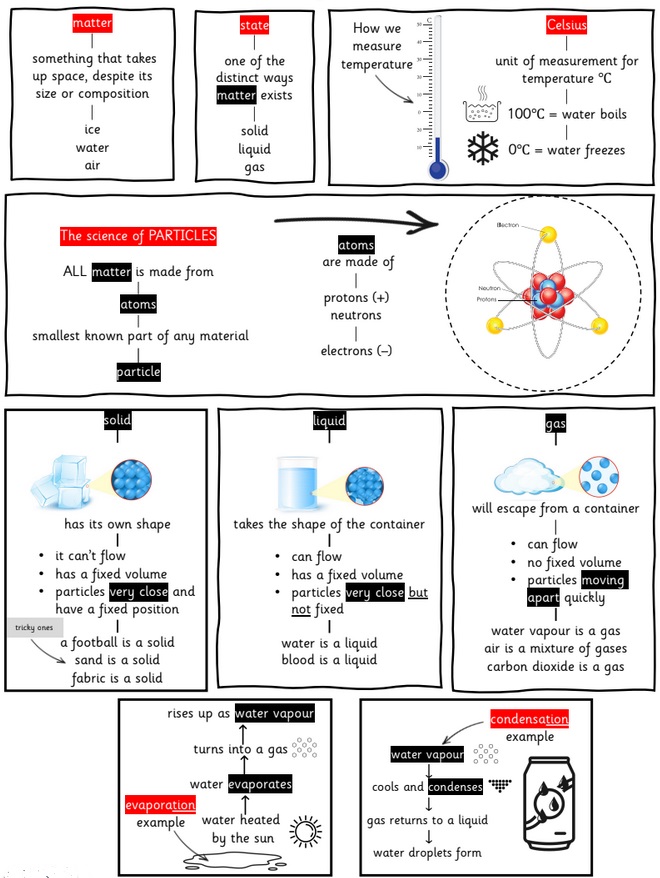
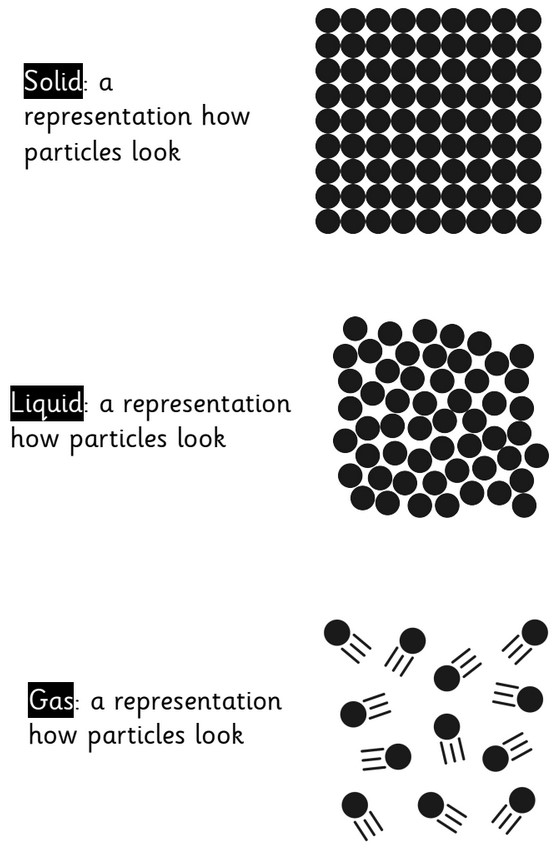
Solids, Liquids and Gases
What is a solid?
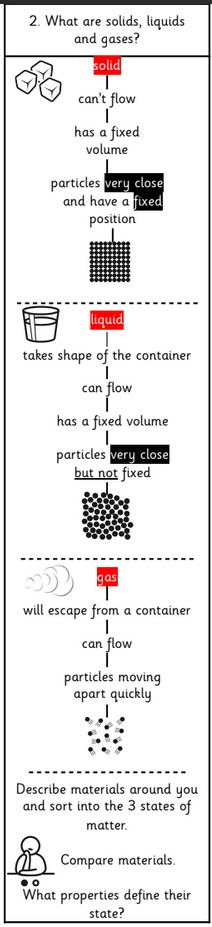
When materials hold their shape. Their particles are closely packed and form a regular pattern. Their shape is fixed and they will always take up the same amount of space. Examples: Ice, Wood, Glass, Diamond.

What is a liquid?
When materials hold the shape of the containers they are in and so can change shape. Their particles are close together but can move over each other. Liquids can be poured. Examples: Water, Milk, washing-up liquid.

What is a gas?
Gases can escape from open containers. They often cannot be seen. They have particles which can spread it and move in all directions. Examples: Steam, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Carbon Dioxide.

