IIT JEE Main Maths -Unit 10- Intercepts on coordinate axes- Study Notes-New Syllabus
IIT JEE Main Maths -Unit 10- Intercepts on coordinate axes – Study Notes – New syllabus
IIT JEE Main Maths -Unit 10- Intercepts on coordinate axes – Study Notes -IIT JEE Main Maths – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- Intercepts on Coordinate Axes
Intercepts on Coordinate Axes
The intercept of a line (or plane in 3D) is the distance at which it meets an axis. For a line in 2D, we mainly talk about the x-intercept and y-intercept.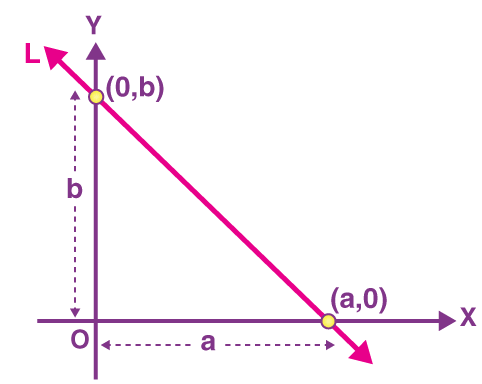
X-Intercept
The point where the line cuts the x-axis.
- On x-axis, \( y = 0 \)
- Substitute \( y = 0 \) into the equation and solve for \( x \)
X-intercept = \( (a, 0) \)
Y-Intercept
The point where the line cuts the y-axis.
- On y-axis, \( x = 0 \)
- Substitute \( x = 0 \) and solve for \( y \)
Y-intercept = \( (0, b) \)
Intercept Form of a Line
If the x-intercept is \( a \) and the y-intercept is \( b \), then the equation of the line is:
\( \dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1 \)
- If either intercept is negative, the graph cuts that axis on negative side.
- A line of the form \( \dfrac{x}{a} + \dfrac{y}{b} = 1 \) never passes through origin.
Converting General Equation to Intercept Form 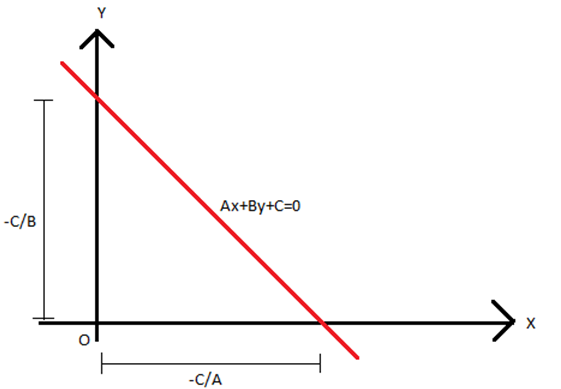
If the line is:
\( ax + by + c = 0 \)
Put it in form:
\( \dfrac{x}{-\frac{c}{a}} + \dfrac{y}{-\frac{c}{b}} = 1 \)
Thus
- X-intercept = \( -\dfrac{c}{a} \)
- Y-intercept = \( -\dfrac{c}{b} \)
Condition for Line to Make Equal Intercepts
If a line makes equal intercepts on coordinate axes, then
\( a = b \) (or magnitudes equal)
For such a line:
Slope = \( -1 \) or \( +1 \)
Example
Find the x-intercept and y-intercept of the line \( 3x + 4y = 12 \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
X-intercept: put \( y = 0 \)
\( 3x = 12 \Rightarrow x = 4 \)
Y-intercept: put \( x = 0 \)
\( 4y = 12 \Rightarrow y = 3 \)
Answer: x-intercept = 4, y-intercept = 3
Example
Convert the equation \( 5x – 2y + 10 = 0 \) into intercept form.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
We compare with \( ax + by + c = 0 \).
X-intercept = \( -\dfrac{c}{a} = -\dfrac{10}{5} = -2 \)
Y-intercept = \( -\dfrac{c}{b} = -\dfrac{10}{-2} = 5 \)
Thus the intercept form is:
\( \dfrac{x}{-2} + \dfrac{y}{5} = 1 \)
Answer: \( \dfrac{x}{-2} + \dfrac{y}{5} = 1 \)
Example
A line cuts the x-axis at \( (3,0) \) and the y-axis at \( (0,-4) \). Find its equation in general form.
▶️ Answer / Explanation
X-intercept \( a = 3 \)
Y-intercept \( b = -4 \)
Use intercept form:
\( \dfrac{x}{3} + \dfrac{y}{-4} = 1 \)
Multiply by 12:
\( 4x – 3y = 12 \)
General form: \( 4x – 3y – 12 = 0 \)
Answer: \( 4x – 3y – 12 = 0 \)
