IIT JEE Main Maths -Unit 10- Distance, section, and midpoint formulas- Study Notes-New Syllabus
IIT JEE Main Maths -Unit 10- Distance, section, and midpoint formulas – Study Notes – New syllabus
IIT JEE Main Maths -Unit 10- Distance, section, and midpoint formulas – Study Notes -IIT JEE Main Maths – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- Distance, Section and Midpoint Formulas
Distance, Section and Midpoint Formulas
These three formulas form the foundation of coordinate geometry and are used repeatedly in Straight Lines, Circles, Conic Sections, and 3D Geometry as well.
Distance Formula
If two points are \( P(x_1, y_1) \) and \( Q(x_2, y_2) \), then distance: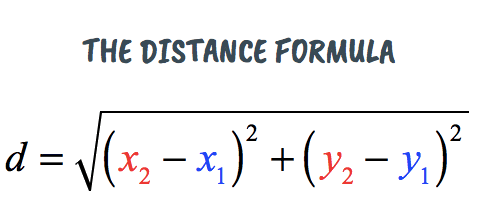
\( PQ = \sqrt{(x_2 – x_1)^2 + (y_2 – y_1)^2} \)
Special cases:
- Horizontal line: distance = \( |x_2 – x_1| \)
- Vertical line: distance = \( |y_2 – y_1| \)
Example
Find the distance between \( (1, 2) \) and \( (4, 6) \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
\( PQ = \sqrt{(4 – 1)^2 + (6 – 2)^2} = \sqrt{3^2 + 4^2} = \sqrt{25} = 5 \)
Answer: 5
Example
Find the distance between \( A(3,-1) \) and \( B(-5,7) \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
\( AB = \sqrt{(-5 – 3)^2 + (7 – (-1))^2} \)
\( = \sqrt{(-8)^2 + (8)^2} = \sqrt{64 + 64} = \sqrt{128} = 8\sqrt{2} \)
Answer: \( 8\sqrt{2} \)
Example
The points \( P(2, k) \) and \( Q(-1, 5) \) are at a distance 5. Find possible values of \( k \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
\( \sqrt{(-1 – 2)^2 + (5 – k)^2} = 5 \)
\( \sqrt{9 + (5 – k)^2} = 5 \)
Square both sides: \( 9 + (5 – k)^2 = 25 \)
\( (5 – k)^2 = 16 \)
\( 5 – k = \pm 4 \)
So \( k = 1 \) or \( k = 9 \)
Answer: \( k = 1,\ 9 \)
Midpoint Formula
If a point \( M \) divides line segment joining \( A(x_1, y_1) \) and \( B(x_2, y_2) \) in the middle, then:
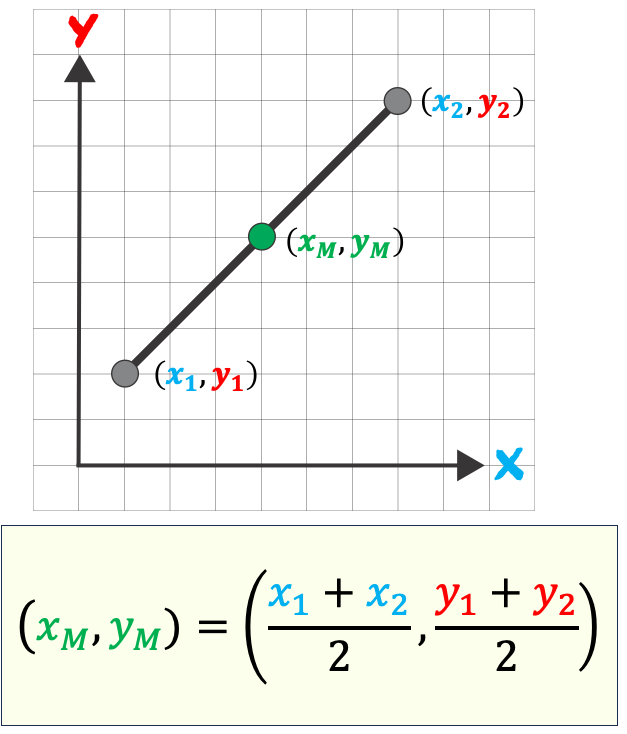
\( M\left( \dfrac{x_1 + x_2}{2},\ \dfrac{y_1 + y_2}{2} \right) \)
Used frequently in geometry problems, locus questions, and coordinate proofs.
