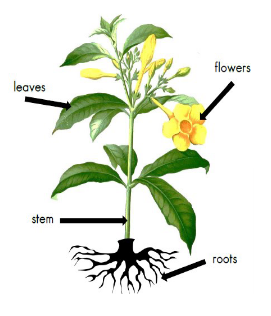
What are the different parts of a plant and what are their functions?
FLOWERS: The flowers are often brightly coloured and smell to attract insects. Insects help with the plants reproduction through pollination.
LEAVES: The leaves use light from the sun, along with carbon dioxide from the air and water to make food for the plant. This process is called photosynthesis.
STEM / TRUNK: The stem carries water and nutrients to different parts of the plant. They keep the plant upright.
ROOTS: The roots of a plant take up water and nutrients from the soil. The roots also keep the plant steady and upright in the soil; they “anchor” the plant.
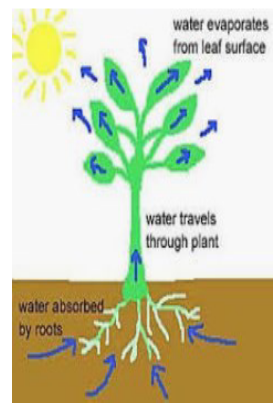
How is water transported in a plant?
Water is absorbed from the soil by the roots. It is then transported from the roots to the stem and then to the rest of the plant. Leaves use this water to make food.

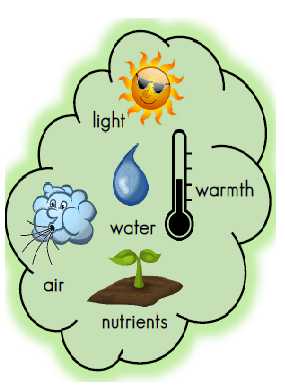
What does a plant need to grow?
Plants need air, water, sunlight, nutrients from the soil, room to grow, sustainable temperature. The amount of each of these may vary depending on the type of plant. For example, cacti need less water than other plants.
How do plants reproduce?
Pollination – Pollen is carried by insects or blown by the wind from one flower to another. This process is called pollination.
Fertilisation – Pollen sticks to the flower and then travels to the ovary where it fertilises egg cells (ovules) to make seeds. This process is called fertilisation.
Seed Dispersal – The seeds are scattered by animals or the wind. This process is called dispersal. Some of the seeds will grow into new plants.
Focus Scientist
Katherine Esau(1898-1997) Russian-born American botanist who did ground- breaking work on the structure and workings of plants. Her book Plant Anatomy is a classic in the field.

Key Vocabulary
flower: the part of a plant which is often brightly coloured and grows at the end of a stem.
leaves: the parts of a tree or plant that are flat, thin, and usually green.
stem/trunk: the thin, upright part of a plant on which the flowers and leaves grow.
roots: the parts of a plant that grow under the ground.
petal: thin coloured or white parts which form part of the flower.
soil: the loose upper layer of the Earth’s surface where plants grow.
function: a useful thing that something does.
reproduction: the process by which a living organism creates copies of itself.
seed: the small, hard part from which a new plant grows.
dispersal: the scattering, separating, or spreading of something over a large area.
pollination: to pollinate a plant or tree means to fertilise it with pollen. This is often done by insects.
fertilisation: in plants, where pollen meets the ovule to form a seed.
absorb: to soak up or take in.
nutrients: substances that help plants and animals to grow.
dissect: to carefully cut something up in order to examine it scientifically.
transportation: taking something from one place to another.
life-cycle: the different stages of life for a living thing.
Year 3 Science Worksheets and Online Tests
Comprehensive Year 3 Preparatory package targeted towards Maths and Science
A plant is made up of many different parts. The three main parts are: the roots, the leaves, and the stem. Each part has a set of jobs to do to keep the plant healthy. The roots absorb water and minerals from the soil and anchor the plant in the ground. The stem supports the plant above ground, and carries the water and minerals to the leaves. The leaves collect energy from the Sun and make food for the plant, using an amazing process called photosynthesis.
