q}{ax^2 + bx + c}\,dx \)
This can be split as:
$ \int \dfrac{px + q}{ax^2 + bx + c}\,dx = \dfrac{p}{2a}\ln|ax^2 + bx + c| + \int \dfrac{\left(q – \dfrac{bp}{2a}\right)\,dx}{ax^2 + bx + c} $
The remaining integral can be solved using the discriminant-based formula from above.
Integrals Involving \( \sqrt{ax^2 + bx + c} \)
Use substitution or completing the square depending on the form.
- If \( b = 0 \), use standard forms from (2).
- If \( b \neq 0 \), complete the square, then substitute \( x + \dfrac{b}{2a} = t \).
Quick Reference — Common Substitutions
| Expression | Substitute | Resulting Simplification |
|---|---|---|
| \( \sqrt{a^2 – x^2} \) | \( x = a\sin\theta \) | \( \sqrt{a^2 – x^2} = a\cos\theta \) |
| \( \sqrt{x^2 + a^2} \) | \( x = a\tan\theta \) | \( \sqrt{x^2 + a^2} = a\sec\theta \) |
| \( \sqrt{x^2 – a^2} \) | \( x = a\sec\theta \) | \( \sqrt{x^2 – a^2} = a\tan\theta \) |
Example
Evaluate \( \displaystyle \int \dfrac{dx}{\sqrt{x^2 + 9}} \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Here \( a = 3 \).
Using standard formula: \( \displaystyle \int \dfrac{dx}{\sqrt{x^2 + a^2}} = \ln|x + \sqrt{x^2 + a^2}| + C. \)
\( \Rightarrow \boxed{\ln|x + \sqrt{x^2 + 9}| + C.} \)
Example
Evaluate \( \displaystyle \int \sqrt{16 – x^2}\,dx \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Using \( \displaystyle \int \sqrt{a^2 – x^2}\,dx = \dfrac{x}{2}\sqrt{a^2 – x^2} + \dfrac{a^2}{2}\sin^{-1}\!\left(\dfrac{x}{a}\right) + C. \)
\( a = 4 \Rightarrow \boxed{2x\sqrt{16 – x^2} + 8\sin^{-1}\!\left(\dfrac{x}{4}\right) + C.} \)
Reduction Formulae and Special Trigonometric Integrals
Some integrals contain powers of trigonometric, exponential, or logarithmic functions that are difficult to evaluate directly. In such cases, reduction formulae help express a given integral in terms of another with a lower power, allowing for recursive evaluation.
Reduction Formula — Concept
If \( I_n = \int f_n(x)\,dx \) and \( I_n \) can be expressed in terms of \( I_{n-1} \), then \( I_n \) is said to have a reduction formula.
That is,
$ I_n = g(x, n) + h(n)\,I_{n-1} $
Reduction Formulae for Trigonometric Integrals
| Integral Type | Reduction Formula |
|---|---|
| \( I_n = \displaystyle \int \sin^n x \, dx \) | \( I_n = -\dfrac{\sin^{n-1}x\cos x}{n} + \dfrac{n-1}{n}I_{n-2} \) |
| \( I_n = \displaystyle \int \cos^n x \, dx \) | \( I_n = \dfrac{\sin x\cos^{n-1}x}{n} + \dfrac{n-1}{n}I_{n-2} \) |
| \( I_n = \displaystyle \int \tan^n x \, dx \) | \( I_n = \dfrac{1}{n-1}\tan^{n-1}x – I_{n-2} \) |
| \( I_n = \displaystyle \int \sec^n x \, dx \) | \( I_n = \dfrac{\sec^{n-2}x\tan x}{n-1} + \dfrac{n-2}{n-1}I_{n-2} \) |
Reduction Formula for Exponential and Logarithmic Forms
| Integral Type | Reduction Formula |
|---|---|
| \( I_n = \displaystyle \int x^n e^{ax}\,dx \) | \( I_n = \dfrac{x^n e^{ax}}{a} – \dfrac{n}{a}I_{n-1} \) |
| \( I_n = \displaystyle \int x^n \sin(ax)\,dx \) | \( I_n = -\dfrac{x^n \cos(ax)}{a} + \dfrac{n}{a}I_{n-1}^\cos \) |
| \( I_n = \displaystyle \int x^n \cos(ax)\,dx \) | \( I_n = \dfrac{x^n \sin(ax)}{a} – \dfrac{n}{a}I_{n-1}^\sin \) |
| \( I_n = \displaystyle \int (\ln x)^n \, dx \) | \( I_n = x(\ln x)^n – nI_{n-1} \) |