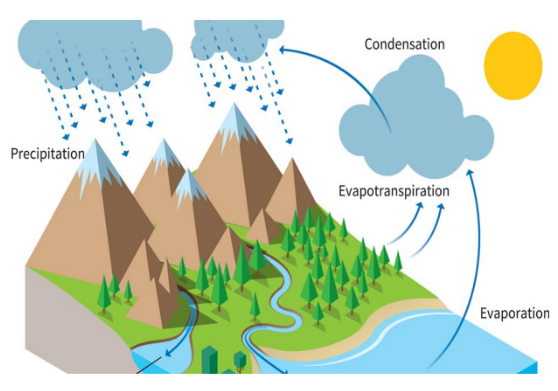
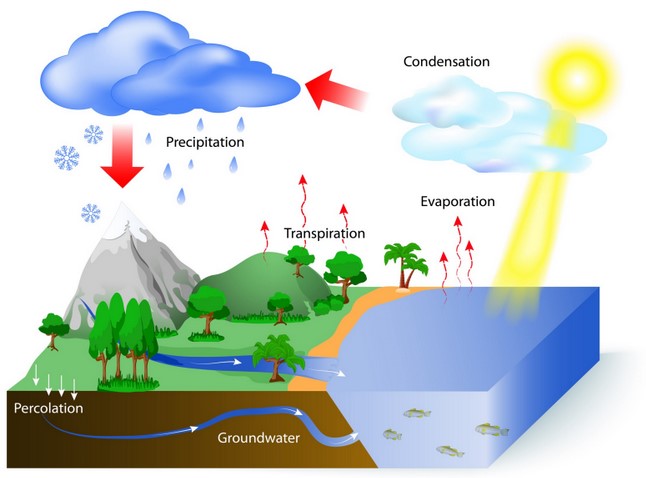
The Water Cycle
Water continually moves around the Earth in the water cycle. The Sun evaporates water into water vapour. When the water vapour cools down it turns into liquid water and it rains. In very cold places the water freezes into snow or ice. Snow and ice, when warmed.
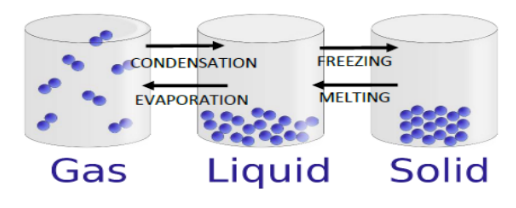
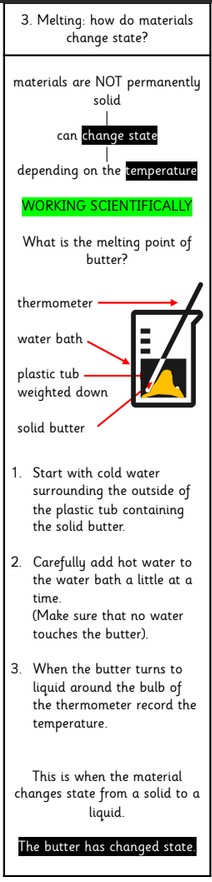
Changes of State (heating and cooling)
Warming solid ice makes it melt into liquid water. Adding more heat makes it evaporate, at 100°C, into steam (a gas). When it is cooled it condenses back into Robert Boyle liquid water. If it is cooled to 0°C it freezes and forms
Focus Scientist
Robert Boyle (1627-1691) studied the behaviour of gases, thought all materials were made of particles and linked states of matter with the movement of particles.

Dorothy Hodgkin (1910- 1994) is the only British woman to have won the Noble Prize for Chemistry. It was for her work on the structure.

Key Vocabulary
solid: firm or stable in shape—with particles very close together.
liquid: a substance that flows easily but has constant volume—with particles close but moving around.
gas: a substance with no fixed shape that will expand to fill the whole of a container—particles far apart and moving around.
heating: raising the temperature of something.
cooling: lowering the temperature of something.
freezing: turning into ice or another solid as a result of cooling.
freezing point: the temperature at which a liquid turns into a solid when cooled.
melting: turning into a liquid as a result of heating.
melting point: the temperature at which a solid will melt.
temperature: a measure of how hot or cold something is.
condensation: the process of turning from vapour (a gas) into liquid.
evaporation: the process of turning from vapour (a gas) into liquid.
precipitation: rain, snow, sleet, dew, etc, formed by condensation of water vapour in the atmosphere.
water cycle: the process by which water on the earth evaporates, then condenses in the atmosphere, and then returns to earth in the form of precipitation.
reversible change: a change that can be changed back again. Melting and heating are examples of reversible changes.
irreversible change: a change that cannot be changed back again. Burning or mixing a liquid with bicarbonate of soda are examples of irreversible changes.
particles: a tiny amount or small piece.
States of matter
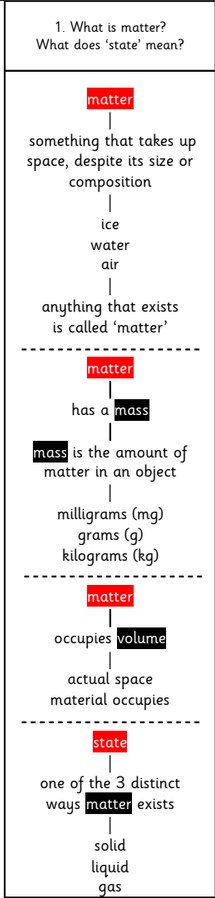


