Reflection and how we see things?
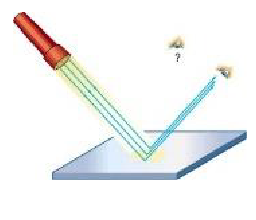
Light beams are projected from the light source (the sun). These light beams travel in a straight line until they meet an object. The light beams are then reflected off the surface it meets, until the light beam enters the eye (see picture). The light activates cells inside our eyes which are processed by our brain into an image. This all happens incredibly fast! All of the objects we can see are only visible when light has reflected from the objects.
Sun Safety
Sunlight can damage your eyes. Protect them by wearing sunglasses or a hat. NEVER look directly at the sun.

Darkness and how shadows are formed?
Darkness is the absence of light. A shadow is an area of darkness produced by an object coming between beams of light and a surface.

They look different depending on the transparency of the object. Transparent objects = faint shadows (more light gets through). Translucent objects = darker than transparent, lighter than opaque object shadows. Opaque objects = dark shadows. The distance between the object and the light source, near or far / high or low, will affect the size of the shadow.

Focus Scientist
Ibn al-Haytham was born in 965BC in what is now present day Iraq. He was the first person to prove that we see because light reflects off objects and into our eyes. He was also one of the first thinkers to use a scientific method.

Key Vocabulary
light: light is a type of energy that makes it possible for us to see the world around us.
light source: an object that emits light.
light beam: a projection of light energy radiating from a light source.
dark/darkness: the absence of light in a place.
reflection: when light hits the surface of an object and then that light travels to our eyes so we can see.
opaque: a material you are not able to see through (not transparent).
transparent: a material allowing light to pass through so that objects behind can be seen clearly.
shadow: an area of darkness produced by an object coming between rays of light and a surface.
translucent: a material allowing light, but not detailed shapes, to pass through (semi-transparent).
torch: a portable battery-powered electric lamp.
mirror: a surface, typically glass coated with metal, which reflects a clear image.
source: where something comes from.
sunglasses: glasses with dark lenses which you wear to protect your eyes from bright sunlight.
protect: to keep from being harmed either by covering or shielding.
illuminate a verb meaning to light up. E.g. A flash of light illuminated the house.
Light
Objectives
Students will be able to
- recognize that they need light in order to see things and that dark is the absence of light.
- notice that light is reflected from surfaces.
- recognize that light from the sun can be dangerous and that there are ways to protect their eyes.
- recognize that shadows are formed when the light from a light source is blocked by an opaque object.
- find patterns in the way that the size of shadows change.
Light
Light is a form of energy that allows us to see. This unit helps students explore the properties of light: where it comes from, how it moves, and how it interacts with objects. Objects can absorb light, reflect it, or both. Certain surfaces absorb more light than others. Absorbed light energy turns into heat energy. When an object blocks light, shadows form on the opposite side and resemble the object. Visible light is made up of all the colors of the rainbow. Objects appear colorful because they absorb certain colors of light and reflect others to our eyes. Understanding the physical properties of light helps us anticipate how light will behave as we use it and interact with it. Light also adds to the beauty and complexity of the world around us.

At primary school children will explore how light behaves, including reflection, shadows and how we see things.
Reflection is how we use light to see around us.
Reflection is when light hits the surface of an object and then that light travels to our eyes so we can see. The reflected light from objects is absorbed by our eyes to form images of the world around us. Smooth surfaces such as mirrors, water and some metals reflect the most light which is why they appear shiny.
The moon reflects sunlight so we can see it shining brightly in the sky.
Shadow
Light travels in straight lines which means it cannot bend. So when something gets in the way it forms a shadow, an area of dark where no light can get to.
Shadows change depending on how close the light source is to the object. If the object is close to the light source you will get a big shadow. If the object is far away from the light source you will get a small shadow.
Shadows – Find a torch or a lamp and put your hand in front of it to make a shadow. See what happens to the size of the shadow when you move your hand forward and back from the light source. What do you notice?
Shadows are created when an opaque (non see-through) object blocks the light source. Shadows change depending on the distance the object is from the light source and the position of the light source.
Light appears to travel in straight lines, travelling from light sources until it hits the surface of an object.
Light Worksheets
Light and Dark
I can explain that I need light to see things, and that dark is the absence of light.
Changing Shadows
Shadows change depending on how close the light source is to the object. If the object is close to the light source you will get a big shadow. If the object is far away from the light source you will get a small shadow.
Year 3 Science Worksheets (Download and print) and Online Tests
Comprehensive Year 3 Preparatory package targeted towards Maths and Science
