Question
a. The diverse functions of biological molecules depend on their structure and shape.
Classify vitamins A, C and D as either mainly fat- or water-soluble, using section 35 of the data booklet.

b(i)The diverse functions of biological molecules depend on their structure and shape.
Deduce the straight chain structure of deoxyribose from its ring structure drawn in section 34 of the data booklet.
b(ii)The diverse functions of biological molecules depend on their structure and shape.
Sucrose is a disaccharide formed in the reaction of glucose with fructose.
Identify the reaction type and the newly formed functional group that joins the monosaccharide units in the product.

▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.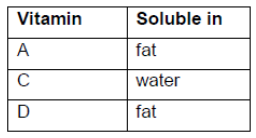
all three correct
b(i).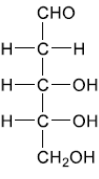
– CH2 – must be placed next to CHO AND 2 OHs on central carbons must be on same side (LHS or RHS) Accept crosses in place of $\mathrm{C}$ on three middle carbons.
b(ii)Reaction type:
condensation
Accept “nucleophilic substitution/ $\mathrm{S}_{\mathrm{N}}$ ” for M1.
Functional group:
acetal/ether/glycosidic «linkage»
Accept “glycoside” for $M 2$.
Question
Ascorbic acid and retinol are two important vitamins.
Explain why ascorbic acid is soluble in water and retinol is not. Use section 35 of the data booklet.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
ascorbic acid: many hydroxyl/OH groups AND retinol: few/one hydroxyl/OH group
OR
ascorbic acid: many hydroxyl/OH groups AND retinol: long hydrocarbon chain [ $\boldsymbol{\sim}$ ]
ascorbic acid: «many» $\mathrm{H}-$ bond with water
OR
retinol: cannot «sufficiently» H-bond with water $[\boldsymbol{M}]$
Note: Do not accept “OH’/hydroxide”.
Question
Phosphatidylcholine is an example of a phospholipid found in lecithin.
Phosphatidylcholine may be formed from propane-1,2,3-triol, two lauric acid molecules, phosphoric acid and the choline cation.
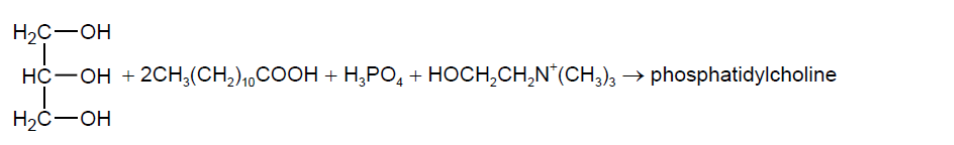
a(i)Deduce the structural formula of phosphatidylcholine.
a(ii)dentify the type of reaction in (a).
b. Lecithin is a major component of cell membranes. Describe the structure of a cell membrane.
c. Predict, giving a reason, the relative energy density of a carbohydrate and a lipid of similar molar mass.
d. Lecithin aids the body’s absorption of vitamin $\mathrm{E}$.
Suggest why vitamin $\mathrm{E}$ is fat-soluble.
e. Phospholipids are also found in lipoprotein structures.
Describe two effects of increased levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) on health.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a(i)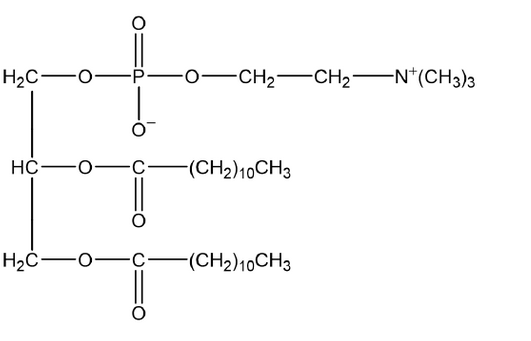
phosphodiester correctly drawn [ $\boldsymbol{V}]$
both ester groups correctly drawn $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
Note: Accept protonated phosphate.
Accept phosphodiester in centre position.
a(ii)ondensation [ $\checkmark$ ]
Note: Accept “esterification”.
Accept “nucleophilic substitution/ $\mathrm{S}_N$ “.
b. phospholipid bilayer/double layer
OR
two layers of phospholipids [ $\boldsymbol{V}]$
polar/hydrophilic heads facing aqueous environment $A N D$ non-polar/hydrophobic tails facing away from aqueous environment [ $\boldsymbol{C}$ ]
Note: Award [2] for a suitably labelled diagram.