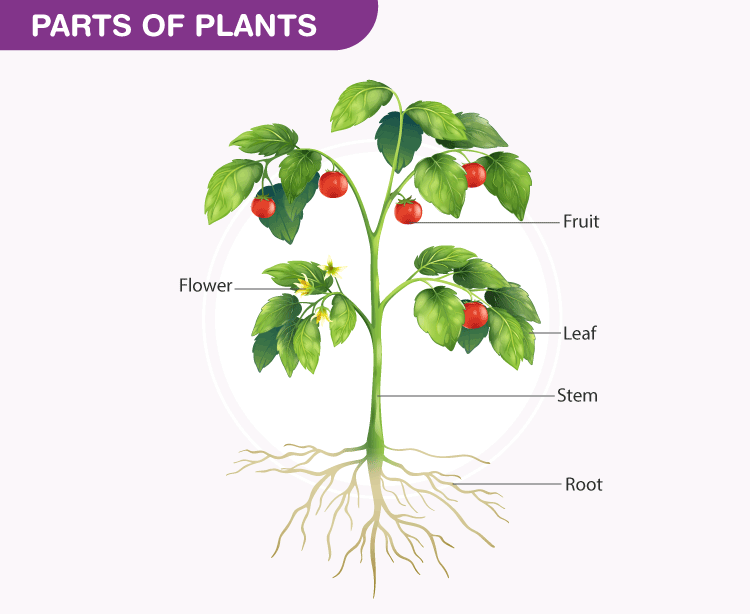
Parts Of Plants
The main parts of a plant include:
- Roots
- Stem
- Leaves
- Flowers
- Fruits
Roots
Roots support the plant, acting as an anchor to prevent it blowing away. The roots are also vital for nutrition. Thousands of tiny root hairs absorb (soak up) water and minerals from the soil. The water and minerals then travel up through the plant.
Stem
The stem is needed for support and for nutrition. It holds the plant up so it can get light, and it transports water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves and flowers. In trees, the stem is known as the trunk.
The important functions of a stem include:
- A stem carries out a number of functions essential for various processes such as photosynthesis.
- Provides a definite framework and structure to a plant which later develops into a tree.
- Support: Primary function of the stem is to hold up buds, flowers, leaves, and fruits to the plant. Along with the roots, a stem anchors the plants and helps them to stand upright and perpendicular to the ground.
- Transportation: It is the part which transports water and minerals from the root and prepared food from leaves to other parts of the plant.
- Storage: Stems are one of the storerooms of plants where the prepared food is stored in the form of starch. The stems of a few plants in the desert areas, such as Opuntia, get modified into thick, fleshy structures that store food and prevent excessive water loss due to transpiration.
- Reproduction: A few stems help in reproduction through vegetative propagation and also help to bear flowers and to produce fruits.
- Guards: Protects Xylem and phloem allowing them to perform their functions. The stem tendrils are spirally coiled and help the plant to climb support. The axillary buds also get modified into thorns that protect the plant from grazing animals.
- The stems of a few plants in the desert areas, such as Opuntia, get modified into thick, fleshy structures that store food and prevent excessive water loss due to transpiration.
Leaves
Leaves are needed for nutrition because they make food for the plant using sunlight and carbon dioxide from the air in a special process called photosynthesis.
A leaf consists of three main parts- petiole, leaf base and lamina.
- The petiole keeps the leaf blade exposed to wind and cools the leaf.
- The leaf base is a protruding part of a leaf.
- The lamina of the leaf contains veins and veinlets that provide rigidity to the leaf blade and help in the transport of mineral nutrients.
Primarily, leaves have three main functions:
- Photosynthesis: Green leaves prepare food for plants by using water and carbon dioxide in the presence of sunlight. This process is called photosynthesis.
- Transpiration: Other than photosynthesis, leaves play a crucial role in the removal of excess of water from plants through tiny pores called stomata. This is the process of transpiration.
- Reproduction: Leaves of some plants helps in reproduction also. For e.g. leaves of Bryophyllum give rise to a new Bryophyllum plant.
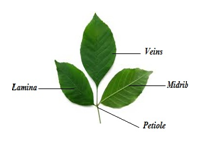
Leaf and its parts
Other Parts of Plants
The other parts of a plant include flowers and fruits.
Flowers
Flowers are needed for reproduction. Colour and scent attract insects. Pollen and eggs are produced by the flowers and these are needed to produce seeds. Flowers are the most beautiful and colourful part of a plant. They are the reproductive part of a plant. A flower has four major parts, namely,
- Petals: It is the colourful part of a flower which attracts insects and birds.
- Sepals: Sepals are green leafy parts present under petals and protect the flower buds from damage.
- Stamens: This is the male part of the flower consisting of anther and filament.
- Pistil: This is the female part of the flower consisting of stigma, style and ovary.
Fruits
Fruits are the main features of a flowering plant. It is a matured ovary that develops after fertilisation. Some fruits are developed without fertilization and are known as parthenocarpic fruits and the process is known as Parthenocarpy.
Thus, we see how different parts of a plant help in the growth and development of a plant. All the plant parts are beneficial and work in coordination with each other.
Water Transport in Plants
Water absorbed by the roots travels up inside the stem of the plant. From the stem, the water can enter the leaves and flowers, helping the plant to grow and be healthy by delivering essential minerals to where they are needed.
Worked Out Examples
Year 3 Science Worksheets and Online Tests
Comprehensive Year 3 Preparatory package targeted towards Maths and Science