Example
Find the midpoint of \( (2, 3) \) and \( (6, 7) \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
\( M = \left( \dfrac{2+6}{2},\ \dfrac{3+7}{2} \right) = (4, 5) \)
Answer: (4, 5)
Example
The midpoint of \( A(4,2) \) and \( B(x,8) \) is \( M(7,5) \). Find \( x \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Midpoint x-coordinate: \( \dfrac{4 + x}{2} = 7 \Rightarrow 4 + x = 14 \Rightarrow x = 10 \)
Answer: \( x = 10 \)
Example
If the midpoint of points \( (p,3) \) and \( (9,q) \) is \( (4,7) \), find \( p \) and \( q \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
For x-coordinate: \( \dfrac{p + 9}{2} = 4 \Rightarrow p + 9 = 8 \Rightarrow p = -1 \)
For y-coordinate: \( \dfrac{3 + q}{2} = 7 \Rightarrow 3 + q = 14 \Rightarrow q = 11 \)
Answer: \( p = -1,\ q = 11 \)
Section Formula (Internal & External Division)
Section formula gives the coordinates of a point dividing a line in a given ratio.
(A) Internal Division
If point \( P \) divides \( A(x_1, y_1) \) and \( B(x_2, y_2) \) in ratio \( m:n \) internally:
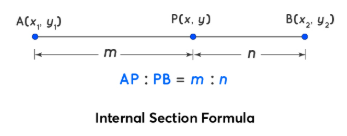
\( P\left( \dfrac{mx_2 + nx_1}{m + n},\ \dfrac{my_2 + ny_1}{m + n} \right) \)
(B) External Division
If point \( P \) divides externally:
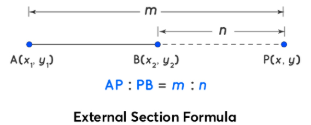
\( P\left( \dfrac{mx_2 – nx_1}{m – n},\ \dfrac{my_2 – ny_1}{m – n} \right) \)
External division appears in JEE locus questions.
Example
Find the point dividing \( (2,4) \) and \( (10,8) \) in ratio \( 1:1 \) internally.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Ratio 1:1 → midpoint
\( P = \left( \dfrac{2+10}{2},\ \dfrac{4+8}{2} \right) = (6,6) \)
Answer: (6, 6)
Example
A point divides the line joining \( A(4, -2) \) and \( B(10, 6) \) in the ratio \( 2:1 \) internally. Find the coordinates.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
\( P = \left( \dfrac{2(10) + 1(4)}{3},\ \dfrac{2(6) + 1(-2)}{3} \right) \)
\( = \left( \dfrac{24}{3},\ \dfrac{10}{3} \right) = (8,\ \dfrac{10}{3}) \)
Answer: \( (8,\ \dfrac{10}{3}) \)
Example
Find the point that divides the line joining \( (3,7) \) and \( (11,-1) \) in ratio \( 3:5 \) externally.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Use external formula:
\( P = \left( \dfrac{3(11) – 5(3)}{3 – 5},\ \dfrac{3(-1) – 5(7)}{3 – 5} \right) \)
\( = \left( \dfrac{33 – 15}{-2},\ \dfrac{-3 – 35}{-2} \right) \)
\( = \left( \dfrac{18}{-2},\ \dfrac{-38}{-2} \right) = (-9,\ 19) \)
Answer: \( (-9,\ 19) \)