Award [1 max] for a correct but unlabelled diagram.
Accept “polar/hydrophilic heads on outside AND non-polar/hydrophobic tails on inside for M2.
c. carbohydrates less energy dense $\boldsymbol{A N D}$ carbohydrates higher ratio of oxygen to carbon/more oxidized/less reduced [ $\boldsymbol{C}$ ]
d. long non-polar/hydrocarbon chain «and only one hydroxyl group»
OR
forms London/dispersion/van der Waals/vdW interactions with fat [ $U$ ]
Note: Accept “alcohol/hydroxy/OH” for “hydroxyl” but not “hydroxide”.
e. atherosclerosis/cholesterol deposition «in artery walls» [ $\boldsymbol{V}]$
increases risk of heart attack/stroke/cardiovascular disease/CHD [ $/]$
Note: Accept “arteries become blocked/walls become thicker”, “increases blood pressure”, or “blood clots”.
Do not accept “high cholesterol”.
Question
Changes in physiology can impact living creatures.
a. The graph shows the change in oxygen partial pressure in blood, measured at different $\mathrm{pH}$ values.
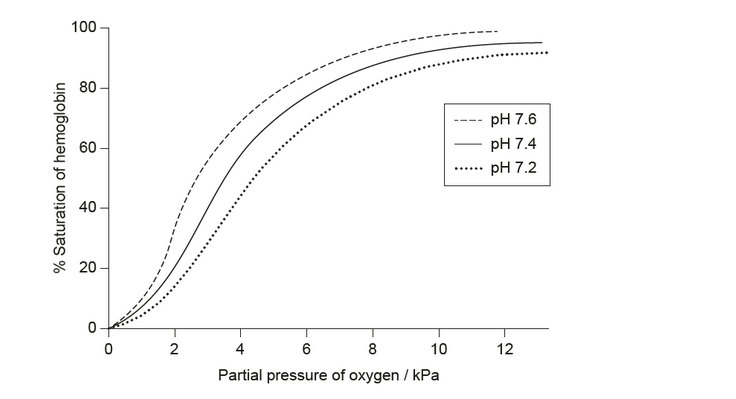
Explain the effect of changing pH on the percentage saturation of hemoglobin at a given partial pressure of oxygen.
b. Explain the biomagnification of the pesticide DDT.
c. Vitamins are organic compounds essential in small amounts.
State the name of one functional group common to all three vitamins shown in section 35 of the data booklet.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. as $\mathrm{pH}$ decreases, protons $/ \mathrm{CO}_2$ bind to allosteric sites
OR
as $\mathrm{pH}$ decreases, protons $/ \mathrm{CO}_2$ act as non-competitive inhibitor
OR
active/binding site changes shape
saturation decreases
OR
more oxygen released
OR
affinity to oxygen decreases
b. accumulates in fat/tissues/living organisms
OR
cannot be metabolized/does not break down «in living organisms»
OR
not excreted / excreted «very» slowly
passes «unchanged» up the food chain
OR
increased concentration as one species feeds on another «up the food chain»
NOTE: Accept “lipids” for “fat”.
c. hydroxyl
NOTE: Accept “hydroxy” but not “hydroxide”.
Accept “alkenyl”.
Do not accept formula.
Question
Dietary recommendations are made by scientists.
a. The formation of proteins from amino acids is an example of an anabolic reaction in the human body.
State the source of energy for such a synthetic reaction.
b. Suggest why it is advisable for those living in northerly or southerly latitudes (that is away from the equator) to take vitamin D supplements during the winter.
c. Explain how a xenobiotic is biomagnified.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. catabolism «of food/nutrients»
OR
«cellular» respiration
Accept “ATP” but not “burning of food/nutrients”.
b. not enough sunlight/UV light «for synthesis of vitamin D in the skin»
c. cannot be metabolized/broken down
OR
not biodegradable
OR
accumulates in lipid/fat tissues
increased concentration as one species feeds on another «in the food chain»
Question
Vitamins are micronutrients essential for good health.
Compare the solubilities of vitamins A and C in water by referring to the structures provided in Table 21 of the Data Booklet.
