IIT JEE Main Maths -Unit 14- Trigonometric functions and graphs- Study Notes-New Syllabus
IIT JEE Main Maths -Unit 14- Trigonometric functions and graphs – Study Notes – New syllabus
IIT JEE Main Maths -Unit 14- Trigonometric functions and graphs – Study Notes -IIT JEE Main Maths – per latest Syllabus.
Key Concepts:
- Trigonometric Functions and Graphs
Trigonometric Functions and Graphs
Trigonometric functions like \( \sin x \), \( \cos x \), and \( \tan x \) are periodic functions. Understanding their graphs helps solve many JEE problems involving inequalities, transformations, periodicity, and maxima minima.
Domain, Range and Period of Standard Functions
| Function | Domain | Range | Period |
| \( \sin x \) | All real numbers | \( [-1,1] \) | \( 2\pi \) |
| \( \cos x \) | All real numbers | \( [-1,1] \) | \( 2\pi \) |
| \( \tan x \) | \( x \ne \dfrac{\pi}{2} + n\pi \) | All real numbers | \( \pi \) |
Standard Graph Shapes
(a) Graph of \( \sin x \)

- Smooth wave
- Passes through origin
- Max value = 1 at \( x = \dfrac{\pi}{2} \)
- Min value = -1 at \( x = \dfrac{3\pi}{2} \)
(b) Graph of \( \cos x \)
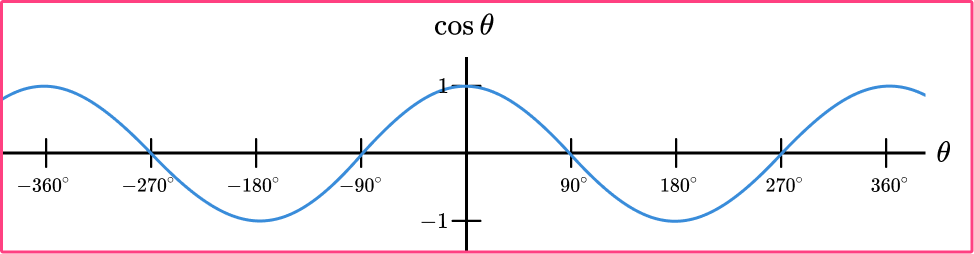
- Same shape as sine wave but starts at 1
- Max at \( x = 0 \)
- Min at \( x = \pi \)
(c) Graph of \( \tan x \)
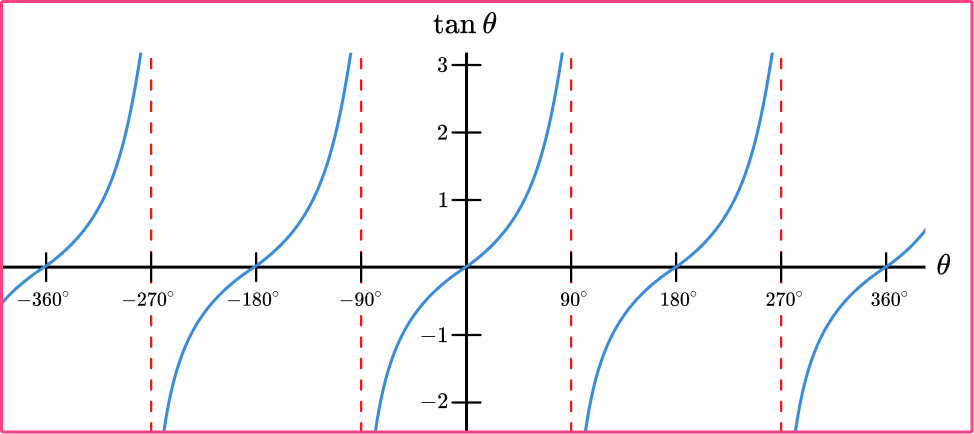
- Asymptotes at \( x = \dfrac{\pi}{2} + n\pi \)
- Increasing curve from \( -\infty \) to \( \infty \)
Transformations of Trigonometric Graphs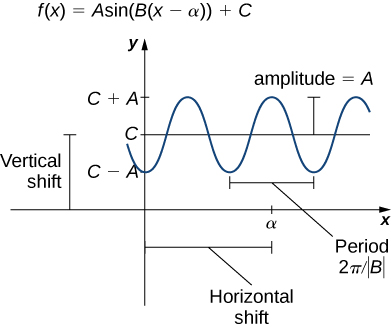
General form:
\( y = A \sin(Bx + C) + D \)
Meaning of parameters:
- A controls amplitude
- B controls period Period = \( \dfrac{2\pi}{|B|} \)
- C shifts graph horizontally (phase shift)
- D shifts graph vertically
Important Graph Properties for JEE
- \( \sin x \) and \( \cos x \) are bounded
- \( \tan x \) is unbounded
- \( \sin x \) is odd, \( \cos x \) is even
- Minima and maxima can be found from amplitude
- Graph shifting is very frequently tested
Special Values on Graphs
- \( \sin x = 0 \Rightarrow x = n\pi \)
- \( \cos x = 0 \Rightarrow x = \dfrac{\pi}{2} + n\pi \)
- \( \tan x = 0 \Rightarrow x = n\pi \)
Example
Find the period of the function \( y = \sin(3x) \).
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Standard period of sine = \( 2\pi \)
Period = \( \dfrac{2\pi}{|3|} = \dfrac{2\pi}{3} \)
Example
What is the amplitude and period of \( y = 4\cos\left(\dfrac{x}{2}\right) \) ?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Amplitude: \( |A| = 4 \)
Period:
Period = \( \dfrac{2\pi}{|B|} \)
Here \( B = \dfrac{1}{2} \)
Period = \( \dfrac{2\pi}{1/2} = 4\pi \)
Example
The minimum value of \( y = 3\sin(2x) – 5 \) is what?
▶️ Answer / Explanation
Range of \( 3\sin(2x) \) is \( [-3, 3] \)
Subtract 5 from entire range:
New range = \( [-3 – 5,\ 3 – 5] = [-8,\ -2] \)
Minimum value = -8