Reduction Formula for Powers of \( (a^2 + x^2) \)
For \( I_n = \displaystyle \int \dfrac{dx}{(a^2 + x^2)^n} \):
$ I_n = \dfrac{x}{2a^2(n – 1)(a^2 + x^2)^{n – 1}} + \dfrac{2n – 3}{2a^2(n – 1)}I_{n-1} $
Reduction Formula for \( \displaystyle \int \sin^m x \cos^n x \, dx \)
- If \( n \) is odd, use \( \cos^2x = 1 – \sin^2x \) and substitute \( \sin x = t \).
- If \( m \) is odd, use \( \sin^2x = 1 – \cos^2x \) and substitute \( \cos x = t \).
- If both are even, use the power-reduction identities:
$ \sin^2x = \dfrac{1 – \cos(2x)}{2}, \quad \cos^2x = \dfrac{1 + \cos(2x)}{2} $
Important Standard Results
- \( \displaystyle \int \sec^2x\,dx = \tan x + C \)
- \( \displaystyle \int \csc^2x\,dx = -\cot x + C \)
- \( \displaystyle \int \sec x \tan x\,dx = \sec x + C \)
- \( \displaystyle \int \csc x \cot x\,dx = -\csc x + C \)
Example
Evaluate \( \displaystyle \int \sin^4x\,dx \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Use \( I_n = -\dfrac{\sin^{n-1}x\cos x}{n} + \dfrac{n-1}{n}I_{n-2} \).
Here, \( n = 4 \): \( I_4 = -\dfrac{\sin^3x\cos x}{4} + \dfrac{3}{4}I_2. \)
Now, \( I_2 = \int \sin^2x\,dx = \dfrac{x}{2} – \dfrac{\sin 2x}{4}. \)
\( \Rightarrow I_4 = -\dfrac{\sin^3x\cos x}{4} + \dfrac{3}{4}\left(\dfrac{x}{2} – \dfrac{\sin 2x}{4}\right) + C. \)
Example
Evaluate \( \displaystyle \int x^2 e^{3x}\,dx \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Use reduction formula \( I_n = \dfrac{x^n e^{3x}}{3} – \dfrac{n}{3}I_{n-1}. \)
Here, \( I_2 = \dfrac{x^2 e^{3x}}{3} – \dfrac{2}{3}I_1. \)
Now, \( I_1 = \dfrac{x e^{3x}}{3} – \dfrac{1}{3}I_0 \), and \( I_0 = \dfrac{e^{3x}}{3}. \)
Substitute back: \( I_1 = \dfrac{e^{3x}}{9}(3x – 1) \). Hence, \( I_2 = \dfrac{e^{3x}}{27}(9x^2 – 6x + 2) + C. \)
Example
Find \( \displaystyle \int \sec^5x\,dx \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Use \( I_n = \dfrac{\sec^{n-2}x\tan x}{n-1} + \dfrac{n-2}{n-1}I_{n-2}. \)
Here, \( n = 5 \): \( I_5 = \dfrac{\sec^3x\tan x}{4} + \dfrac{3}{4}I_3. \)
Now, \( I_3 = \dfrac{\sec x\tan x}{2} + \dfrac{1}{2}I_1 = \dfrac{\sec x\tan x}{2} + \dfrac{1}{2}\ln|\sec x + \tan x|. \)
Substitute back: \( I_5 = \dfrac{\sec^3x\tan x}{4} + \dfrac{3}{8}\sec x\tan x + \dfrac{3}{8}\ln|\sec x + \tan x| + C. \)
Notes and Study Materials
- Concepts of definite integrals
- definite integrals Master File
- definite integrals Revision Notes
- definite integrals Formulae
- definite integrals Reference Book
- definite integrals Past Many Years Questions and Answer
Examples and Exercise
IIT JEE (Main) Mathematics ,”definite integrals” Notes ,Test Papers, Sample Papers, Past Years Papers , NCERT , S. L. Loney and Hall & Knight Solutions and Help from Ex- IITian
About this unit
Integral as an anti – derivative. Fundamental integrals involving algebraic, trigonometric, exponential and logarithmic functions. Integration by substitution, by parts, and by partial fractions. Integration using trigonometric identities Integral as limit of a sum. Evaluation of simple integrals: Fundamental Theorem of Calculus. Properties of definite integrals, evaluation of definite integrals, determining areas of the regions bounded by simple curves in standard form.
IITian Academy Notes for IIT JEE (Main) Mathematics – definite integrals