Describe the effect of deficiency of one of these vitamins and suggest two possible solutions.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
vitamin A: not water-soluble because it has only one OH / is not very/less polar / contains long hydrocarbon group;
vitamin C: water-soluble because it has 4/many OH (and 1 C=O)/extensive hydrogen bonding;
Accept reference to polarity in one case but not in both.
effect: vitamin A: xerophthalmia/night blindness / vitamin C: scurvy / bleeding gums / less resistance to infection / bleeding lesions on legs/thighs / scorbutus;
Accept either of the following for the second mark:
solution for vitamin A: providing food composed of liver/fresh (orange and green) fruits/vegetables/spinach/eggs/carrots / providing genetically modified food containing vitamin A;
Examiners report
Most candidates answered that vitamin C is water soluble and vitamin A not, although some were vague in their explanations why.
Many candidates identified correctly the deficiency symptoms and named at least one solution.
Question
A balanced diet is needed for good health.
By comparing the structures of vitamins A, C and D given in Table 21 of the Data Booklet, state and explain which of the three vitamins is most soluble in water.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(vitamin) C/ascorbic acid;
more/many/several hydroxyl/OH groups that can form hydrogen bonds (with water);
M2 cannot be awarded for incorrect vitamin.
Examiners report
This was generally well done, although some candidates did not refer to hydrogen bonds when explaining the solubility of vitamin C in water.
Question
State the causes of the three deficiency diseases, beriberi, goitre and pellagra.
Beriberi:
Goitre:
Pellagra:
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Beriberi
lack/deficiency of vitamin B1/thiamine;
Goitre
lack/deficiency of iodine;
Pellagra
lack/deficiency of vitamin B3/niacin;
Examiners report
Many candidates were unable to state the causes of the deficiency diseases. Some simply guessed the same answer three times. The cause of goitre was best known of the three diseases.
Question
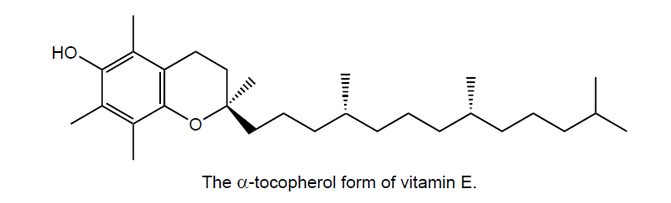
The structure of one form of vitamin E is shown below.
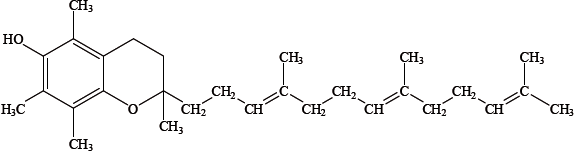
State and explain whether vitamin E is fat soluble or water soluble.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
fat soluble as long non-polar/hydrocarbon chain;
with few polar groups;
cannot form hydrogen bonds with water;
Examiners report
Most candidates knew that vitamin E is fat soluble but could not explain further to achieve the marks.
Question
Macronutrients and micronutrients are essential components of a balanced diet.
State the difference between macronutrients and micronutrients.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
micronutrients required in much smaller quantities/very small amounts/less than 0.005% of body mass;
Accept opposite statement for macronutrients.
Examiners report
Most candidates gained full marks for this question and was answered quite well.
Question
The two diagrams below show the arrangement of molecules in two different types of polyethene, labelled A and B.

Predict which type of polyethene (A or B) has the strongest intermolecular forces, highest density and greatest flexibility.
(i) Strongest intermolecular forces:
(ii) Highest density:
(iii) Greatest flexibility:
The polymer polyvinyl chloride (PVC), also known as poly(chloroethene), is hard and brittle when pure. Explain, in terms of intermolecular forces, how adding a plasticizer to PVC modifies the properties of the polymer.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
(i) A;
(ii) A;
(iii) B;
closely packed molecules with crystalline structure;
(plasticizers) separate the PVC molecules/polymer chains / disrupt crystalline structure;
decrease/weaken intermolecular forces/intermolecular dipole-dipole interactions/van der Waals’/London Dispersion;
Do not accept mention of H-bonding
makes it (PVC) softer/more flexible/more easily moulded;
Examiners report
Many candidates were able to score three marks in (a) and most gave a good account of (b). Many, however, neglected to mention intermolecular forces, specifically requested in the question.
