IIT JEE Main Maths -Unit 14- Properties and transformations- Study Notes-New Syllabus
IIT JEE Main Maths -Unit 14- Properties and transformations – Study Notes – New syllabus
IIT JEE Main Maths -Unit 14- Properties and transformations – Study Notes -IIT JEE Main Maths – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- Properties of Triangle (Trigonometric Form)
Properties of Triangle (Trigonometric Form)
These formulas relate the sides and angles of a triangle using trigonometric functions. They are essential in JEE for solving geometry, trigonometry, and vector problems.
Notation Used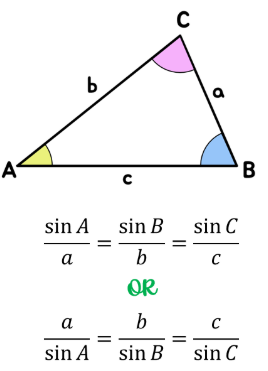
For triangle \( ABC \):
- Side \( a \) opposite angle \( A \)
- Side \( b \) opposite angle \( B \)
- Side \( c \) opposite angle \( C \)
Sine Rule
\( \dfrac{a}{\sin A} = \dfrac{b}{\sin B} = \dfrac{c}{\sin C} = 2R \)
- R = circumradius
- Useful when two angles and one side are known
- Useful in ambiguous case (SSA condition)
Cosine Rule![]()
\( a^2 = b^2 + c^2 – 2bc\cos A \)
Similarly:
- \( b^2 = a^2 + c^2 – 2ac\cos B \)
- \( c^2 = a^2 + b^2 – 2ab\cos C \)
Uses:
- When two sides and included angle are known
- Checking if triangle is acute, obtuse, or right
Projection Rule
\( b = a\cos C + c\cos A \)
Similarly:
- \( a = b\cos C + c\cos B \)
- \( c = a\cos B + b\cos A \)
Use: Decomposing sides into projections; helpful in vector geometry.
Napier’s Analogy
For any triangle:
\( \tan\dfrac{A – B}{2} = \dfrac{a – b}{a + b} \cot\dfrac{C}{2} \)
Very useful in solving triangles when one side is known to be slightly larger or smaller.
Area of Triangle
(a) Standard Formula
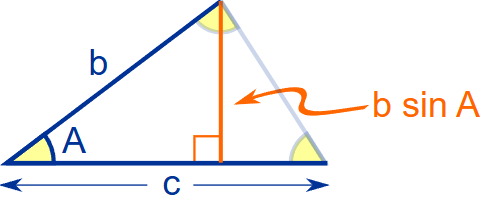
Area \( = \dfrac{1}{2} bc\sin A = \dfrac{1}{2} ca\sin B = \dfrac{1}{2} ab\sin C \)
(b) Using Circumradius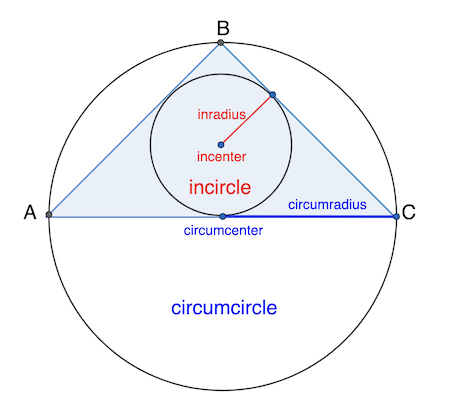
Area \( = \dfrac{abc}{4R} \)
(c) Using Inradius
Area \( = r s \) where \( s = \dfrac{a + b + c}{2} \)
(d) Heron’s Formula
Area \( = \sqrt{s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)} \)
Half Angle Formulas (Important)
- \( \sin\dfrac{A}{2} = \sqrt{\dfrac{(s – b)(s – c)}{bc}} \)
- \( \cos\dfrac{A}{2} = \sqrt{\dfrac{s(s – a)}{bc}} \)
- \( \tan\dfrac{A}{2} = \sqrt{\dfrac{(s – b)(s – c)}{s(s – a)}} \)
Checks for Right Triangle
If \( c \) is the largest side:
- \( c^2 = a^2 + b^2 \Rightarrow \) right triangle
- \( c^2 > a^2 + b^2 \Rightarrow \) obtuse triangle
- \( c^2 < a^2 + b^2 \Rightarrow \) acute triangle
Example
In a triangle, \( A = 30^\circ \), \( B = 60^\circ \), and \( a = 10 \). Find side \( b \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Use Sine Rule:
\( \dfrac{a}{\sin A} = \dfrac{b}{\sin B} \Rightarrow \dfrac{10}{\dfrac{1}{2}} = \dfrac{b}{\dfrac{\sqrt{3}}{2}} \)
\( 20 = \dfrac{2b}{\sqrt{3}} \Rightarrow b = 10\sqrt{3} \)
Answer: \( b = 10\sqrt{3} \)
Example
In triangle \( ABC \), sides are \( a = 8 \), \( b = 6 \), \( c = 7 \). Find angle \( A \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Use Cosine Rule:
\( a^2 = b^2 + c^2 – 2bc\cos A \)
\( 8^2 = 6^2 + 7^2 – 2(6)(7)\cos A \)
\( 64 = 36 + 49 – 84\cos A \)
\( 64 = 85 – 84\cos A \Rightarrow 84\cos A = 21 \Rightarrow \cos A = \dfrac{1}{4} \)
\( A = \cos^{-1}\left(\dfrac{1}{4}\right) \)
Answer: \( A = \cos^{-1}\left(\dfrac{1}{4}\right) \)
Example
In triangle \( ABC \), \( a = 10 \), \( b = 7 \), and \( C = 120^\circ \). Find side \( c \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Use Cosine Rule:
\( c^2 = a^2 + b^2 – 2ab\cos C \)
Since \( \cos 120^\circ = -\dfrac{1}{2} \):
\( c^2 = 10^2 + 7^2 – 2(10)(7)\left(-\dfrac{1}{2}\right) \)
\( c^2 = 100 + 49 + 70 = 219 \)
\( c = \sqrt{219} \)
Answer: \( c = \sqrt{219} \)
