Question
Organic chemistry can be used to synthesize a variety of products.
(a) Several compounds can be synthesized from but-2-ene. Draw the structure of the final product for each of the following chemical reactions. [2]
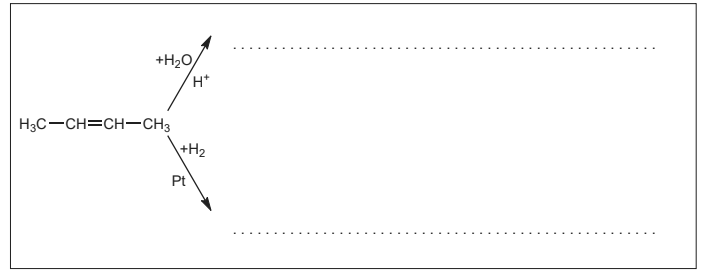
Answer/Explanation
Ans
a
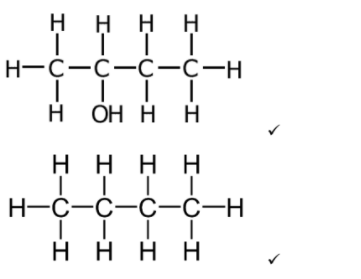
Penalize missing hydrogens in displayed structural formulas once only.
Accept condensed structural formulas: CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3 /CH3CH2CH2CH3 or skeletal structures.
Question
Ethanol is obtained by the hydration of ethene, C2H4.
(a) (i) State the class of compound to which ethene belongs. [1]
(ii) State the molecular formula of the next member of the homologous series to which ethene belongs. [1]
(b) (i) Justify why ethene has only a single signal in its 1H NMR spectrum. [1]
(ii) Deduce the chemical shift of this signal. Use section 27 of the data booklet. [1]
(c) Suggest two possible products of the incomplete combustion of ethene that would not be formed by complete combustion. [1]
(d) A white solid was formed when ethene was subjected to high pressure.
Deduce the type of reaction that occurred. [1]
(e) Alternative synthetic routes exist to produce alcohols.
(i) Sketch the mechanism for the reaction of propene with hydrogen bromide using curly arrows. [3]
(ii) Explain why the major organic product is 2-bromopropane and not 1-bromopropane. [2]
(iii) 2-bromopropane can be converted directly to propan-2-ol. Identify the reagent required. [1]
(iv) Propan-2-ol can also be formed in one step from a compound containing a carbonyl group.
State the name of this compound and the type of reaction that occurs. [2]
Name of carbonyl compound:
Type of reaction:
Answer/Explanation
Ans:
a i alkene
a ii C3H6 Accept structural formula.
b i hydrogen atoms/protons in same chemical environment Accept “all H atoms/protons are equivalent”. Accept “symmetrical”
b ii 4.5 to 6.0 «ppm» Accept a single value within this range.
c carbon monoxide/CO AND carbon/C/soot
d «addition» polymerization
e i
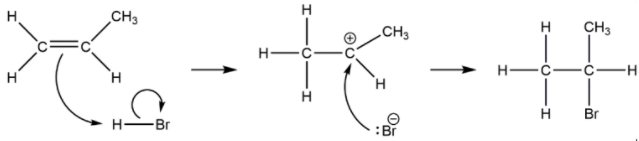
curly arrow going from C=C to H of HBr AND curly arrow showing Br leaving representation of carbocation
curly arrow going from lone pair/negative charge on Br− to C+
Award [2 max] for mechanism producing 1-brompropane.3 .
e ii
«2-bromopropane involves» formation of more stable «secondary» carbocation/carbonium ion/intermediate
OR 1-bromopropane involves formation of less stable «primary» carbocation/ carbonium ion/intermediate «increased» positive inductive/electron-releasing effect of extra –R group/–CH3/methyl «increases stability of secondary carbocation»
Award [1] for “more stable due to positive inductive effect”. Do not award marks for quoting Markovnikov’s rule without any explanation.
e iii sodium hydroxide/NaOH/potassium hydroxide/KOH Accept «aqueous» hydroxide ions/OH−
e iv Name of carbonyl compound: propanone ✔ Type of reaction: reduction ✔ Accept other valid alternatives, such as “2-propyl ethanoate” for M1 and “hydrolysis” for M2.