Many candidates were able to score three marks in (a) and most gave a good account of (b). Many, however, neglected to mention intermolecular forces, specifically requested in the question.
Question
The structures of retinol (vitamin A) and vitamin D are given in Table 21 of the Data Booklet. Deduce whether each vitamin is water-soluble or fat-soluble and explain your answer by referring to their structures.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
both fat soluble;
both contain mainly non-polar/hydrocarbon parts (and only one OH group) / OWTTE;
Do not award ECF if water soluble is stated for either vitamin.
Do not award M2 for answers such as “since both do not have many OH groups present”.
Examiners report
The majority of candidates identified the solubility of both vitamins correctly in part (a). The explanation was correctly scored by only half of the candidates, while the rest talked about the OH group and did not discuss the main part of the molecule.
Question
Vitamins are organic micronutrients essential for good health. The structures of vitamins A, C and D are given in Table 21 of the Data Booklet.
Only one of these three vitamins is soluble in water.
Vitamin D is the only vitamin that can be synthesized in the body, by the action of sunlight on the skin.
Identify by name two functional groups that are common to all three of these vitamins.
Identify this vitamin.
Explain why this vitamin is soluble in water.
State one effect of vitamin D deficiency.
Suggest why vitamin D deficiency diseases are becoming increasingly common in young people.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
alcohol/hydroxyl group and alkene;
Accept carbon-carbon double bond.
Do not accept just double bond.
Do not accept hydroxide.
vitamin C / ascorbic acid;
several OH groups / polar molecule;
able to form hydrogen bonds with water;
softening/malfunctioning of bones / causes low/deficiency in calcium;
Accept rickets.
less time outdoors / skin not exposed due to clothing/sunscreen / OWTTE;
Accept answers that show link with outdoors/sunlight.
Examiners report
In (a) the alkenyl group was usually replaced by something else but it was pleasing to see the general absence of the answer “hydroxide”. Parts (b) and (c) were answered well and candidates seemed well aware of the dangers of modern technology keeping them indoors.
In (a) the alkenyl group was usually replaced by something else but it was pleasing to see the general absence of the answer “hydroxide”. Parts (b) and (c) were answered well and candidates seemed well aware of the dangers of modern technology keeping them indoors.
In (a) the alkenyl group was usually replaced by something else but it was pleasing to see the general absence of the answer “hydroxide”. Parts (b) and (c) were answered well and candidates seemed well aware of the dangers of modern technology keeping them indoors.
In (a) the alkenyl group was usually replaced by something else but it was pleasing to see the general absence of the answer “hydroxide”. Parts (b) and (c) were answered well and candidates seemed well aware of the dangers of modern technology keeping them indoors.
In (a) the alkenyl group was usually replaced by something else but it was pleasing to see the general absence of the answer “hydroxide”. Parts (b) and (c) were answered well and candidates seemed well aware of the dangers of modern technology keeping them indoors.
Question
Lipids are a diverse group of compounds found in the body.
Cholesterol is one of the most important steroids. It plays an essential role in metabolism and is the starting point for the synthesis of many important chemicals in the body.
Compare the structures and polarities of fats and phospholipids, giving one similarity and one difference in structure and one difference in polarity.
Similarity in structure:
Difference in structure:
Difference in polarity:
Vitamin D is produced from cholesterol. The structures of both molecules are given in table 21 of the data booklet. Outline one structural difference between the molecules.
Distinguish between HDL and LDL cholesterol in terms of their composition and their effect on health.
Composition:
One effect on health:
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Similarity in structure:
both are (tri)esters / both made from glycerol/propane-1,2,3-triol/HOCH2CH(OH)CH2OH;
Difference in structure:
phospholipids have phosphate group/phosphorus and fats are triglycerides/made from three fatty/carboxylic acids / one fatty/carboxylic acid (in fat) replaced by phosphate in phospholipid;
Difference in polarity:
phospholipids are more polar / phospholipids have hydrophilic (heads/section/part/end) / fats are less polar/non-polar / fats are hydrophobic ;
(two) more carbon−carbon double bonds/alkenyl groups in vitamin D;
Accept alkene for alkenyl.
extra hexagon/6-membered ring in cholesterol / more fused rings in cholesterol / four fused rings in cholesterol and two fused rings in vitamin D;
Accept “(some) conjugation in vitamin D / (some) alternating C=C and C−C bonds in vitamin D”.