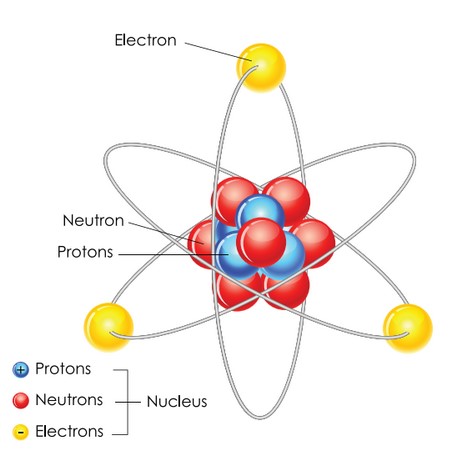
Everything is made from atoms
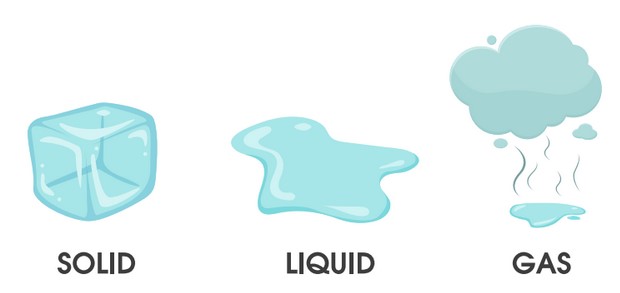
Different states of matter
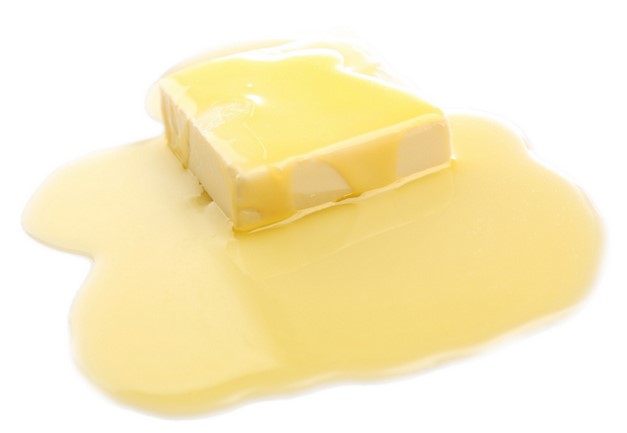
Butter changing its state of matter –
melting from a solid to a liquid

We measure temperature using units
called Celsius or °C for short
Water cycle
Solids Liquids and Gases
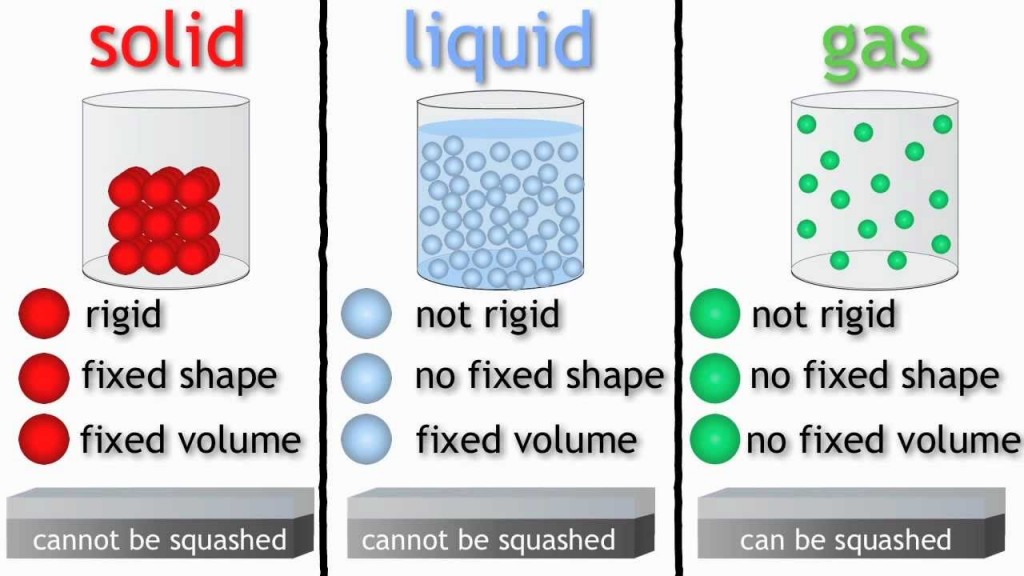
All materials can be put into one of three categories or states:
1.Solids – the shape of a solid does not change on its own – it is rigid. They also have a fixed volume.
2. Liquids – the shape of a liquid does change, it is not rigid. It fits the shape of the container it is put in. Liquids flow. They also have a fixed volume.
3. Gases – gases do not have a shape, they completely fill any container they are put into. They do not have a fixed volume but the same volume as the container.
Materials can change from one of these states to another.