The success mantra of the JEE is practice and hard work. Gone are the days when students used to spend hours in attempting one question. Now it is an era of multiple choice questions. The JEE Mathematics questions test a student’s acquired knowledge as well as his aptitude. We have excellent notes prepared by Ex-IITian to best match the requirement of the exam.Focus is given on problem solving skills and small tips and tricks to do it faster and easier. We , Ex-IITian at https://www.iitianacademy.com. will make sure you understand the concept well.
IIT JEE (Main) Mathematics, definite integrals Solved Examples and Practice Papers.
Get excellent practice papers and Solved examples to grasp the concept and check for speed and make you ready for big day. These Question Papers are prepared by Ex-IITIan for IIT JEE (Main) Mathematics , definite integrals.
S. L. Loney IIT JEE (Main) Mathematics
This book is the one of the most beautifully written book by the author. Trigonometry is considered to be one of the easiest topics in mathematics by the aspirants of IIT JEE, AIEEE and other state level engineering examination preparation. It would not be untrue to say that most of the sources have taken inspiration from this book as it is the most reliable source. The best part of this book is its coverage in Heights and Distances and Inverse Trigonometric Functions. The book gives a very good learning experience and the exercises which follow are not only comprehensive but they have both basic and standard questions.. I will help you online for any doubt / clarification.
Hall & Knight IIT JEE (Main) Mathematics
Algebra by Hall and Knight is one of the best books for JEE preparation. Students preparing for IIT JEE and other engineering entrance exams as well as students appearing for board exams should read this everyday, especially to master Algebra and Probability. Hall and Knight have explained the concepts logically in their book.
IIT JEE (Main) Mathematics Assignments
Chapter wise assignments are being given by teachers to students to make them understand the chapter concepts. Its extremely critical for all CBSE students to practice all assignments which will help them in gaining better marks in examinations. All assignments available for free download on the website are developed by the best teachers having many years of teaching experience in CBSE schools all over the country. Students, teachers and parents are advised to contact me online incase of any doubt / clarification.
Past Many Years (40 Years) Questions IIT JEE (Main) Mathematics Solutions definite integrals
Past 40 Years Question Papers Solutions for IIT JEE (Main) Mathematics definite integrals are provided here with simple step-by-step explanations. These solutions for definite integrals are extremely popular among IIT JEE (Main) students for Chemistry . definite integrals Solutions come handy for quickly completing your homework and preparing for exams. All questions and answers from the Past Many Years Question Papers Book of IIT JEE (Main) Mathematics Chapter definite integrals are provided here for . I will help you online for any doubt / clarification.