Accept “cholesterol has a steroid backbone/structure but vitamin D does not”.
Composition:
HDL has more protein and less cholesterol/fat/lipid (and vice-versa);
Accept “HDL has more protein and LDL has more cholesterol (and vice-versa)”.
Accept “HDL has higher phospholipid content compared to LDL (and vice-versa)”.
Accept “HDL particles are smaller than LDL particles (and vice-versa)” but do not penalize if “molecules” are used instead of “particles”.
One effect on health:
cardiovascular problems/increased risk of heart disease/obesity/atherosclerosis/blocked arteries from high ratio of LDL to HDL;
Accept “from (high) LDL” instead of “from high ratio of LDL to HDL”.
Accept “can result in a heart attack/stroke from high ratio of LDL to HDL”.
Accept “large amounts of HDL in blood correlate with good health / OWTTE”.
Reference must be made to LDL or HDL.
Examiners report
About half the candidates seemed familiar with the structures of fats and phospholipids, but only a few gave the detailed answers expected by the markscheme. Some of the answers were far too general such as stating “both contain C, H and O” for the similarity in structure.
About a third of the candidates scored the mark by stating an accurate structural difference between vitamin D and cholesterol. Some answers were not specific enough about the numbers and types of rings.
Only a few candidates were able to distinguish between the composition of HDL and LDL cholesterol, but the majority of candidates understood their effects on health well and gained the second mark. There was a comment on a G2 form that this question went beyond the syllabus, however, the question is covered in part B.4.2 (“outline the difference between HDL and LDL cholesterol”) and has also appeared in a past paper.
Question
Peptidase enzyme in the digestive system hydrolyses peptide bonds.
A tripeptide Ala-Asp-Lys was hydrolysed and electrophoresis of the mixture of the amino acids was carried out at a pH of 6.0. Refer to section 33 of the data booklet.
Identify the type of metabolic process that occurs in the hydrolysis of the peptide during digestion.
Identify the name of the amino acid that does not move under the influence of the applied voltage.
Deduce, giving a reason, which amino acid will develop closest to the negative electrode.
The breakdown of a dipeptide in the presence of peptidase was investigated between 18 °C and 43 °C. The results are shown below.
Comment on the rate of reaction at temperature X in terms of the enzyme’s active site.
The solubility of a vitamin depends on its structure.
Identify the vitamin given in section 35 of the data booklet that is the most soluble in water.
Pollution from heavy metal ions has become a health concern.
Outline how the presence of heavy metal ions decreases the action of enzymes.
Outline how lead ions could be removed from an individual suffering from lead poisoning.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
catabolism/catabolic
[1 mark]
alanine
Do not accept ala.
[1 mark]
Lys/lysine
pH «buffer» < pI «Lys»
OR
buffer more acidic than Lys «at isoelectric point»
OR
«Lys» exists as
OR
«Lys» charged positively/has +1/1+ «overall» charge «and moves to negative electrode»
Do not apply ECF from M1.
Accept converse argument.
Do not accept just “has H3N+ group” for M2 (as H3N+ is also present in zwitterion).
Do not penalize if COOH is given in the structure of lysine at pH 6 instead of COO–.
[2 marks]
highest frequency of successful collisions between active site and substrate
OR
highest frequency of collisions between active site and substrate with sufficient energy/\(E \geqslant {E_{\text{a}}}\) AND correct orientation/conformation
OR
optimal shape/conformation of the active site «that matches the substrate»
OR
best ability of the active site to bind «to the substrate»
Accept “number of collisions per unit time” for “frequency”.
Do not accept “all active sites are occupied”.
[1 mark]
ascorbic acid/vitamin C
[1 mark]
react/bind/chelate with enzyme
OR
disrupt ionic salt bridges
OR
affect shape of tertiary/quaternary structures
OR
precipitate enzymes
OR
break/disrupt disulfide bridges/bonds
Do not accept “changes shape of active site” by itself.
[1 mark]
«use of» host-guest chemistry
OR
chelation «therapy»
Accept specific medication/chelating agent such as EDTA, CaNa2 EDTA, succimer, D-penicillamine, dimercaprol.
[1 mark]
Question
Suggest, in terms of its structure, why vitamin D is fat-soluble using section 35 of the data booklet.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
«mostly» non-polar
OR
hydrocarbon backbone
OR
only 1 hydroxyl «group so mostly non-polar»
Accept “alcohol/hydroxy” for “hydroxyl” but not “hydroxide”.
[1 mark]
Examiners report
Question
Vitamins can be water-soluble or fat-soluble.
Explain, at the molecular level, why vitamin D is soluble in fats. Use section 35 of the data booklet.
State one function of vitamin D in the body.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
«mainly» hydrocarbon/non-polar «structure»
forms London/dispersion/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole forces «with fats»
Accept “forms van der Waals’/vdW forces”.
Award [1 max] for “contains only one OH/hydroxyl AND cannot form «enough» H-bonds”.
helps absorb calcium
OR
helps build bones
OR
helps keep bones healthy
OR
helps block the release of parathyroid hormone
OR
helps in muscle function
OR
helps immune system function
OR
cell growth
OR
reduction of inflammation
OR
protection from osteoporosis
OR
prevents rickets
Accept helps prevent colon/breast/prostate cancer.
Accept treat/prevent diabetes/heart disease/high blood pressure/multiple sclerosis.
Accept other correct answers.
Question
Saturated lipids found in butter and unsaturated lipids found in fish oil readily become rancid.
Identify the type of rancidity occurring in saturated lipids and the structural feature that causes it.
State one factor that increases the rate at which saturated lipids become rancid.
Butter contains varying proportions of oleic, myristic, palmitic and stearic acids. Explain in terms of their structures why stearic acid has a higher melting point than oleic acid, using section 34 of the data booklet.
Fish oil is an excellent dietary source of omega-3 fatty acids. Outline one impact on health of consuming omega-3 fatty acids.
Predict the solubility of retinol (vitamin A) in body fat, giving a reason. Use section 35 of the data booklet.
Explain why sharks and swordfish sometimes contain high concentrations of mercury and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs).
Plastics are another source of marine pollution. Outline one way in which plastics can be made more biodegradable.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
hydrolytic «rancidity»
ester group
Accept a formula for ester group.
[2 marks]
«presence of» moisture/water
OR
«increase in» temperature
OR
«presence of» enzymes/bacteria/fungi/mould
OR
low pH/«presence of» acid
Accept “heat”.
[1 mark]
«stearic acid» straight chain/chain has no kinks/more regular structure
OR
«stearic acid» saturated/no «carbon–carbon» double bonds
«stearic acid» chains pack more closely together
stronger London/dispersion/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole forces «between molecules»
Accept “«stearic acid» greater surface area/electron density”.
[3 marks]
lowers risk of heart disease/atherosclerosis
OR
lowers LDL cholesterol
OR
increases HDL cholesterol
OR
aids brain/neurological development «in children»
OR
relieves rheumatoid arthritis
[1 mark]
soluble AND non-polar hydrocarbon chain
Accept as reasons “«predominantly» non-polar” OR “long hydrocarbon chain”.
[1 mark]
not biodegradable
OR
stored/accumulate in fat
biomagnification occurs
OR
concentration increases along food chain
Accept “stored/accumulate in bodies of prey/animals eaten”.
Accept “not excreted”.
[2 marks]
add starch/cellulose/carbohydrates/additives/catalysts «to plastic during manufacture to allow digestion by micro-organisms»
OR
replace traditional plastics with polylactic acid/PLA-based ones
OR
blend traditional and polylactic acid/PLA-based plastics
Accept reference to biodegradable plastics other than PLA; for example polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), poly(butylene succinate) (PBS), polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT) and polycaprolactone (PCL).
[1 mark]
Question
Explain the solubility of vitamins A and C using section 35 of the data booklet.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Vitamin A:
fat soluble/soluble in non-polar solvents AND non-polar/long hydrocarbon backbone/chain
Vitamin C:
water soluble AND contains 4 hydroxyl groups/contains many hydroxyl groups/forms «many» H-bonds with water
Accept “Vitamin A: fat soluble/soluble in non-polar solvents as it contains only one hydroxyl group whose H-bonds with water are not strong enough to overcome London/dispersion/vdW forces between Vitamin A molecules”.
Accept “lipid” for “fats”.
Accept “alcohol” OR “hydroxy” OR “OH groups” for “hydroxyl” but not “hydroxide”.
Award [1 max] for “Vitamin A: fat soluble AND Vitamin C: water soluble” with no or incomplete explanation.
[2 marks]

